Microsoft recently released its new flagship Windows Server operating system – Windows Server 2022. It contains the latest and most significant features available to Microsoft customers for running their business-critical workloads. Many of the new features and capabilities in Windows Server 2022 enable customers to take security and hybrid cloud capabilities to the next level. Let’s look more closely at the new features found in Windows Server 2022 and how these will benefit the enterprise.
Windows Server 2022 New Features
There are many great new features contained in Windows Server 2022 that make this the most sophisticated and powerful Windows Server operating system to date. The new Windows Server 2022 features include enhancements in the following:
- Security
- Hybrid cloud
- Windows Admin Center
- Application improvements
- Storage
- Networking
- Virtualization
Windows Server 2022 provides a robust new Windows Server platform
Security
There couldn’t be a more important topic on the minds of businesses today than security. Microsoft has introduced Secured-core server as part of the implementation of Windows Server 2022. What is a Secured-core server?
The Secured-core server is a technology that builds on the Secure-core PC, which Microsoft has already introduced as part of Windows 10. Microsoft introduces the same core features that build a secure platform based on various security pillars built into the operating system with a Secure-core server. These security features include simplified security, advanced protection, and preventative defense.
With Secured-core servers, Microsoft is working with manufacturing partners to ensure the OEM server hardware has both the hardware and firmware security features needed to enable the features of the Secured-core model. Additionally, as part of the simplification of ensuring your server is configured using the Secure-core model, Microsoft has provided this as part of the Security dashboard found in Windows Admin Center.
At the time of this writing, the Secured-core server Windows Admin Center extension requires you to use the “insider” Windows Admin Center extensions feed. The current version of the Security extension does not include the Secured-core functionality and configuration.
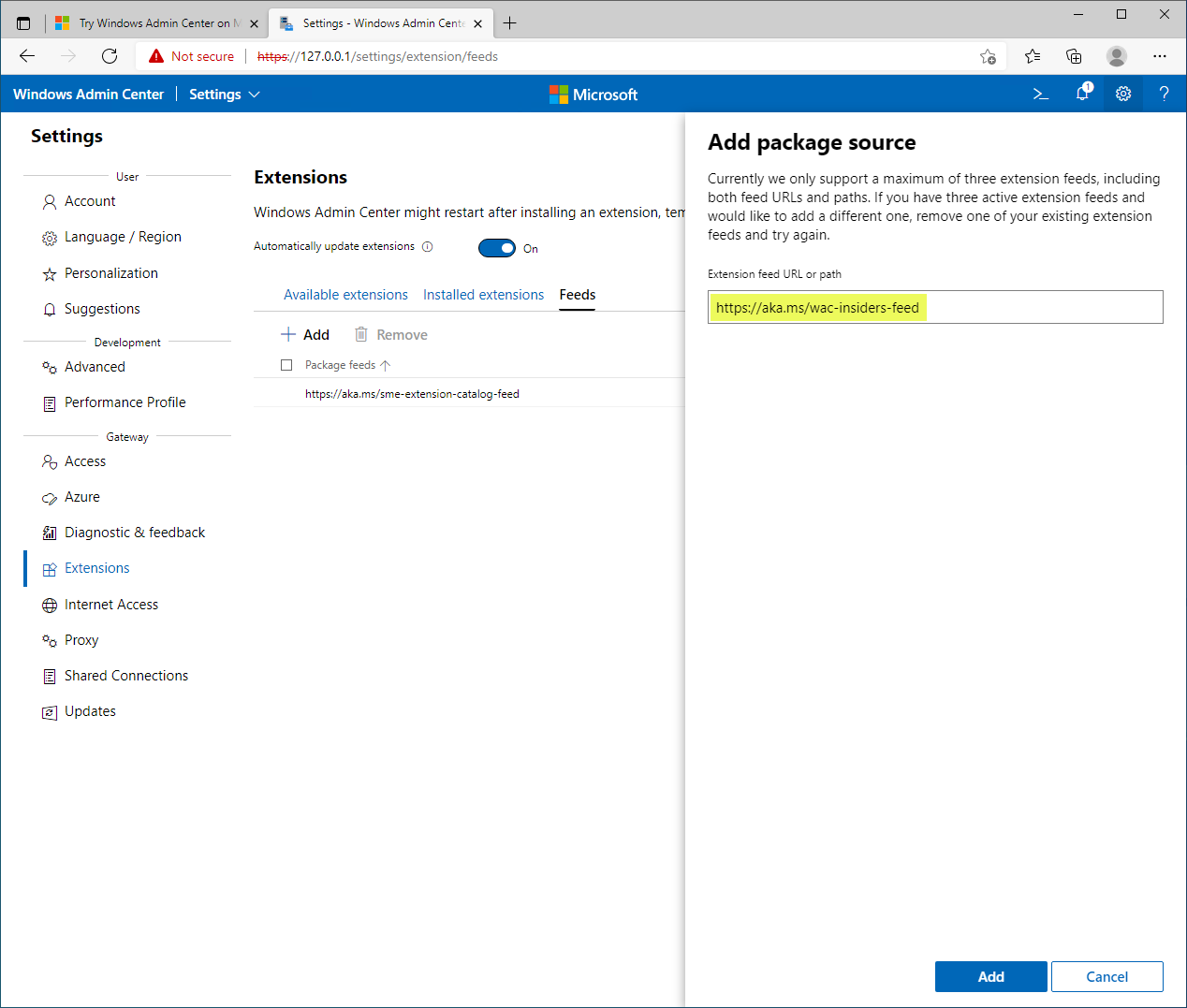
Using the Windows Admin Center Insiders feed extensions URL
After configuring the “insider’s” extension URL, you will see a new option for the Security extension (later version listed).
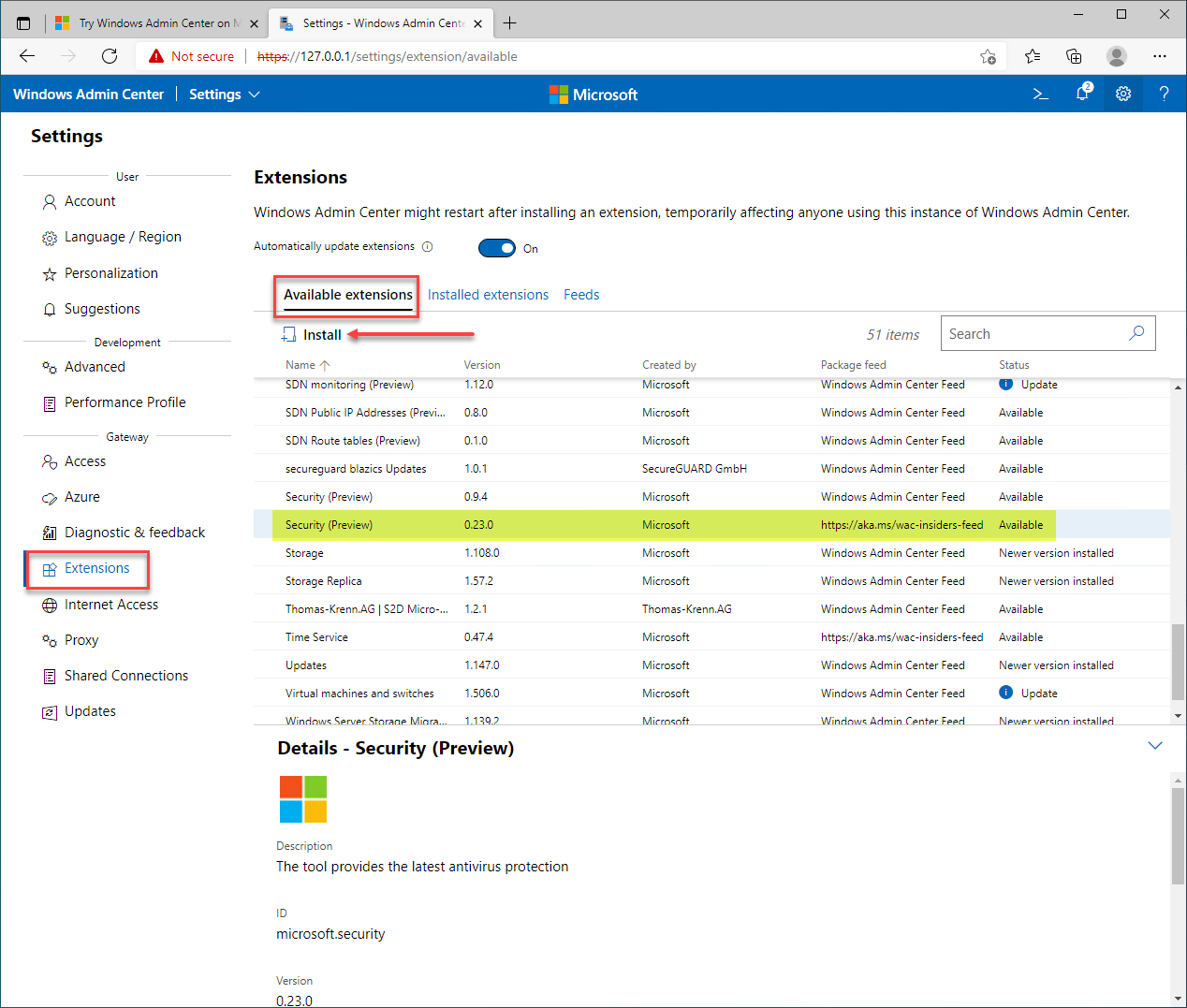
Installing the “insiders” version of the Security extension
On the Secured-core server configuration, you can enable missing features that are supported on your Windows Server 2022 server. Note, the below screenshot is taken from a Windows Server 2022 VM that is missing the underlying hardware components for full Secured-core implementation. It is great to see you have quick visibility to the hardware and other components needed for Secured-core.
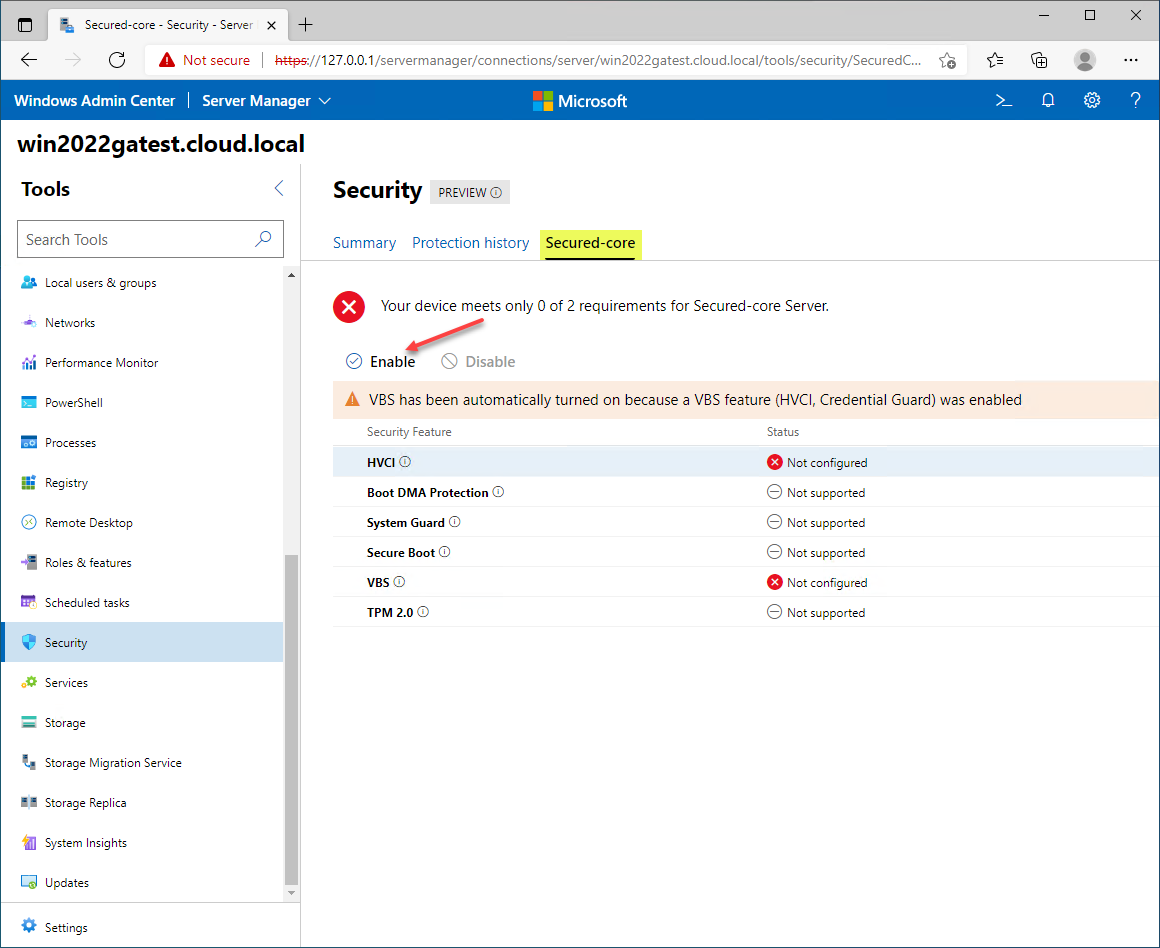
The Secured-core server configuration
Let’s look at the individual components of the Secured-core server. These include:
- HVI
- Boot DMA Protection
- System Guard
- Secure Boot
- VBS
- TPM 2.0
HVCI
HVCI stands for Hypervisor Enforced Code Integrity. It is used with Virtualization Based Security (VBS) and helps to protect Windows operating systems from malicious drivers and insecure or malicious system files. It also monitors for tampering with CFG, Control Flow Guard and ensures valid certificates are used with Windows security components such as Credential Guard.
Boot DMA Protection
The Secured-core Boot DMA Protection component protects against drive-by Direct Memory Access (DMA) attacks. These types of attacks can present themselves by means of hotplug PCI devices or internal/external PCIe port devices. DMA drive-by attacks are dangerous since they can lead to malware injection and bypassing security controls such as the lock screen. The DMA Protection component allows preventing any malicious drivers from starting and initiating DMA.
System Guard
Another feature of the Secured-core server implementation is the Microsoft Windows Defender System Guard protection. The primary role of the System Guard Secured-core server component is to protect the integrity of the Windows system to ensure there is no tampering. The System Guard component uses local and remote attestation to validate system integrity.
With Secured-core server implementations using modern hardware, Windows Server 2022 System Guard protects against malicious bootkits and prevents any unauthorized firmware or software from instantiating itself before the Windows bootloader.
Secure Boot
Microsoft Secured-core server uses Secure Boot, ensuring the boot firmware is validated and trusted by the OEM hardware vendor. In addition, it checks boot signatures and UEFI firmware drivers to ensure these are valid and authorized. This validation process helps to protect against boot tampering and other malicious code injection during the boot process.
Virtualization-based Security (VBS)
Virtualization-based Security (VBS) is a component of a Secured-core server that uses hardware virtualization to create a protected area, a secure region of memory, that is isolated from the operating system. This isolated area memory is carved out and for security-specific tasks. The operating system can access the specialized area of memory. However, it is only allowed limited access to the VBS-protected memory. This protection makes it much more difficult for an attacker to compromise protected information such as credential hashes and other sensitive information.
The HVCI Secured-core server feature uses VBS to provide code integrity enforcement. What type of virtualization is used? In the background, Windows Server 2022 uses Hyper-V to provide the virtual secure mode used for protecting the system and critical operating system components.
TPM 2.0
A Trusted Platform Module or TPM is a hardware device used for security-related tasks. The TPM device is a crypto-processor that generates, stores, and protects cryptographic keys. The protected keys are used for attestation, which identifies any tampering by attackers or malicious code. Windows Server 2022 can take advantage of the TPM 2.0 features and capabilities to provide robust security protections as part of the Secure-core server model.
Secured connectivity features
Microsoft has also tightened security with connectivity services aside from the Secured-core server features in Windows Server 2022. What do these enhancements include?
- HTTPS and TLS 1.3 are enabled by default
- DNS-over-HTTPS
- SMB AES-256 encryption
- Internal cluster communication SMB encryption
- SMB Direct and RDMA encryption
HTTPS and TLS 1.3 are enabled by default
Enforcing the latest security protocols and standards is a great way to help ensure your business-critical data is protected by vulnerabilities in lower-level protocols and standards. With Windows Server 2022, HTTPS and TLS 1.3 are enabled by default.
DNS-over-HTTPS
DNS is getting more secure in Windows Server 2022 with DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH). With the new DNS-over-HTTPS, DNS queries are encrypted using the HTTPS protocol. This helps to keep private DNS queries secure by preventing eavesdropping by an attacker or anyone snooping around the network.
SMB AES-256 encryption
When it comes to Server Message Block (SMB), businesses want to ensure file tranfers are as secure as possible. With Windows Server 2022, it now allows AES-256-GCM and AES-256-CCM encryption for SMB and signing. Microsoft has still built-in compabitility with older cipher suites to communicate with older versions of Windows. However, in ultra-secure environments, you can mandate the use of the more robust encryption ciphers using Group Policy.
Internal cluster communication SMB encryption
There are also security improvements in Windows Failover Server Cluster (WFSC) as you can now encrypt and sign intra-node storage communications for Cluster Shared Volumes used in WFSC. Additionally, when using Storage Spaces Direct (S2D), you can turn on encryption for east-west communications intra-server clusters to have the ultimate security for data communications.
SMB Direct and RDMA encryption
Microsoft has solved some performance issues in previous versions of Windows-related to encrypting SMB data traffic using SMB Direct and RDMA encryption. Microsoft mentions the performance impact was due to encryption disabling direct data placement. Now, with Windows Server 2022, data is encrypted before placement which drastically improves performance with these technologies.
SMB over QUIC
New in Windows Server 2022, you can use the QUIC protocol with SMB 3.1.1. It allows accessing data from edge file servers running in Azure, and users no longer need to establish a VPN connection to access data.
Hybrid cloud
With each successive Windows Server operating system, it has been easy to see the progression of hybrid cloud features and integration with Microsoft Azure. Windows Server 2019 brought about significant advancements in the area of hybrid cloud integration.
The writing has been on the wall, especially since Windows Server 2019, that Azure integration would be baked into every Windows version moving forward. Microsoft provides easy integration between the Windows Server operating system and Azure.
There is a wide variety of Azure services that integrate directly with Windows Server 2022. In addition, Microsoft is making it easier than ever to integrate with Azure using the Windows Admin Center management tool. Windows Admin Center, as shown above, provides an easy way to manage on-premises servers and integrate with Azure services right from the Windows Admin Center dashboard and extensions.
Below is a look at the Windows Admin Center connected to a Windows Server 2022 server and the default Azure extensions that are preinstalled. Note how you have access to:
- Azure hybrid center
- Azure Kubernetes Service
- Azure Backup
- Azure File Sync
- Azure Monitor
- Azure Security Center
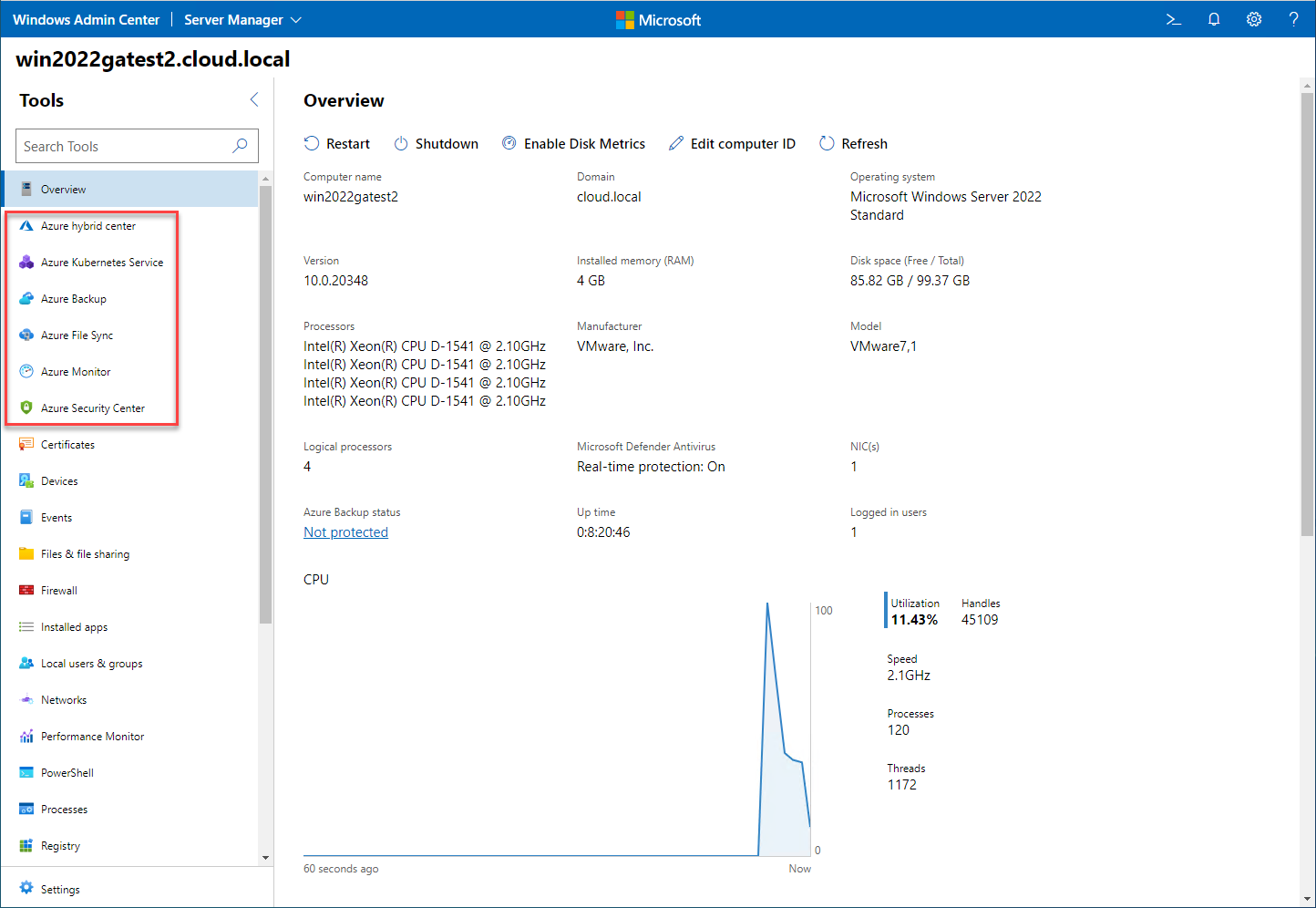
Viewing default Azure services extensions preinstalled with Windows Admin Center
From another view, there are still more services that are available for installation.
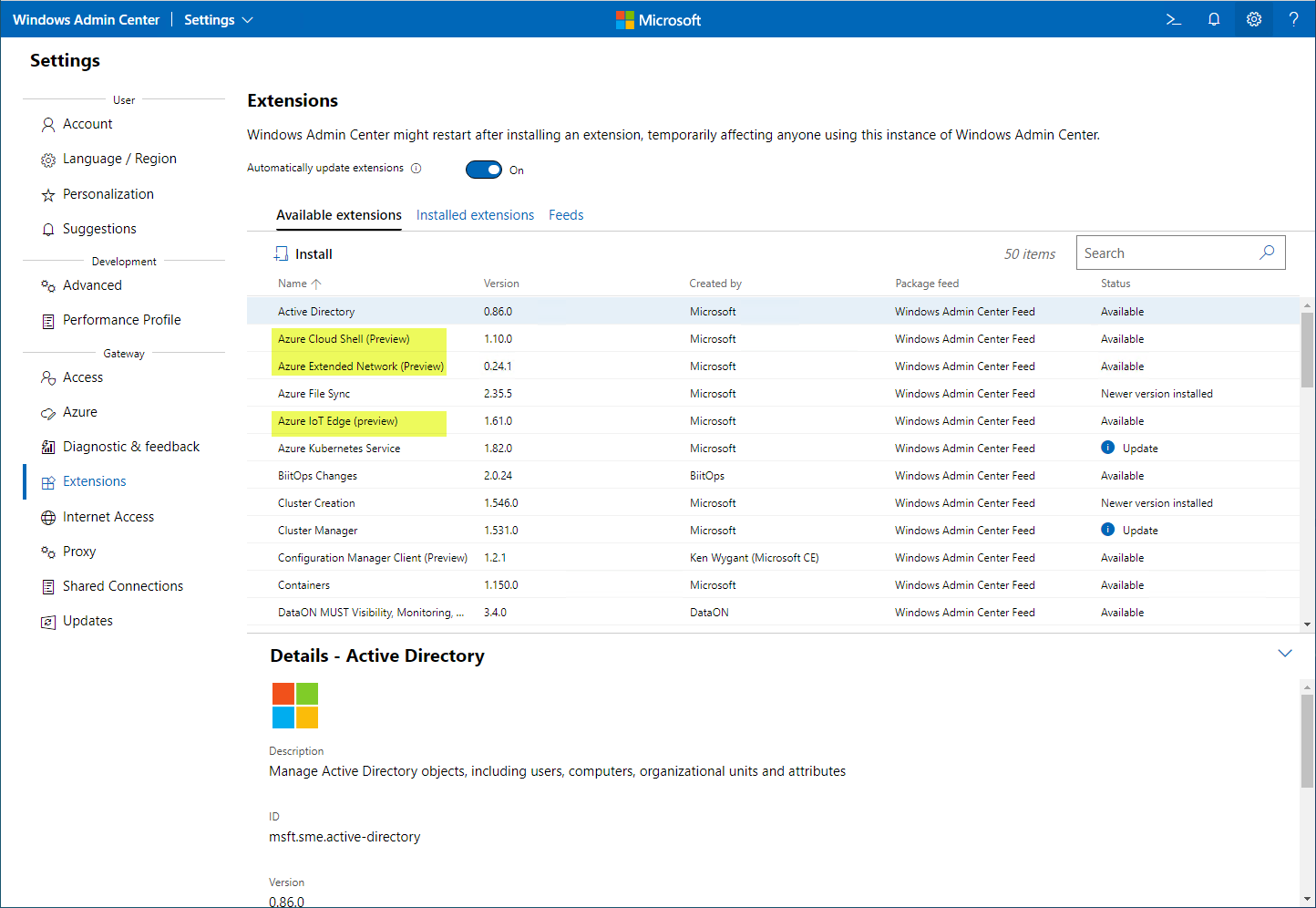
Many Azure services are available for installation in Windows Admin Center
With the tight integration between Windows Server 2022, Windows Admin Center, and Microsoft Azure, it is easier than ever for IT admins to take advantage of the hybrid services in Azure.
Azure Arc
One of the headaches for IT admins is having multiple management interfaces, processes, solutions, and other tools needed to manage the entire estate of enterprise resources. In addition, these processes and tools can become even more disparate between on-premises and cloud environments.
Microsoft Arc helps to alleviate this challenge by allowing organizations to extend the boundaries of the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) to on-premises environments. Azure Resource Manager (ARM) controls and automates resources across the Azure environment. With Azure Arc, organizations can manage and control their on-premises resources (Windows, Linux, VMware vSphere VMs, and even other public cloud resources) from the Azure management plane.
On-premises resources managed with Azure Arc are managed as native resources in Azure. These objects receive an Azure resource identifier and are organized using the Resource Groups in the Azure subscription. As a result, organizations will be able to manage their on-premises and cloud-hosted Windows Server 2022 instances in the same way and using the same processes and tooling.
Windows Admin Center
We have already discussed a great deal of the functionality of the Windows Admin Center, covering the other new Windows Server 2022 features as many of these are exposed using Windows Admin Center. The Windows Admin Center tool is the modern way to manage Windows Servers. It was released in tandem with Windows Server 2019, and Microsoft has been making steady improvements to the tool ever since.
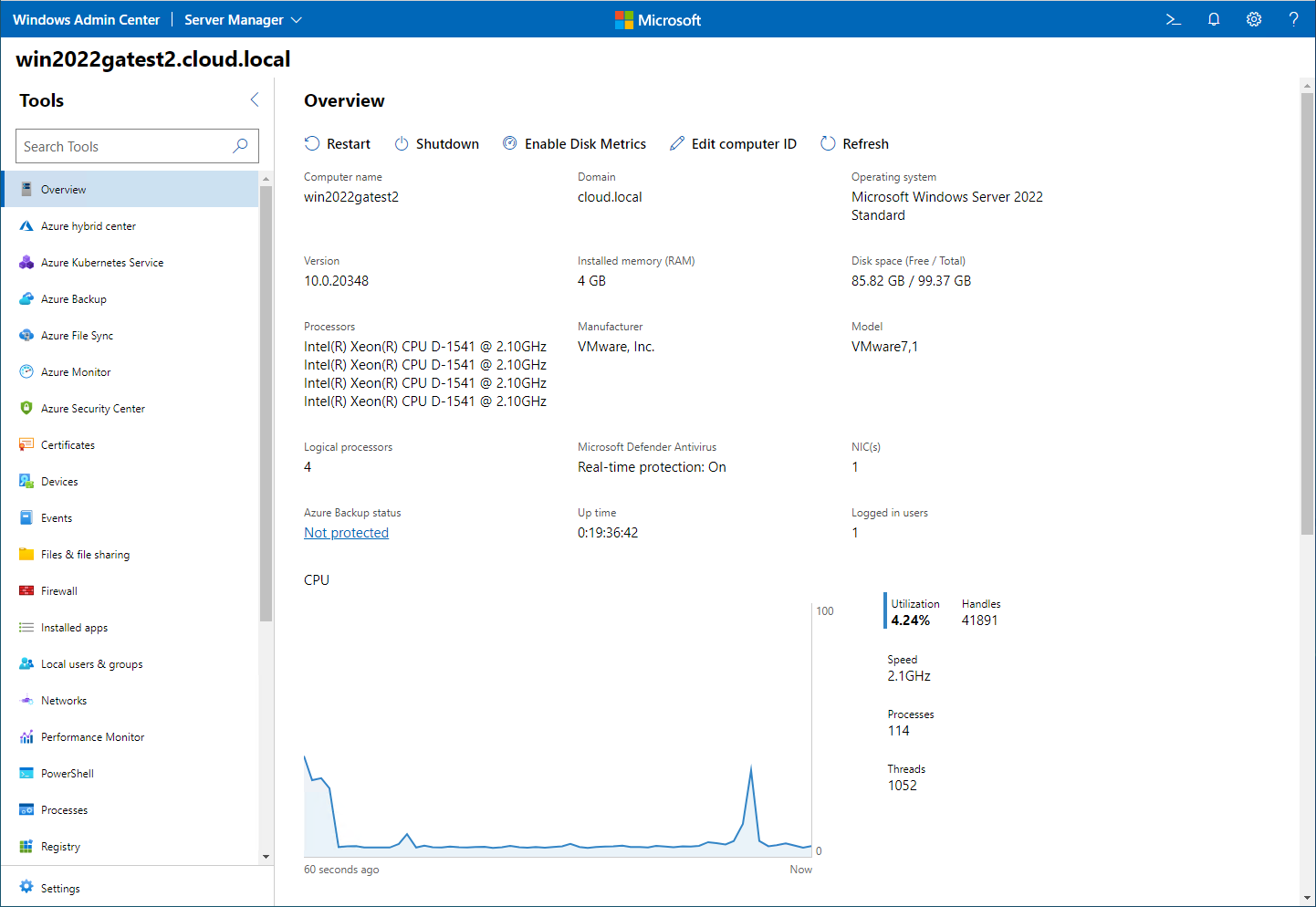
Windows Admin Center provides a single-pane-of-glass interface to manage Windows Server 2022
There are no cumbersome MSC dashboard console tools to remember or install. Once you have Windows Admin Center installed in Gateway mode, it allows a management workstation/server to manage multiple remote Windows Servers, all in a modern and straightforward web interface.
Windows Admin Center for Windows Server 2022 is not built into Server 2022 by default. However, it is available for download for free from the Microsoft Evaluation site. While Windows Admin Center is not new with Windows Server 2022, its maturity since Windows Server 2019 increases the robust feel with Windows Server 2022.
Application improvements
Windows Server 2022 containers represent a major step forward for running modern applications on containerized infrastructure. With Windows Server 2022, the container image size has been reduced by 40%. Having lean, efficient containers backing the applications is key to performance and other crucial benefits with containers and containerized applications.
Using group Managed Services Accounts (gMSA) allows running applications that depend on Azure Active Directory without domain joining a Windows Server 2022 container host. In addition, containers in Windows Server 2022 now support Microsoft Distributed Transaction Control (MSDTC) and Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ).
Note the following enhancements with Kubernetes as well:
- Host-process containers for node configuration
- IPv6
- Consistent network policy implementation with Calico
- Windows Admin Center can containerize .NET applications
- Host it on Azure Container Registry
Storage
There have been many new improvements with Windows Server 2022 and storage capabilities. One of the key enhancements of Windows Server 2022 storage is an enhanced version of the Storage Migration Service. With the new Storage Migration Service, you have the following capabilities with Windows Server 2022:
- Migrate local users and groups to the new server
- Migrate storage from:
– failover clusters
– migrate to failover clusters
– migrate between standalone servers and failover clusters
- Migrate Linux Samba shares
- Synchronize migrated shares into Azure by using Azure File Sync
- Migrate to new networks such as Azure
- Migrate NetApp CIFS servers from NetApp FAS arrays
Another new Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) feature is providing user-adjustable storage repair speed. This new capability allows having more control over the data resync process to repair data copies while not sacrificing performance. In addition, new SMB compression enhancements in Windows Server 2022 allow compression during a network copy. This feature means you no longer must first zip a file before copying it across the network. Lastly, storage bus cache is now available for standalone servers.
Networking
Microsoft has made various networking performance improvements across the board. These new improvements include:
- UDP performance improvements – includes UDP Segmentation Offload (USO), UDP Receive Side Scaling, and improved UDP data path
- TCP performance improvements – Windows Server 2022 uses TCP HyStart++, RACK, and smoother network data flow
- Hyper-V virtual switch improvements – Enhanced Receive Segment Coalescing (RSC), improved performance in both network traffic from an external host and received by a virtual NIC, and virtual NIC to another virtual NIC
Virtualization
One of the great new virtualization features in Windows Server 2022 is the new ability to use AMD processors in nested virtualization. Nested virtualization provides the ability to run Hyper-V inside of a Hyper-V virtual machine. It is an excellent tool for labs, POCs, and other test environments.
Wrapping Up
The new Windows Server 2022 release provides many new features across the board with the Windows Server operating system. It effectively brings together hybrid cloud features for businesses to take advantage of the power of Microsoft Azure. Windows Admin Center is designed to help IT admins realize the best management experience as well as easily unlock the hybrid cloud features contained in Windows Server 2022. In addition, Windows Server 2022 provides enhancements in security, applications, networking, storage, and virtualization.
You can download an evaluation copy of Windows Server 2022 here.




