Post-process deduplication vs In-line deduplication
There are two main deduplication methods – post-process and in-line, the both having advantages and drawbacks and each can be effectively used for specific applications.Overleaping, let’s specify that StarWind solution provides in-line type of deduplication, and a reason of this choice will be clarified below.
Post-process deduplication: A block of data comes into the appliance and is written to storage entirely. Then a separate process reads the block and checks it for redundancy. If it has been processed before (is considered to be a duplicate), it is deleted and replaced with a reference. If the block does not have matches, no changes are made. This method shortens time of data transfer from the source to storage but it requires more free space on a server disk and a lot more I/O than in-line.
In-line deduplication: It can be performed on the client side or when data is being transferred from the source to server. A block of data comes into the appliance, which analyses if that block has been processed before. If so, it throws away the redundant block and writes a reference to it. If the block of data is unique, the appliance writes it to the storage. Thus, data block analysis is initiated before it is written. This method of deduplication performs most of the work in RAM, which minimizes I/O overhead and provides disk space savings. However, it requires substantial resources and can become a network’s bottleneck. Nevertheless, despite its resource-intensity and possible delays, in-line method increases efficiency of global deduplication since immediate processing of data stream coming from several sources allows eliminating duplicates on the fly.
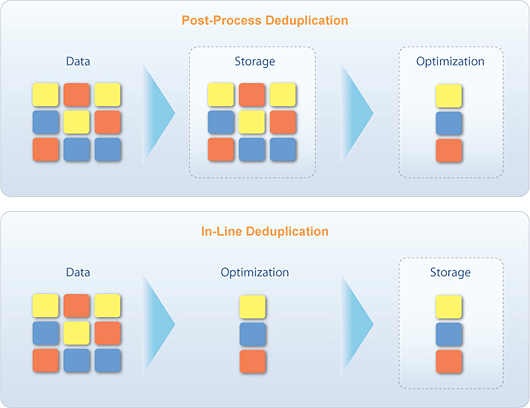
Post-process deduplication is mostly used in the backup applications, virtual tape libraries and the like, where reduction of backup time is required. At the same time this method turns out to be absolutely ineffective if rapid data recovery is needed because when a client addresses storage, the system can be busy with deduplication of the next portion of data. Type of the data being processed also substantially influences the effectiveness of deduplication. Let’s examine deduplication for a backup application making everyday shots of VM image. Obviously, there will be only slight difference between such shots as they mostly contain OS and applications’ files. The post-process deduplication will be able to figure out whether they are duplicates only when the shots are written to the storage, while in-line deduplication will determine redundancies before shots are stored. The more node-clients need to be processed, the less effective post-process deduplication appears to be, while in-line on the contrary shows increasing effectiveness.
| Live demo | Free 30-day trial | How to buy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Request now |  |
Download free trial |  |
Request a quote |
