Introduction
In our support work very often we face different environments. They can range from three VMs to a hundred of those, with the number of nodes from two to ten.
Today, I will tell you about the main features of Failover Cluster 2016, which are applicable to any environment.
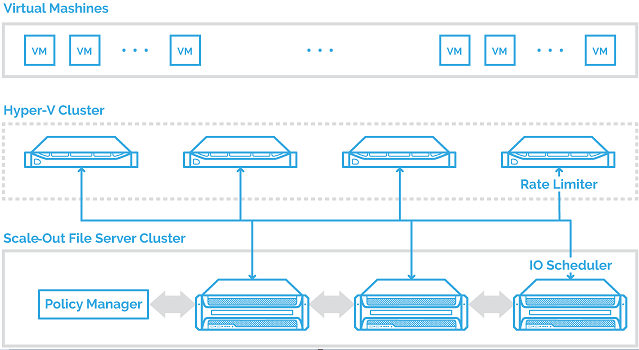
Storage QoS
This feature was introduced in 2012R2, but it did not work in a cluster. In 2016, it is possible to work with it in a cluster. Shortly, you can leverage the performance of VMs using Hyper-V and Scale-Out File Server roles.
This feature distributes resources between VMs using the same file server and permits to configure min and max IOPs.
You can read more about QoS in 2016 at our StarWind blog.
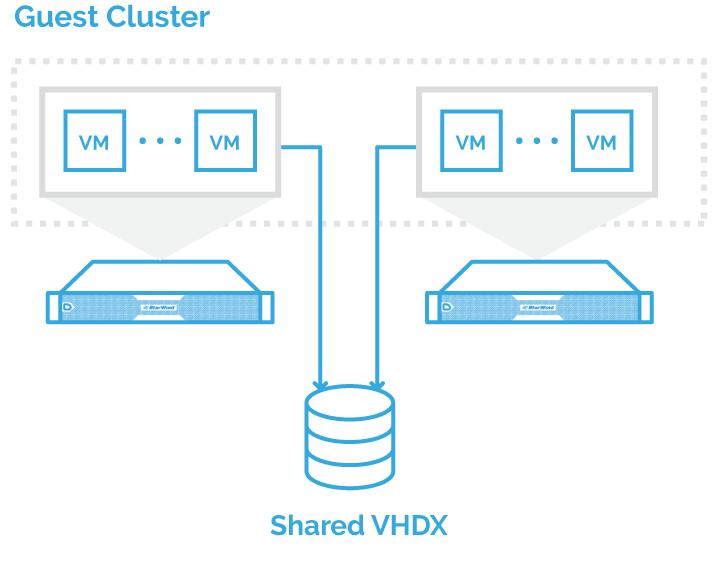
Shared VHDX
One of the useful features of Failover Cluster 2016 is shared VHDX integration. It was implemented in 2012R2. It allows the VHDX file, which is stored on a Cluster Shared Volume (CSV), to be connected to several VMs. It looks like a shared storage and could be used as a cluster storage for guest VMs.
The main difference between 2012R2 and 2016 is that the guest clusters are able to resize Shared VHDX without downtime.
Be aware that checkpoints and storage migration features do not work with Shared VHDX.
Evolving CSV Cache
The CSV cache is a write-through cache, which uses RAM, so all Hyper-V IO is unbuffered IO. This feature allows caching the frequently read data. Thus, CSV cache can accelerate the VM performance. It is disabled by default and also operates in file system redirected mode, thus allowing to work with Deduplication and Spaces Direct.

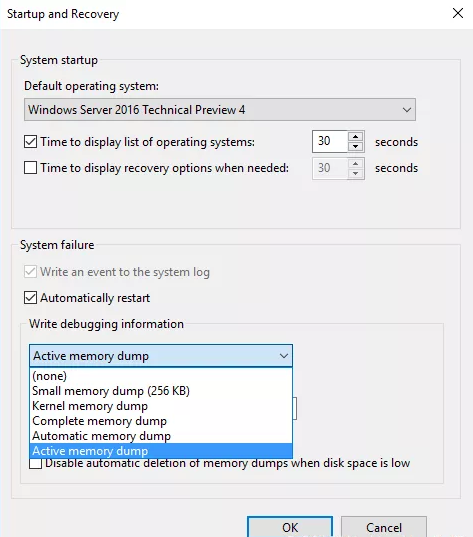
Active Dump
From the diagnosability perspective, the problem of the clients with Hyper-V systems having 128GB+ of RAM is that it is quite difficult to first collect the dump file and then to send it via the Internet to get any issues investigated. Usually, it takes plenty of GBs. Now such new feature as Active Dump makes the procedure much easier. Basically, Active Dump disregards all memory which is allocated to VMs, CSV cache etc. Eventually, the dump is about a couple of GB instead of 128GB+.
Thunderbolt
If you are going to have some sort of internode communication, ThunderBolt is a good solution for that. You do not need to buy another dedicated NIC and configure the IPs. It has to be auto-configured IPv6 and will show up as a 20Gb cluster network. This results in simplicity of internode communication inside the cluster.

Source: technet.microsoft.com
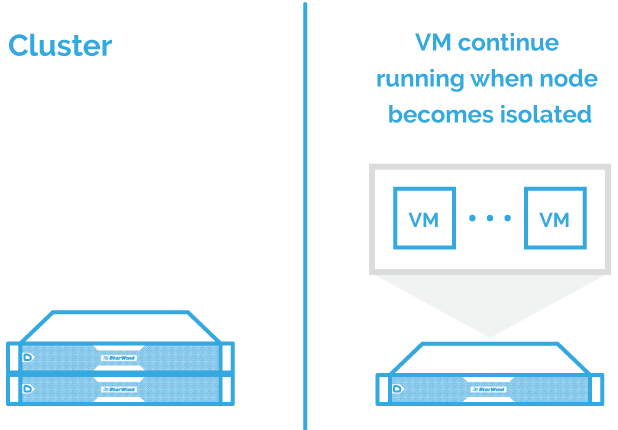
VM Compute Resiliency
Compute Resiliency slows down the failover of a Hyper-V cluster. These days, the quality of hardware becomes higher to the point when hardware failures are not common, but transient failures are more common instead. Very often, the problem is related to networking or other external issues. Thus, by default, Microsoft decided to wait for the response for 4 minutes. This time is enough to understand that either a switch was restarted after a crash, or network had some hiccup, etc. During this period, a problem node is in an isolated state in the cluster and failovers will not occur. This feature is configurable, and if you prefer to disable it, you can do this.
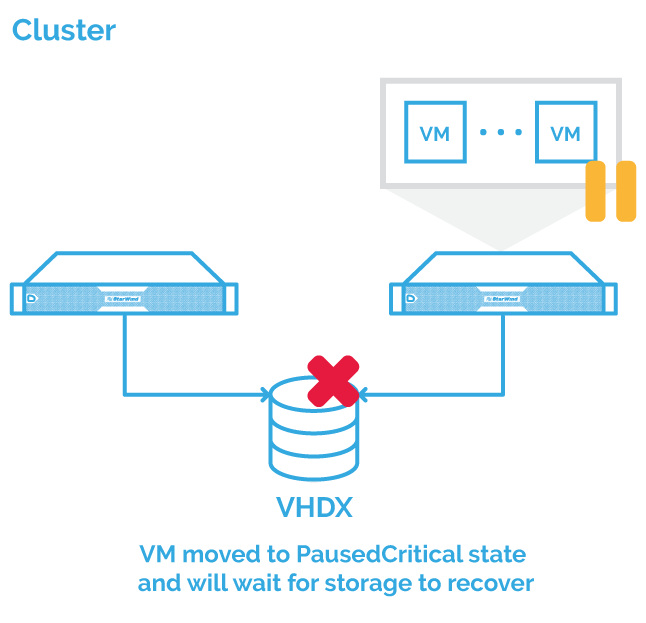
VM Storage Resiliency
Further, Failover Cluster 2016 is resilient to the transient issues at the storage layer. It will freeze the VMs when storage goes unresponsive. This status retains all the session state. When storage is available again all VMs start working seamlessly from the client’s perspective.
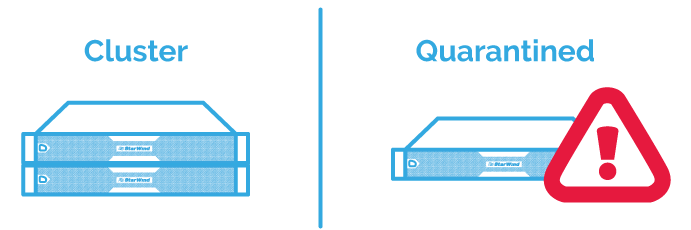
Quarantine of Flapping Nodes
This is a new feature which was implemented in WS 2016. It definitely, relates to Virtual Machine Compute Resiliency.
Basically, after 3 failure events, the problem node becomes quarantined instead of isolated. QuarantineThreshold is configurable meaning, by default, it is 3.
The QuarantineDuration parameter which is responsible for defining the period of time, during which the problem node is not able to join the cluster. Usually, it is about two hours.
However, you can use PowerShell to get the node back to the cluster:
Start-ClusterNode -ClearQuarantine
Any VMs running there will be live migrated off to another node automatically. The quarantined node will be drained and all resources owned by that node will then be moved off.
VM Start Ordering
Do not worry about VMs start priority in WS 2016. Now you can group all VMs into tiers and configure start ordering for different tiers. Thus, you can set up to start the important VMs such as Active Directory, Appliance, etc in the first row. The other VMs will not start before VMs with higher priority are started.
Domainless
Before all servers, which are members of the cluster, had to be joined to the domain, and it had to be the same domain.
Now, you can have clusters, which have nodes from different domains, or even a domainless cluster.
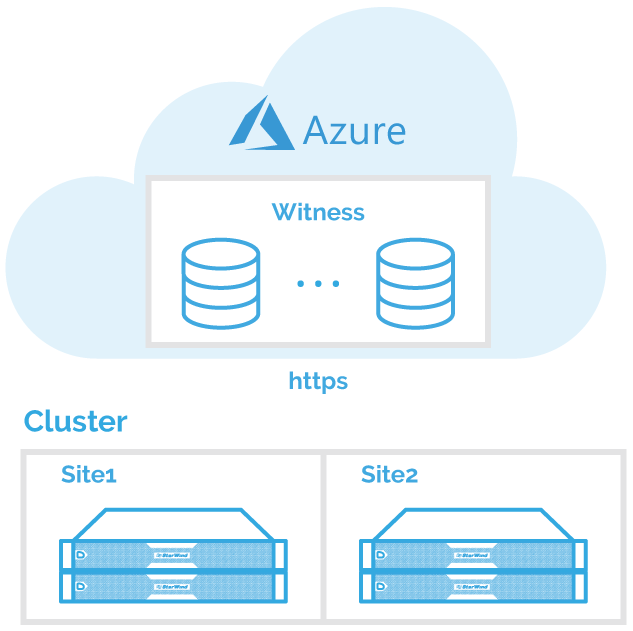
Cloud Witness
The very important new feature is Cloud Azure Witness. So, you can configure the stress cluster with some nodes at one site, other nodes at the second site and the Witness could be at the third site. Thus, if a datacenter is lost the cluster can survive. It works almost the same way. It contains a small amount of data, rather than the whole copy of the cluster database. It has a tag that is used for determining, which node has to stay up and drop out. There is no sensitive information or node names.
VM Load Balancing
The environment may have a node which got rebooted some time ago. All VMs have failed over and now there is nothing running on it. You have got everything running on the partner node. So, it is a problem. For this purpose, the Microsoft team introduced a new feature that is called VM Load Balancing. It allows to identify idle nodes in the cluster and distributes VMs to utilize them. Utilization is determined by VM memory usage and CPU pressure. VMs are live migrated to idle nodes with no downtime.
Conclusion
Thus, I recommend upgrading the previous versions of Failover Cluster to the newest version. You can take advantage of all new features which are implemented there and get more resiliency and redundancy. If you are after this, take a look at the guide on how to perform Cluster Rolling Upgrade without any downtime at our blog.




