StarWind SAN & NAS CVM 2-node Converged Scenario with Windows Server
- May 23, 2023
- 28 min read
- Download as PDF
Introduction
StarWind SAN & NAS Controller Virtual Machine (CVM) comes as a prepackaged Linux Virtual Machine (VM) to be deployed on any industry-standard hypervisor. The solution is a fully certified shared storage for Windows Server and Microsoft Hyper-V Server, allowing you to repurpose your existing hardware running industry-standard hypervisor into high-performing storage.
StarWind SAN & NAS supports hardware and software-based storage redundancy configurations. The solution allows turning your server with internal storage into a redundant storage array presented as NAS or SAN, exposing standard protocols such as iSCSI, SMB, and NFS. It features Web-based UI, Text-based UI, and Command-line interface for your cluster-wide operations.
This guide describes the deployment and configuration process of the StarWind SAN & NAS CVM.
StarWind SAN & NAS virtual machine requirements
Prior to installing StarWind SAN & NAS virtual storage appliance, please make sure that the system meets the requirements, which are available at the following link: https://www.starwindsoftware.com/system-requirements
Pre-Configuring the Servers
The diagrams below illustrate the common network and storage configurations of the solution for specific deployment configurations.
Please select your deployment scenario:
Highly available shared storage servers
- Dedicated 2 storage servers expose highly available shared storage for vSphere and Hyper-V clusters:
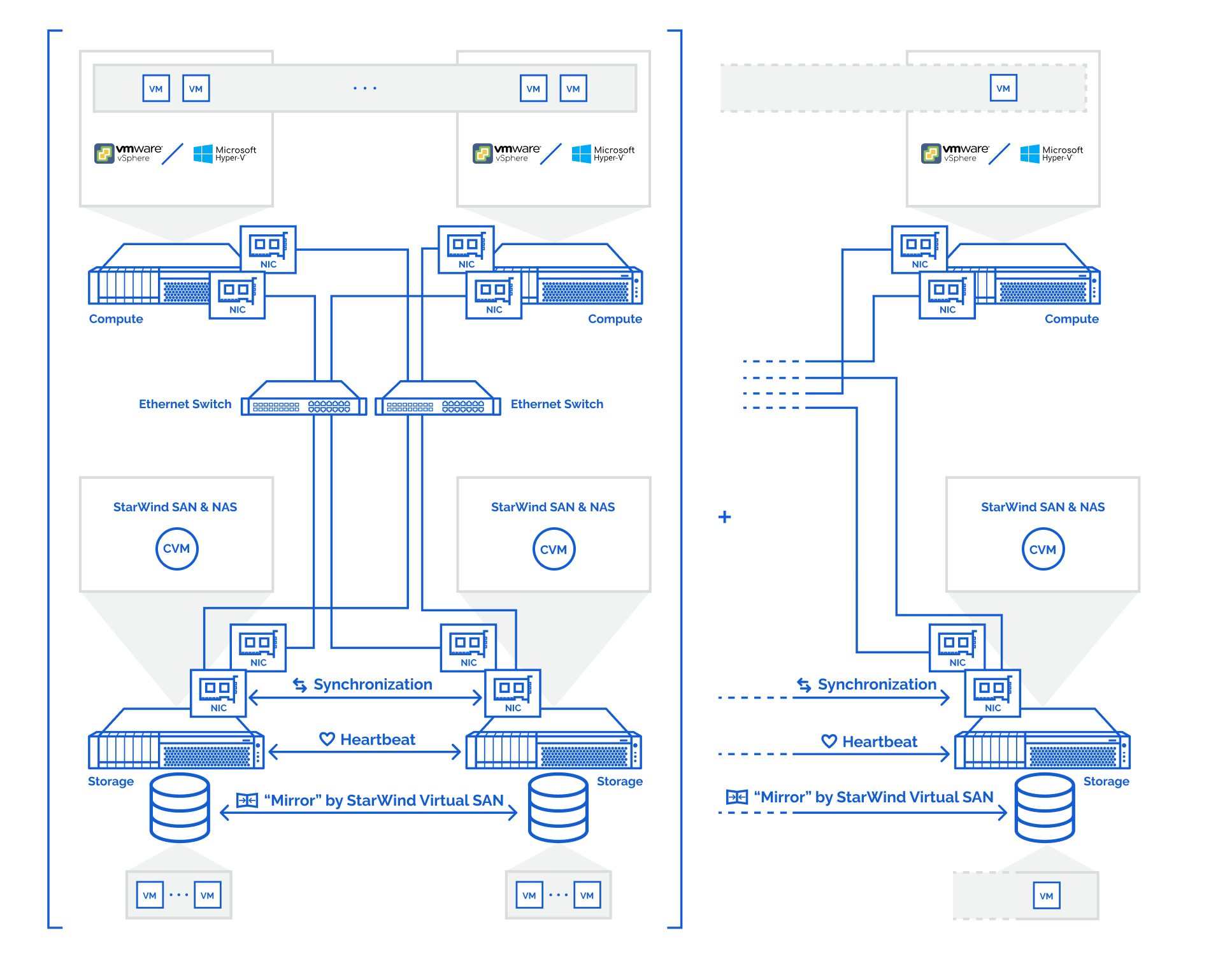
1. Install the hypervisor of your choice, VMware vSphere Hypervisor ESXi or Hyper-V Server, on two dedicated storage servers, and on the compute servers that are intended to connect and utilize the shared storage provisioned by the appliance.
2. StarWind SAN & NAS CVM is deployed on each Hyper-V Server or VMware ESXi server with commodity direct-attached storage.
3. The network interfaces on each node for Management, Data/iSCSI, and Replication interfaces should be connected to different subnets and connected directly according to the network diagram above. Here, the 172.16.10.x subnet is used for the Data (iSCSI) storage traffic, and 172.16.20.x subnet is used for the Replication storage traffic.
NOTE: The vCenter server is recommended for the deployment of multiple ESXi servers.
NOTE: The Failover Cluster feature is recommended for the deployment of multiple Hyper-V servers.
Setting up StarWind SAN & NAS
This part describes how to prepare the environment to deploy and install StarWind SAN & NAS using your hypervisor of choice, either VMware ESXi and VMware vSphere web clients or Microsoft Hyper-V Server.
Please select the required option:
Configuring converged storage server with Hyper-V Server
Configuring Networks on Microsoft Hyper-V Server
Configure external virtual switches on a hypervisor server, at least one for Management, one for Data, and one for Replication. Ensure the interfaces are in different subnets and connected physically according to the network diagram above. All actions below should be applied to each Hyper-V server for running StarWind SAN & NAS. In this document, the 172.16.10.x subnet is used for Data traffic and 172.16.20.x subnet is used for Replication traffic.
NOTE: It is recommended to set jumbo frames to 9000 on the virtual switch and network interfaces used for Data/iSCSI traffic.
1. Using Virtual Switch Manager create a new external virtual switch for the Management network.
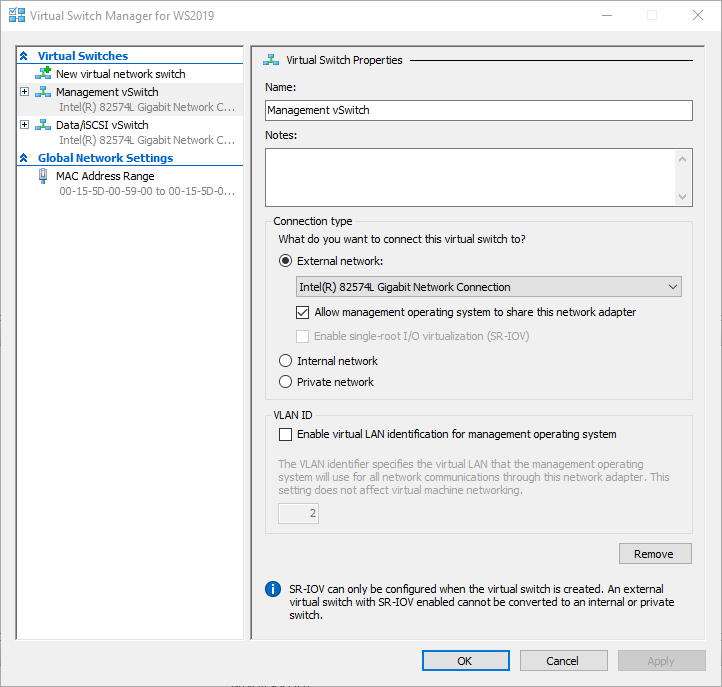
2. Create a second external virtual switch for the Data network.
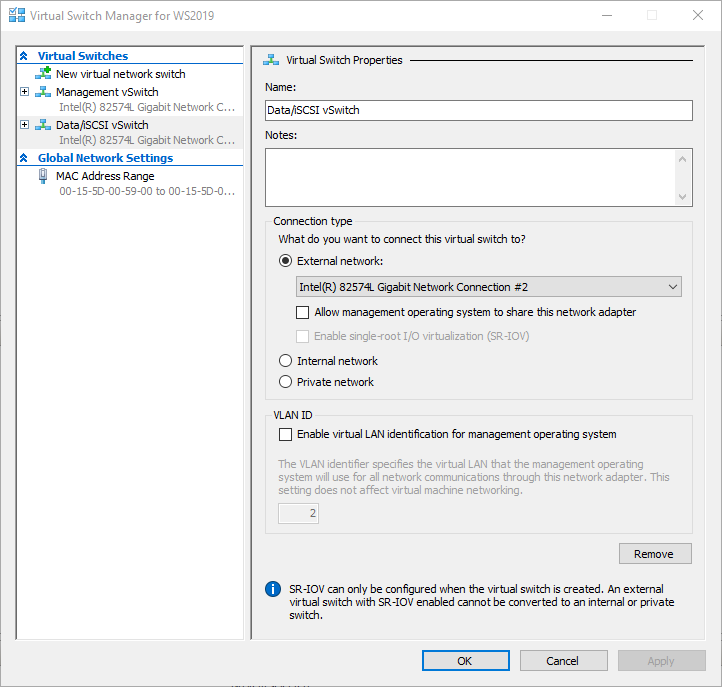
3. Repeat the procedure, create a third external virtual switch for the Replication (Synchronization) network.
Deploying StarWind SAN & NAS CVM on Hyper-V Servers
1. Download the zip archive that contains StarWind SAN & NAS CVM
https://www.starwindsoftware.com/san-and-nas#download
2. Extract the virtual machine files.
3. Deploy the control virtual machine to the Microsoft Hyper-V Server using the “Import Virtual Machine” wizard in Hyper-V Manager.
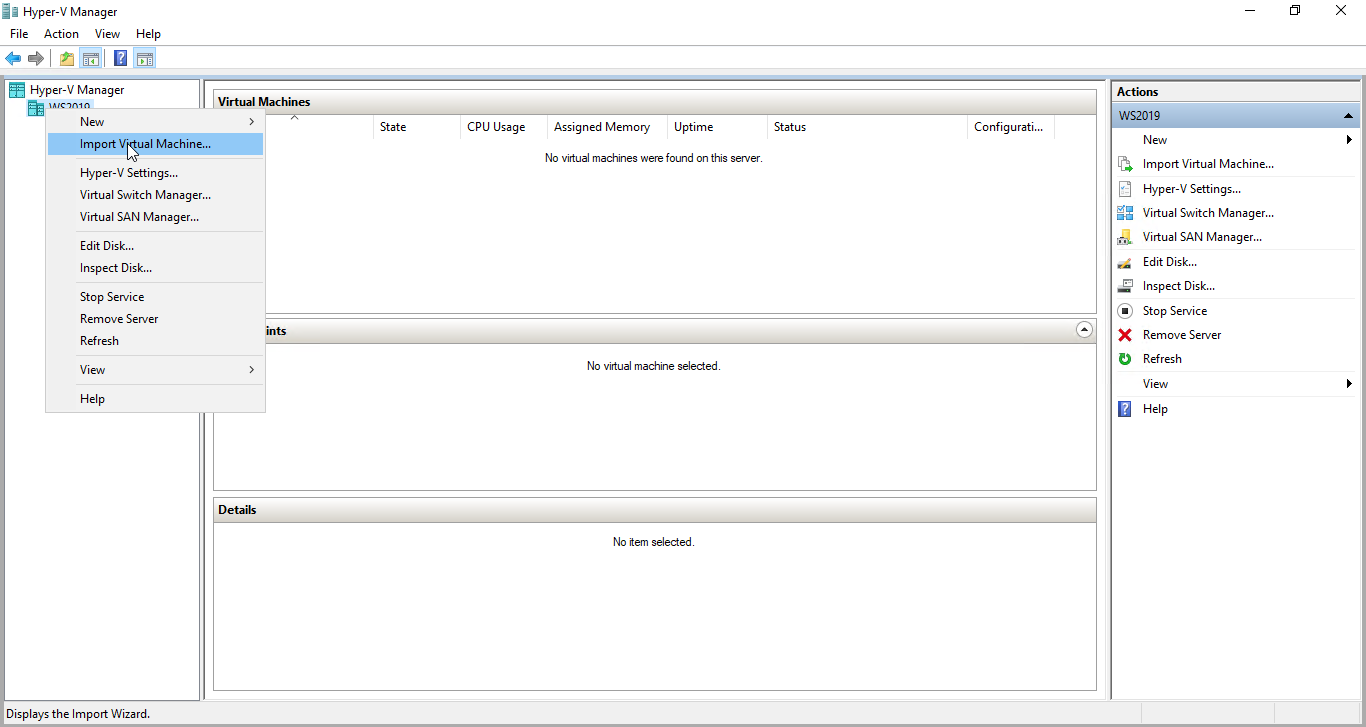
4. On the second page of the wizard, point to the location of the VM template. Select the VM folder and click Next.
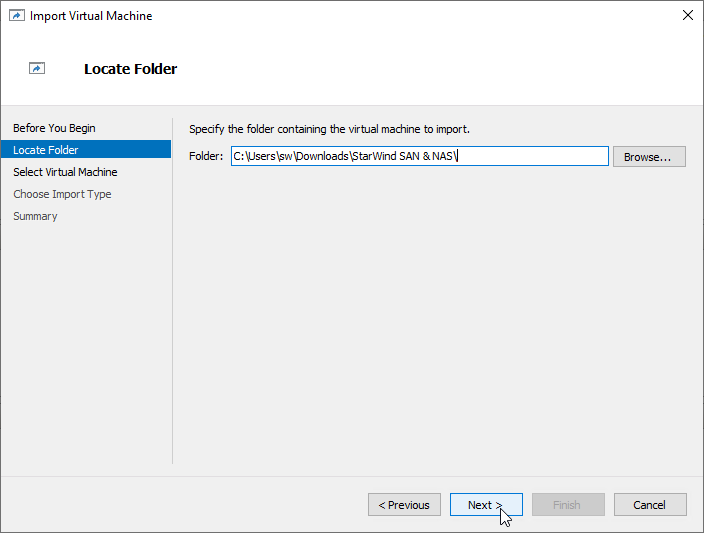
5. Click Next on the “Select Virtual Machine” step.
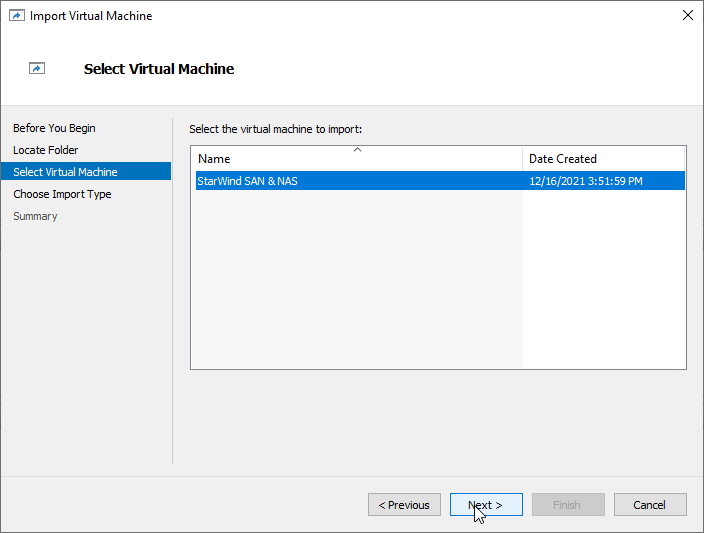
6. Select the “Copy the virtual machine” import type and click Next.
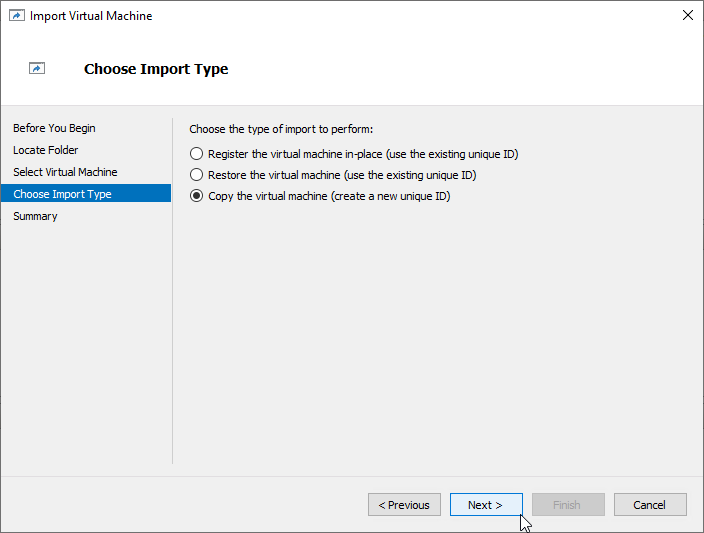
7. Specify new or existing folders to store virtual machine files, such as configuration, snapshots, smart paging, and virtual disk. Click Next.
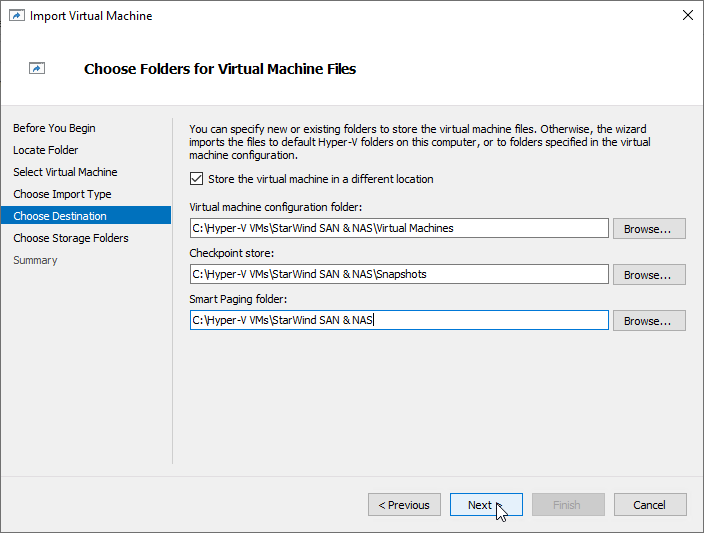
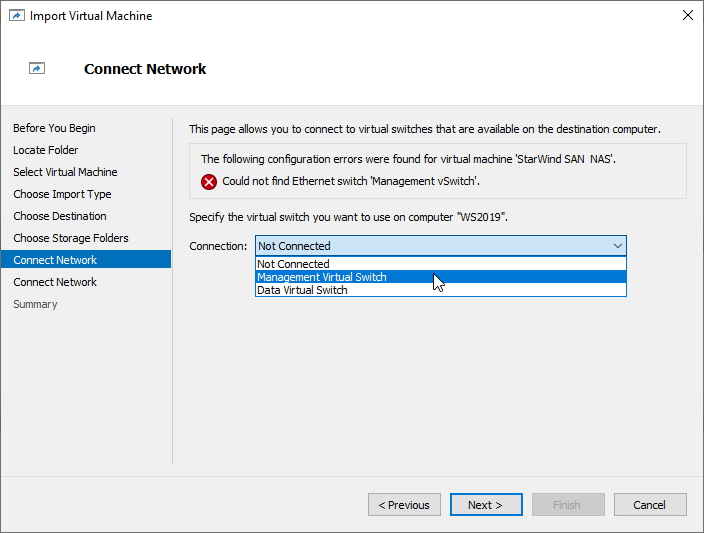
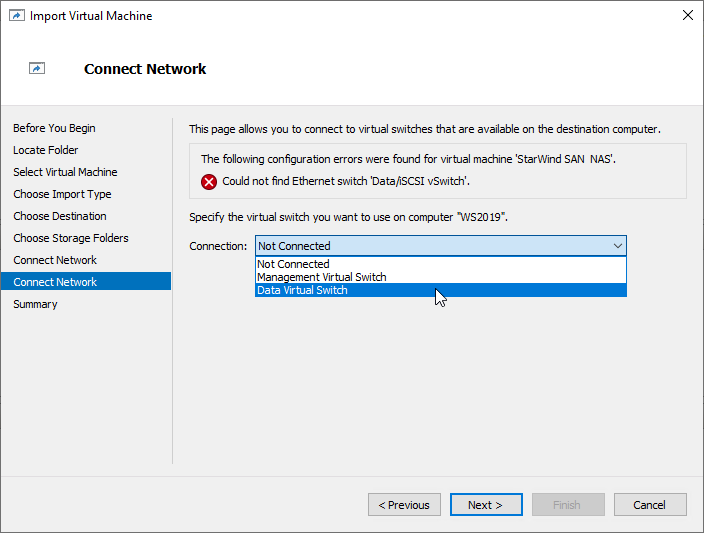
8. In the second step of the wizard, the “VM import” wizard will validate the network.
The default naming for virtual switches:
- the Management virtual switch is “Management vSwitch”,
- the iSCSI virtual switch is “Data/iSCSI vSwitch”,
- the Synchronization virtual switch is “Replication/Sync vSwitch “.
If existing virtual switches have different names, specify corresponding network connections. Click Next.
9. Review the import configuration and click Finish to complete the import.
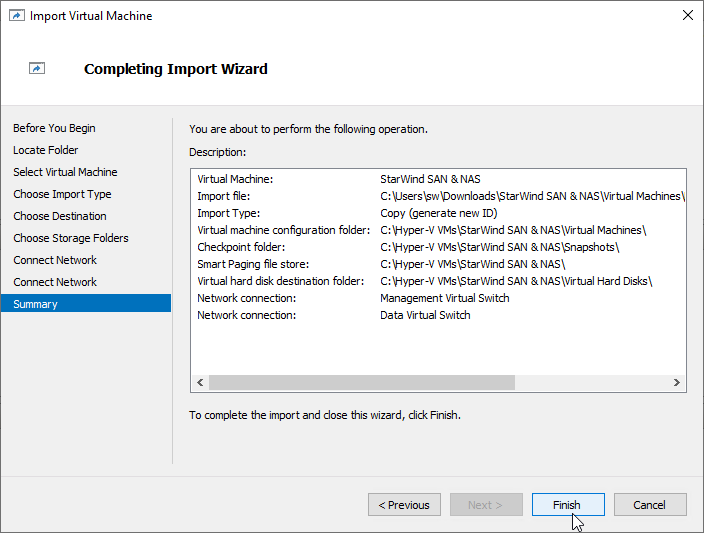
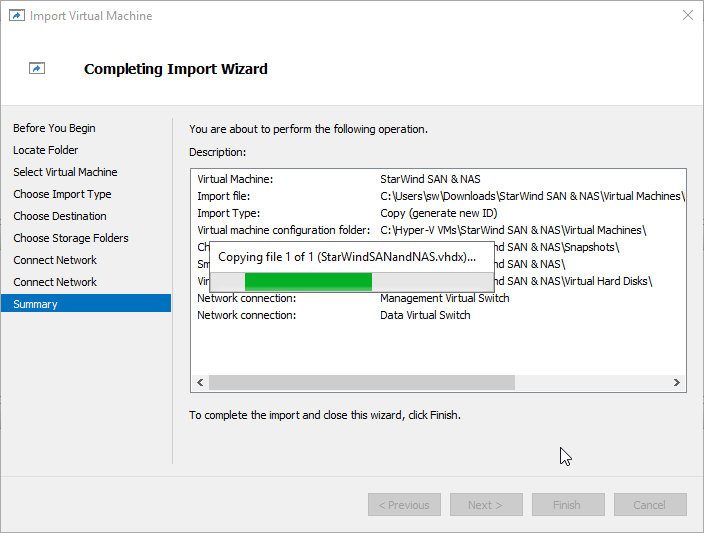
10. Repeat the VM deployment on each partner server which is used for configuring 2-node or 3-node highly available storage according to your licensing.
Configuring Appliances
Getting started with StarWind SAN & NAS
1. Start StarWind SAN & NAS CVM.
2. Launch Console to see the VM boot process and get the IPv4 address of the Management network interface.
Note: in case VM has no IPv4 address obtained from a DHCP server, use the Text-based User Interface (TUI) to set up a Management network.
3. Using the web browser, open a new tab and enter the VM IPv4 address to open StarWind SAN & NAS Web Interface. Click “Advanced” and then “Continue to…”
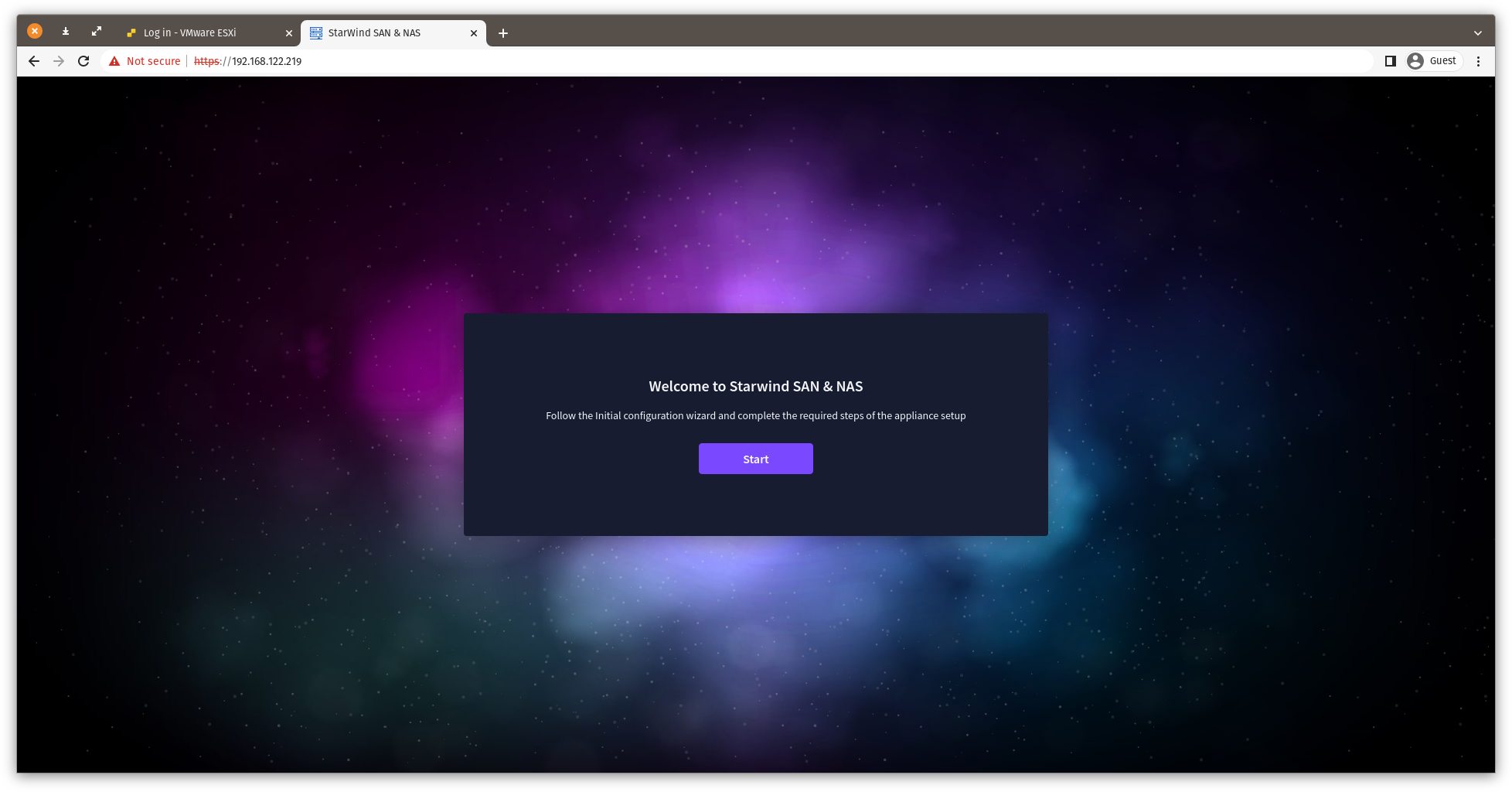
4. StarWind SAN & NAS welcomes you, and the “Initial configuration” wizard will guide you through the deployment process.
5. In the following step, upload the license file.
6. Read and accept the End User License Agreement to proceed.
7. Review or edit the Network settings and click Next.
Note: Static network settings are recommended for the configuration.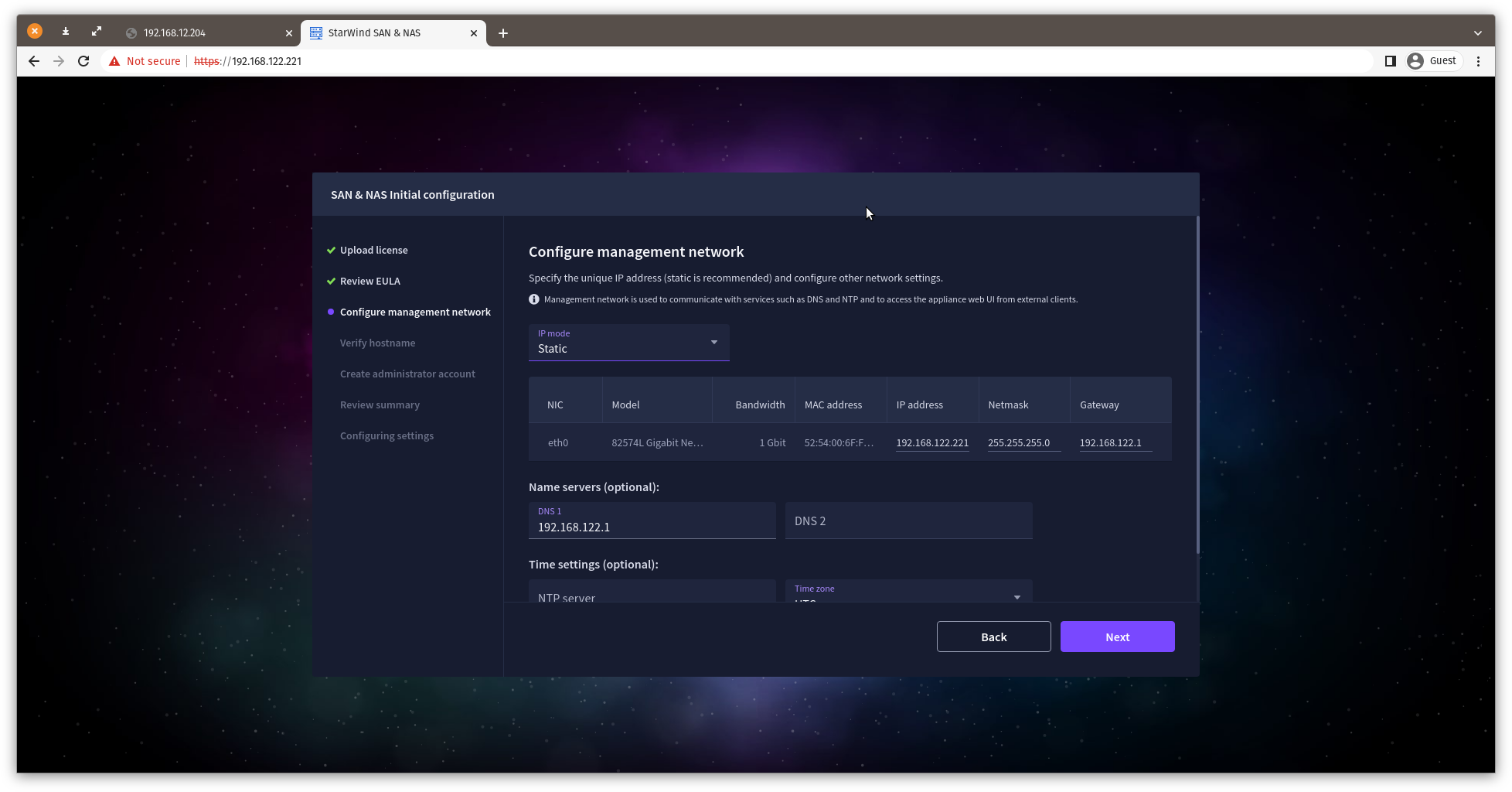
8. Specify the hostname for the virtual machine and click Next.
9. Create an administrator account. Click Next.
10. Review your settings selection before setting up StarWind SAN & NAS.
11. Please standby until the Initial Configuration Wizard configures StarWind SAN & NAS for you.
12. The appliance is set and ready. Click on the Done button to install StarWind vCenter Plugin right now or uncheck the checkbox to skip this step and proceed to the Login page.
13. Repeat the initial configuration on other StarWind SAN & NAS CVMs that will be used to create 2-node or 3-node HA shared storage.
Add Appliance
To create 2-way or 3-way synchronously replicated highly available storage, add partner appliances that use the same license key.
1. Add StarWind appliance(s) in the web console, on the Appliances page.
NOTE: The newly added appliance will be linked to already connected partners.
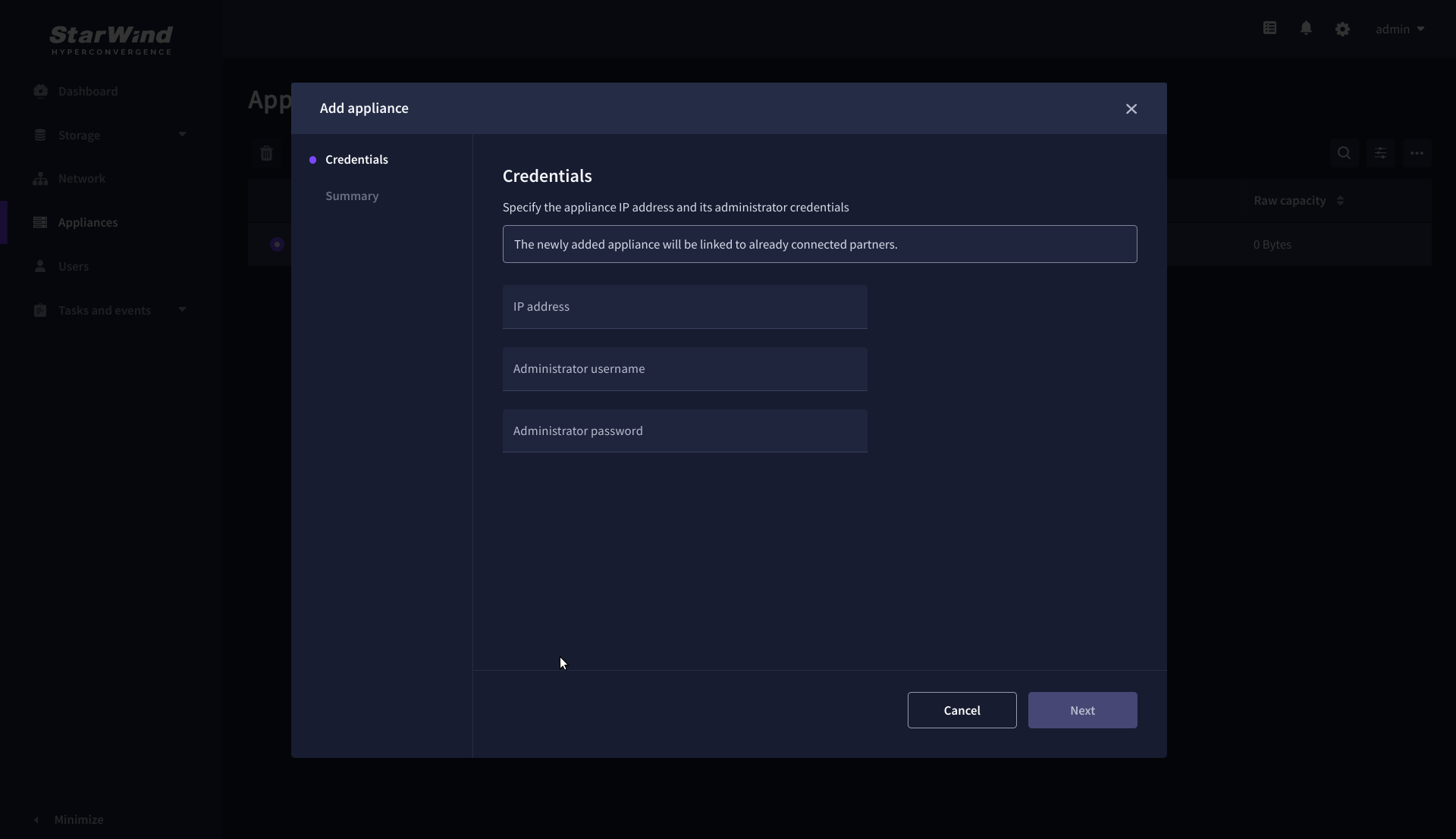
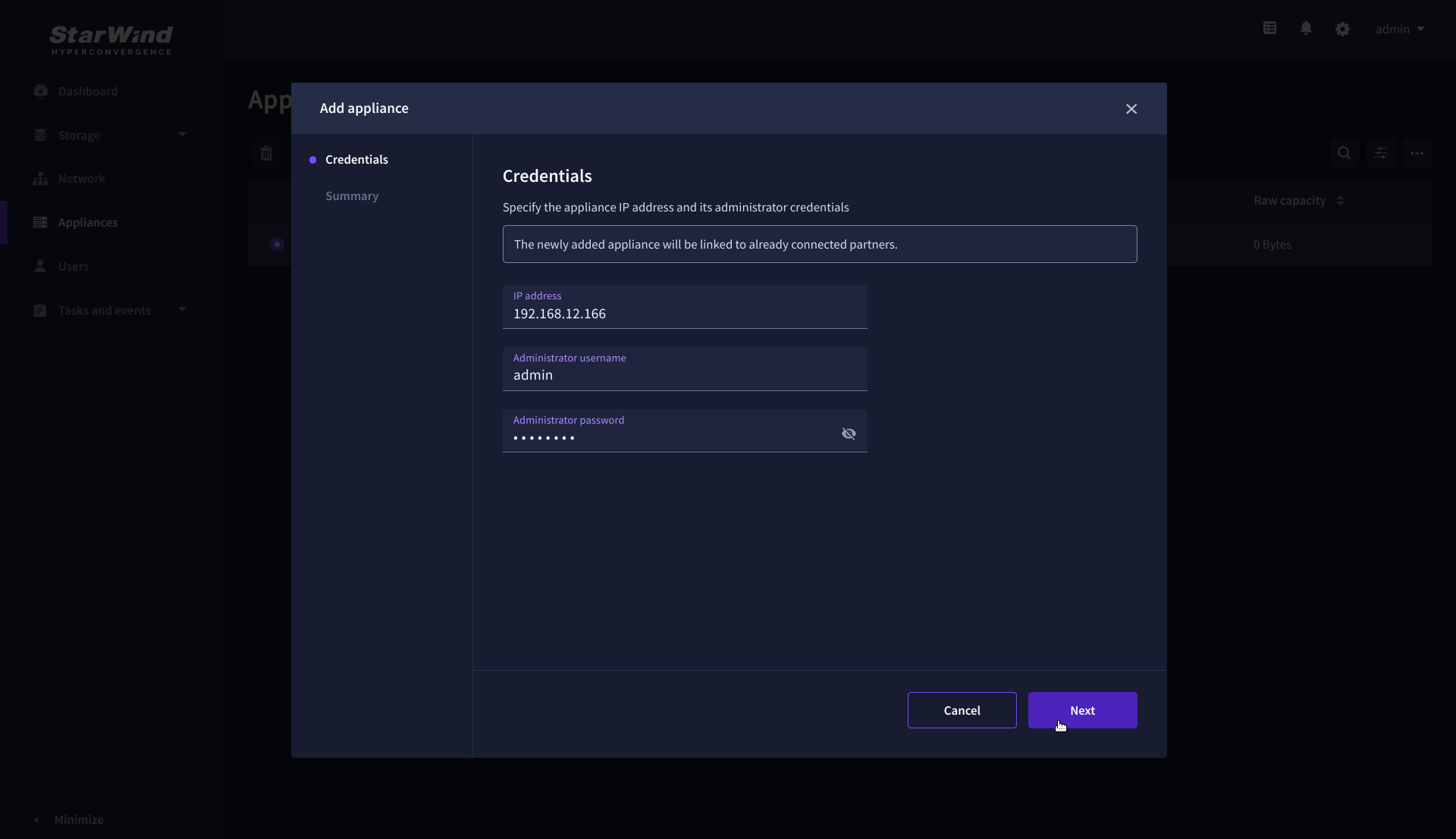
2. Provide credentials of partner appliance.
3. Wait for connection and validation of settings.
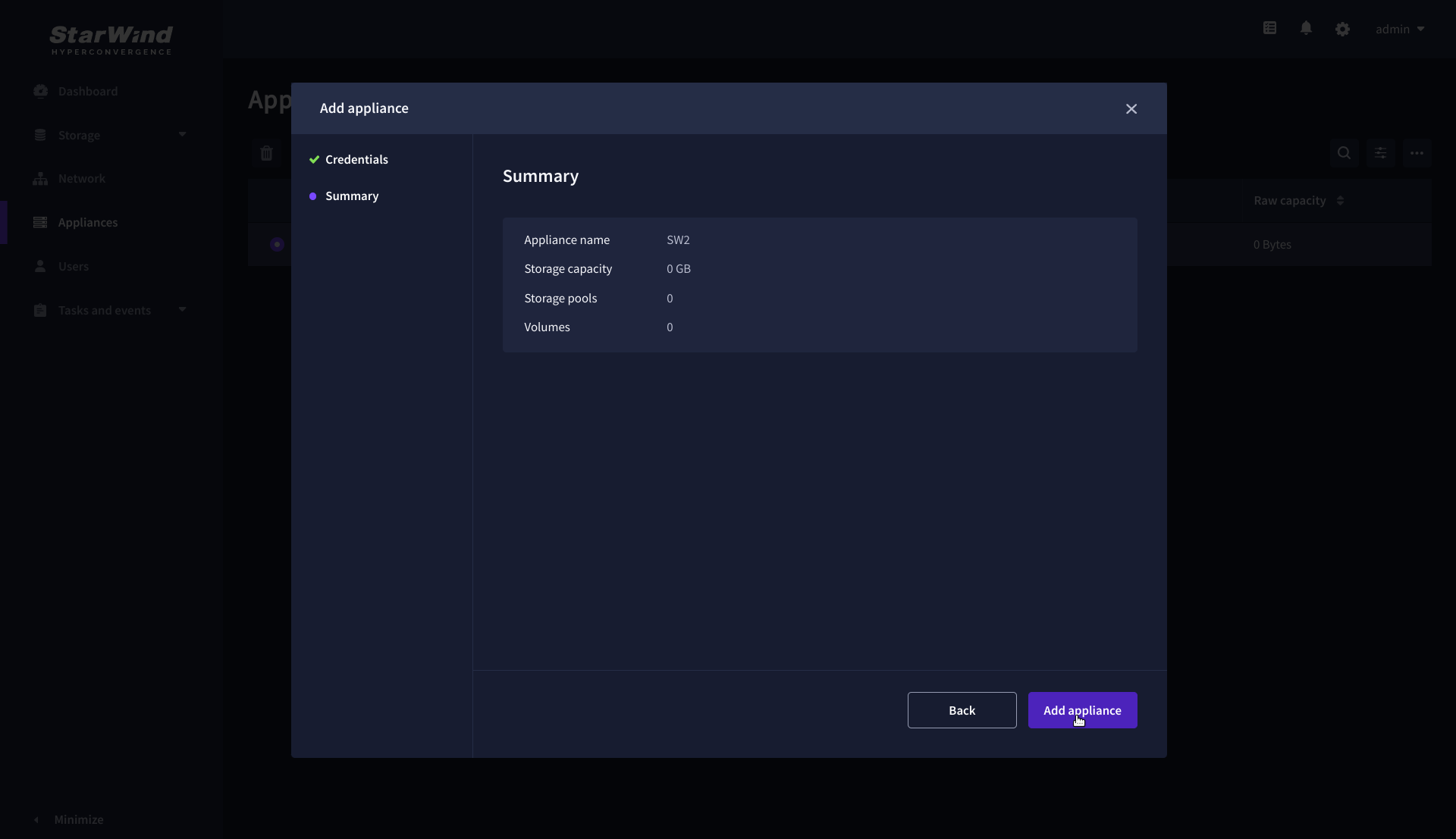
4. Review the summary and click “Add appliance”.
Configure HA networking
1. Launch the “Configure HA Networking” wizard.
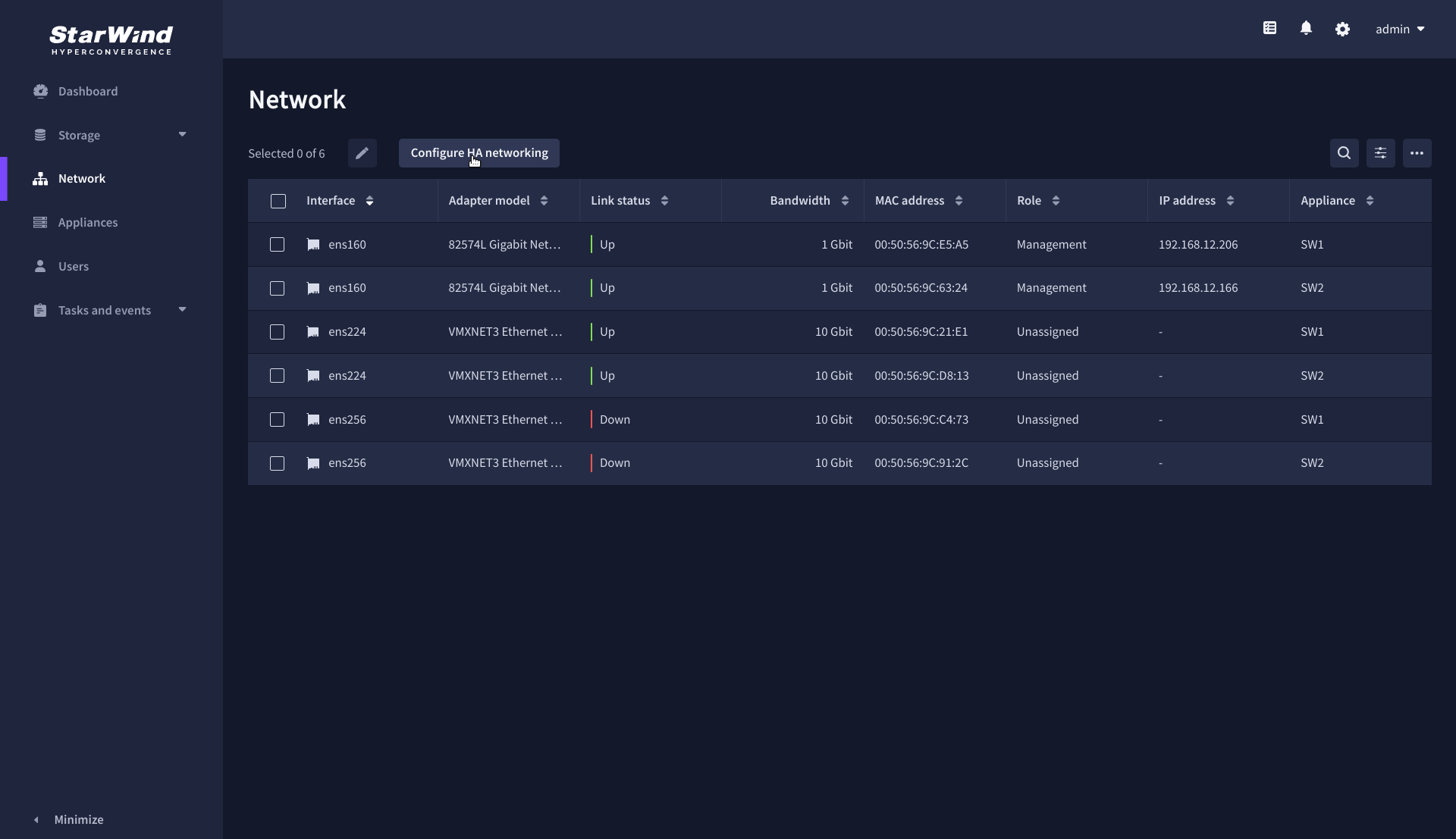
2. Select appliances for network configuration.
NOTE: the number of appliances to select is limited by your license, so can be either two or three appliances at a time.
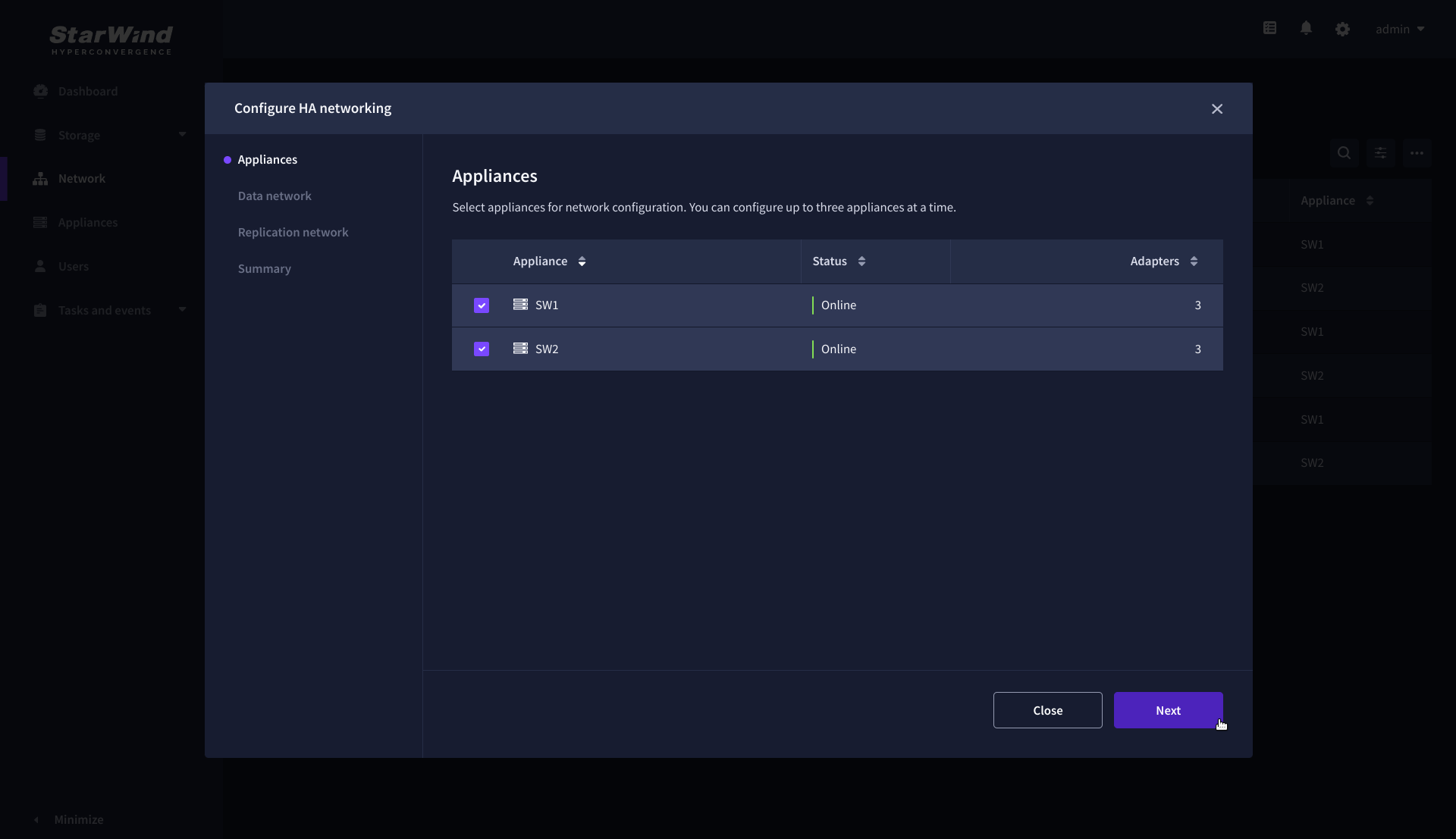
3. Configure the “Data” network. Select interfaces to carry storage traffic, configure them with static IP addresses in unique networks, and specify subnet masks:
- assign and configure at least one interface on each node
- for redundant configuration, select two interfaces on each node
- ensure interfaces are connected to client hosts directly or through redundant switches
4. Assign MTU value to all selected network adapters, e.g. 1500 or 9000. Ensure the switches have the same MTU value set.

5. Click Next to validate Data network settings.
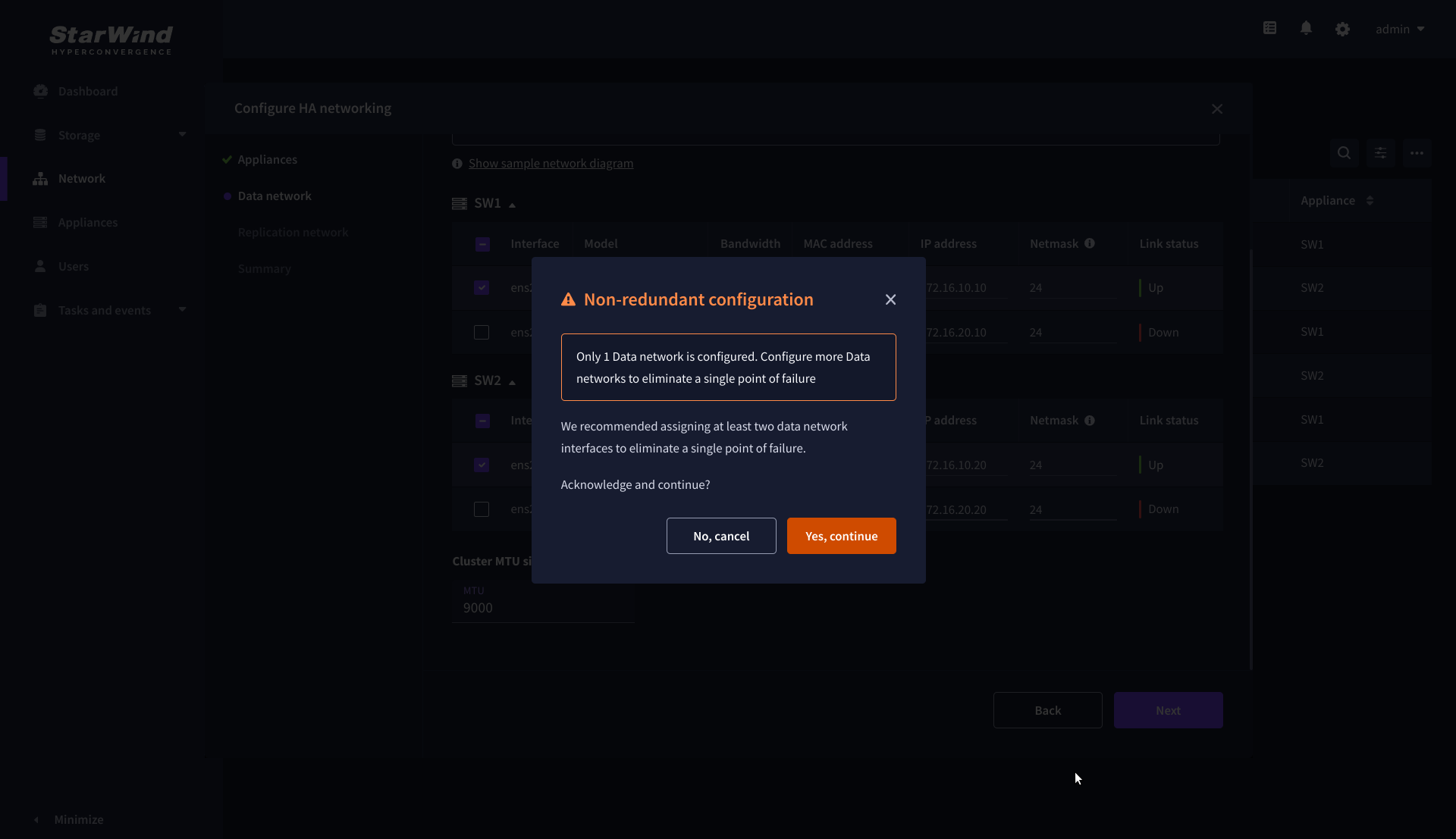
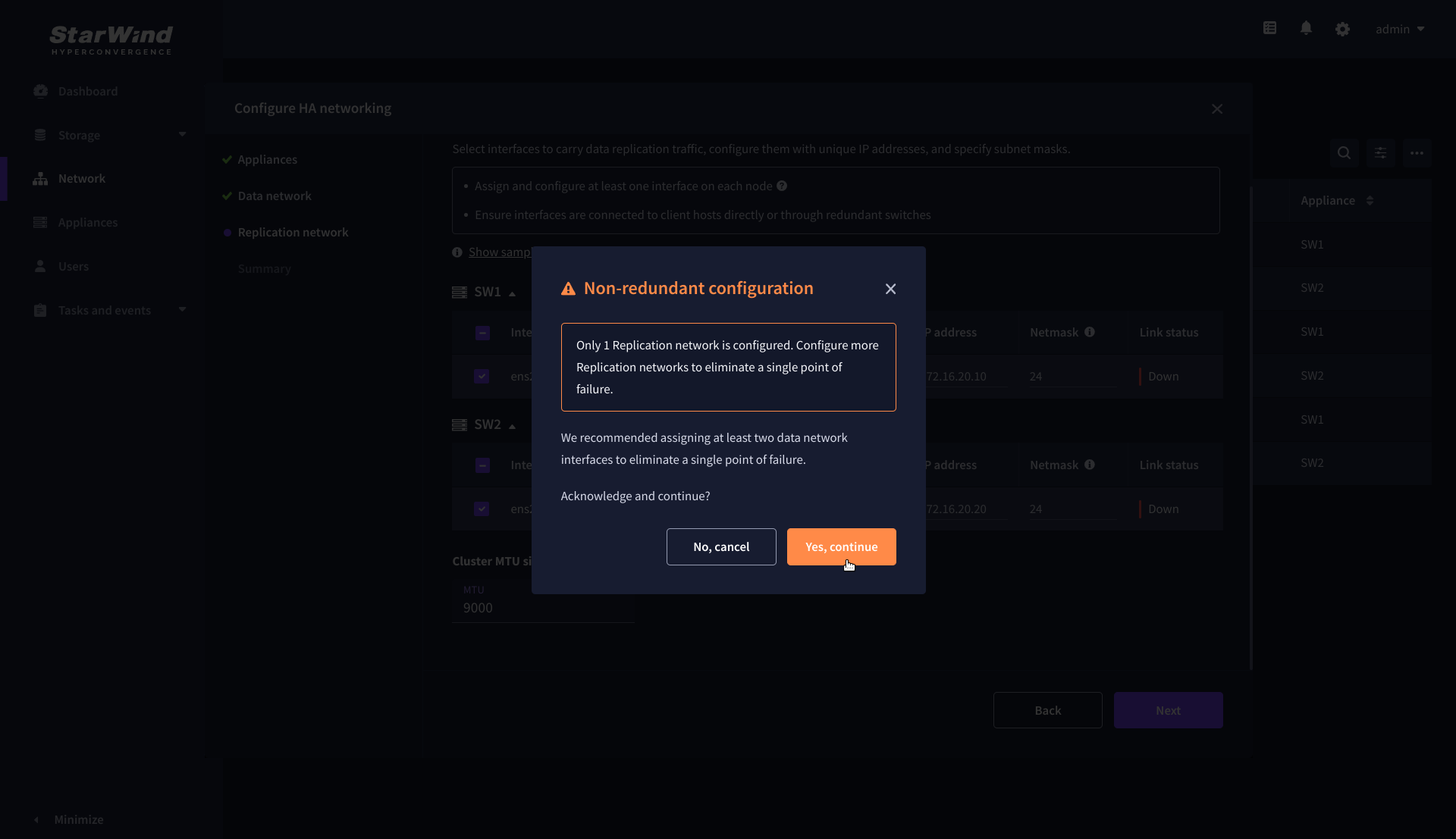
6. Configure the “Replication” network. Select interfaces to carry storage traffic, configure them with static IP addresses in unique networks, and specify subnet masks:
- assign and configure at least one interface on each node
- for redundant configuration, select two interfaces on each node
- ensure interfaces are connected to client hosts directly or through redundant switches
7. Assign MTU value to all selected network adapters, e.g. 1500 or 9000. Ensure the switches have the same MTU value set.
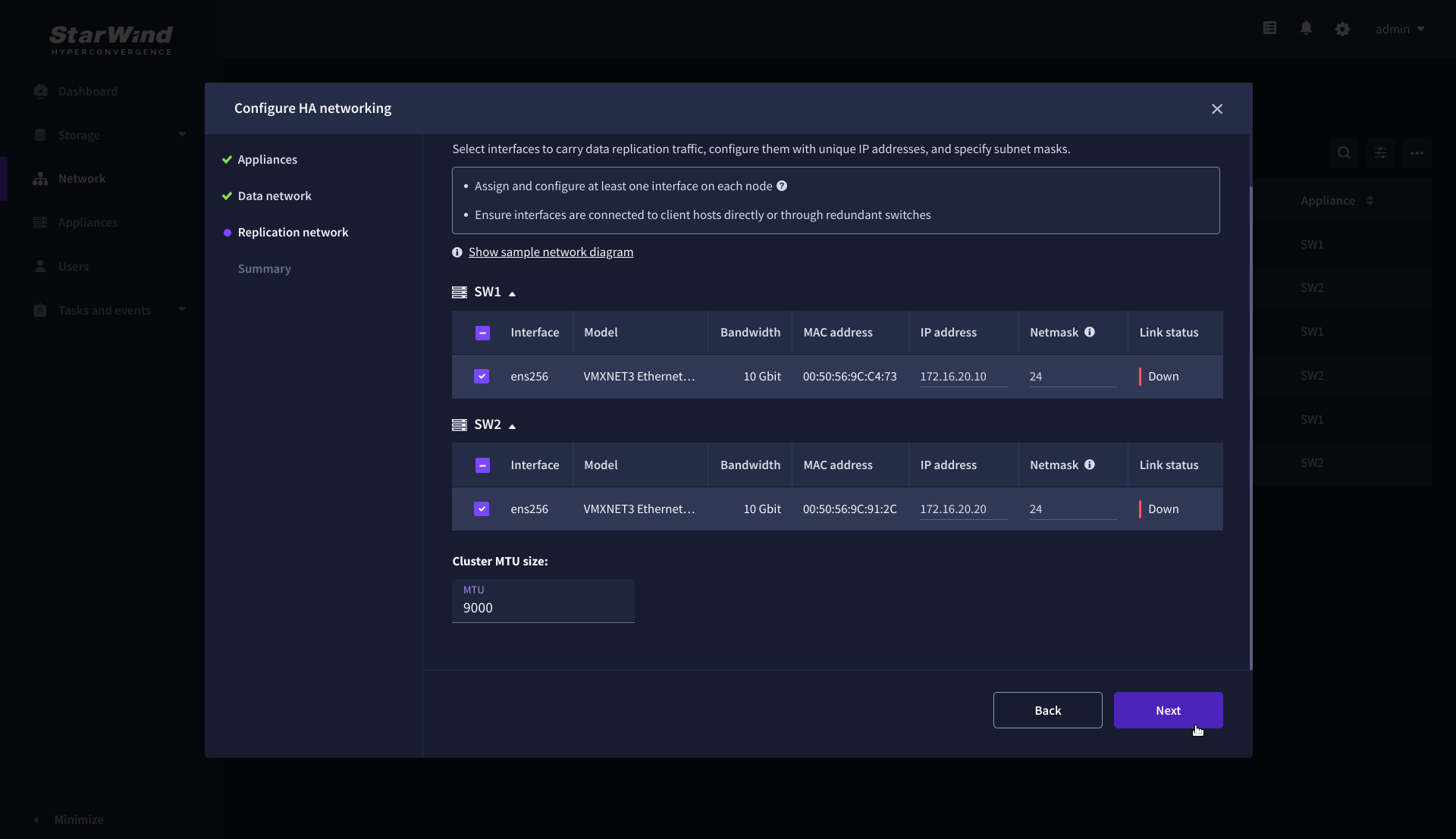
8. Click Next to validate the Replication network settings completion.
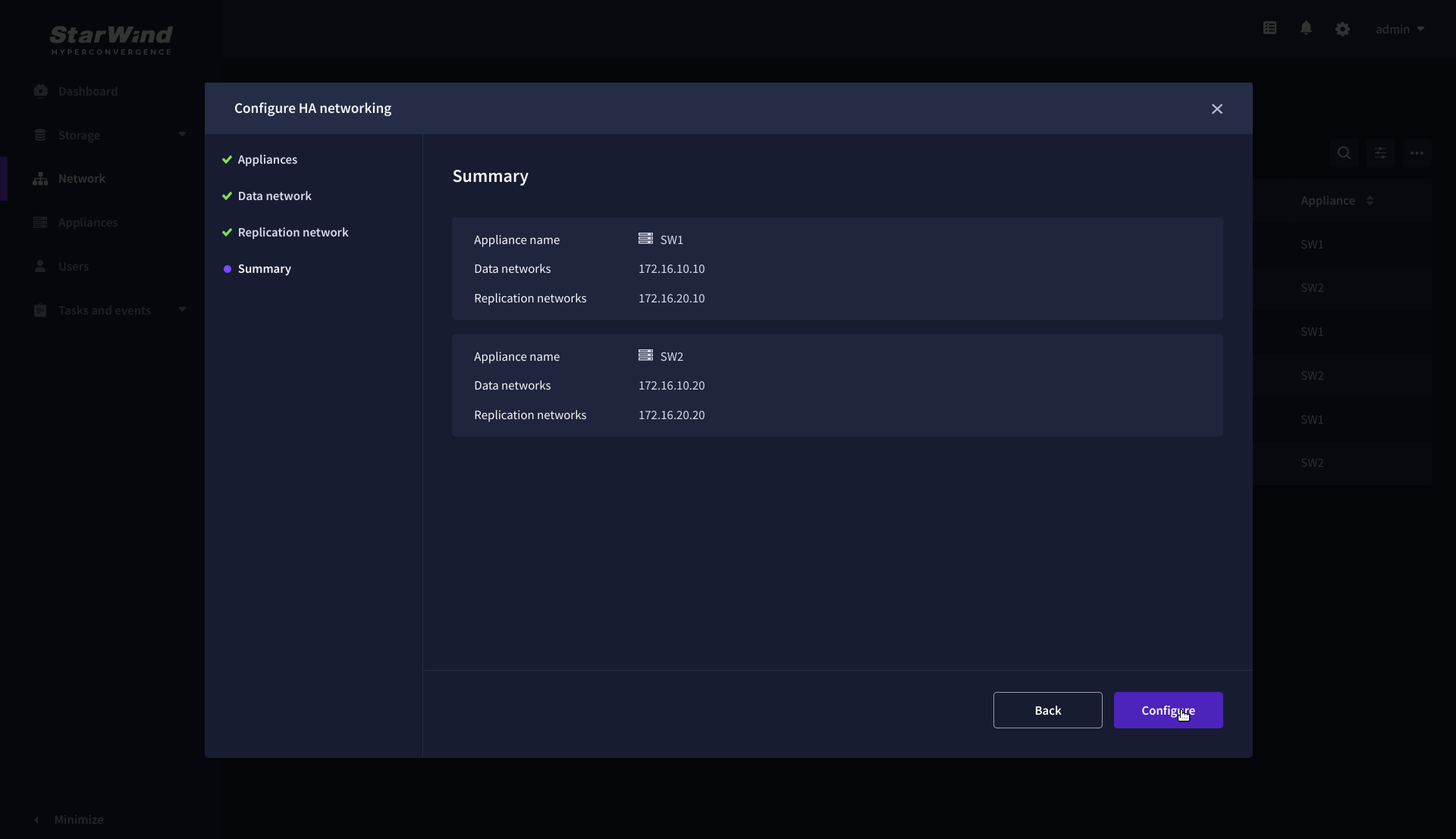
9. Review the summary and click Configure.
Add physical disks
Attach physical storage to StarWind Virtual SAN Controller VM:
- Ensure that all physical drives are connected through an HBA or RAID controller.
- Deploy StarWind VSAN CVM on each server that will be used to configure fault-tolerant standalone or highly available storage.
- Store StarWind VSAN CVM on a separate storage device accessible to the hypervisor host (e.g., SSD, HDD).
- Add HBA, RAID controllers, or NVMe SSD drives to StarWind CVM via a passthrough device.
Learn more about storage provisioning guidelines in the KB article.
Create Storage Pool
1. Click the “Add” button to create a storage pool.
2. Select two storage nodes to create a storage pool on them simultaneously.
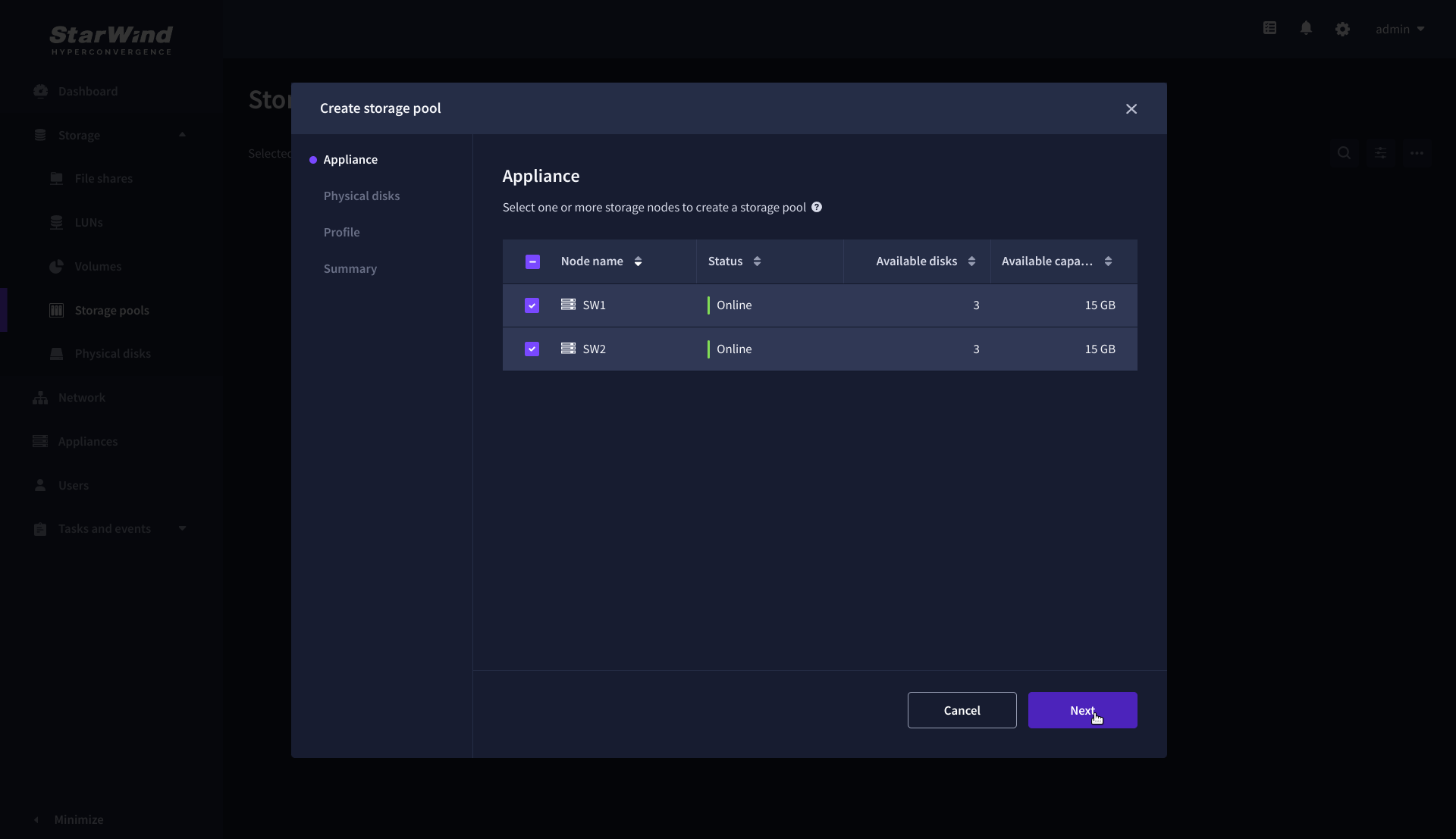
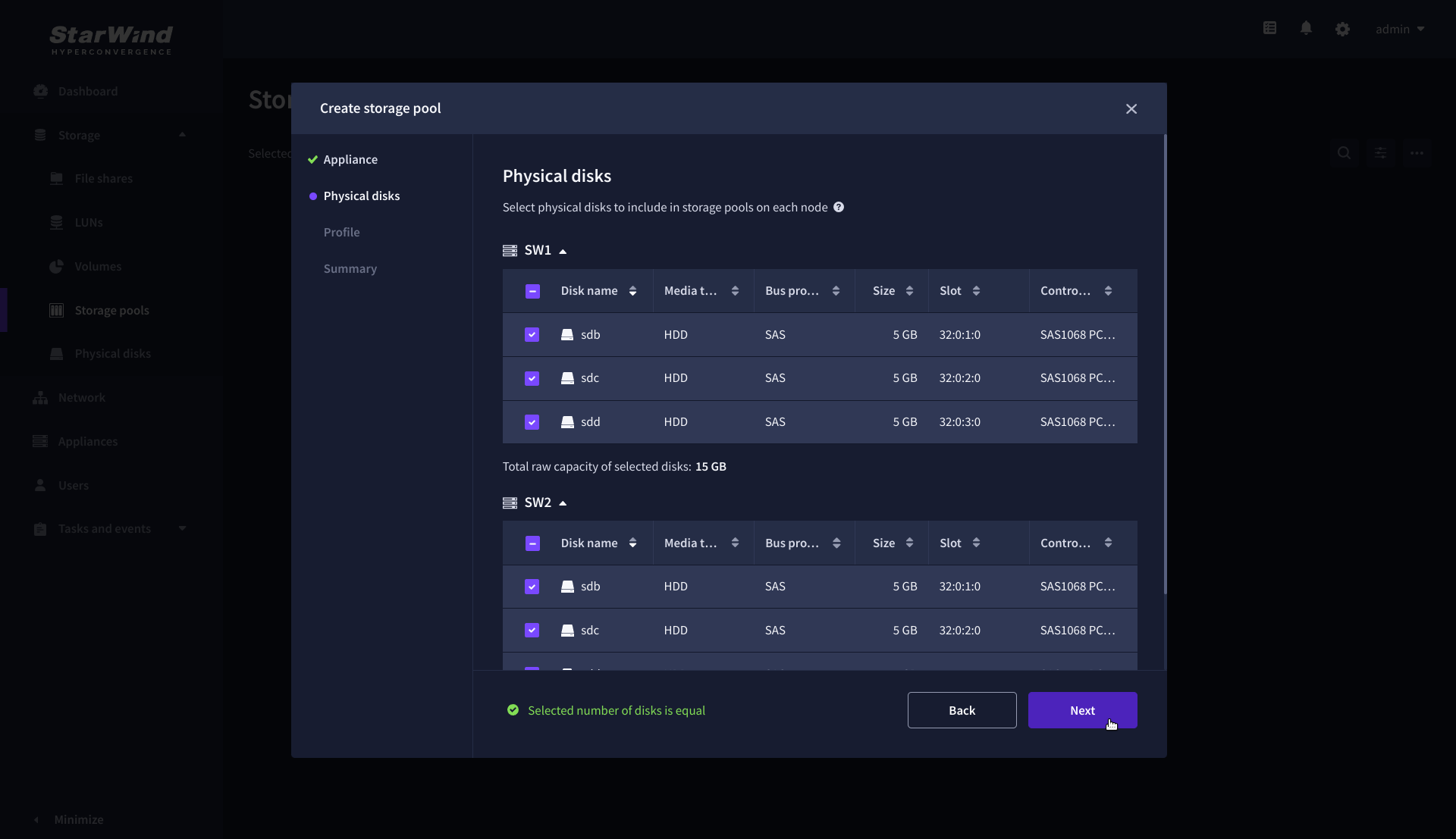
3. Select physical disks to include in the storage pool name and click the “Next” button.
NOTE: Select identical type and number of disks on each storage node to create identical storage pools.
4. Select one of the preconfigured storage profiles or create a redundancy layout for the new storage pool manually according to your redundancy, capacity, and performance requirements.
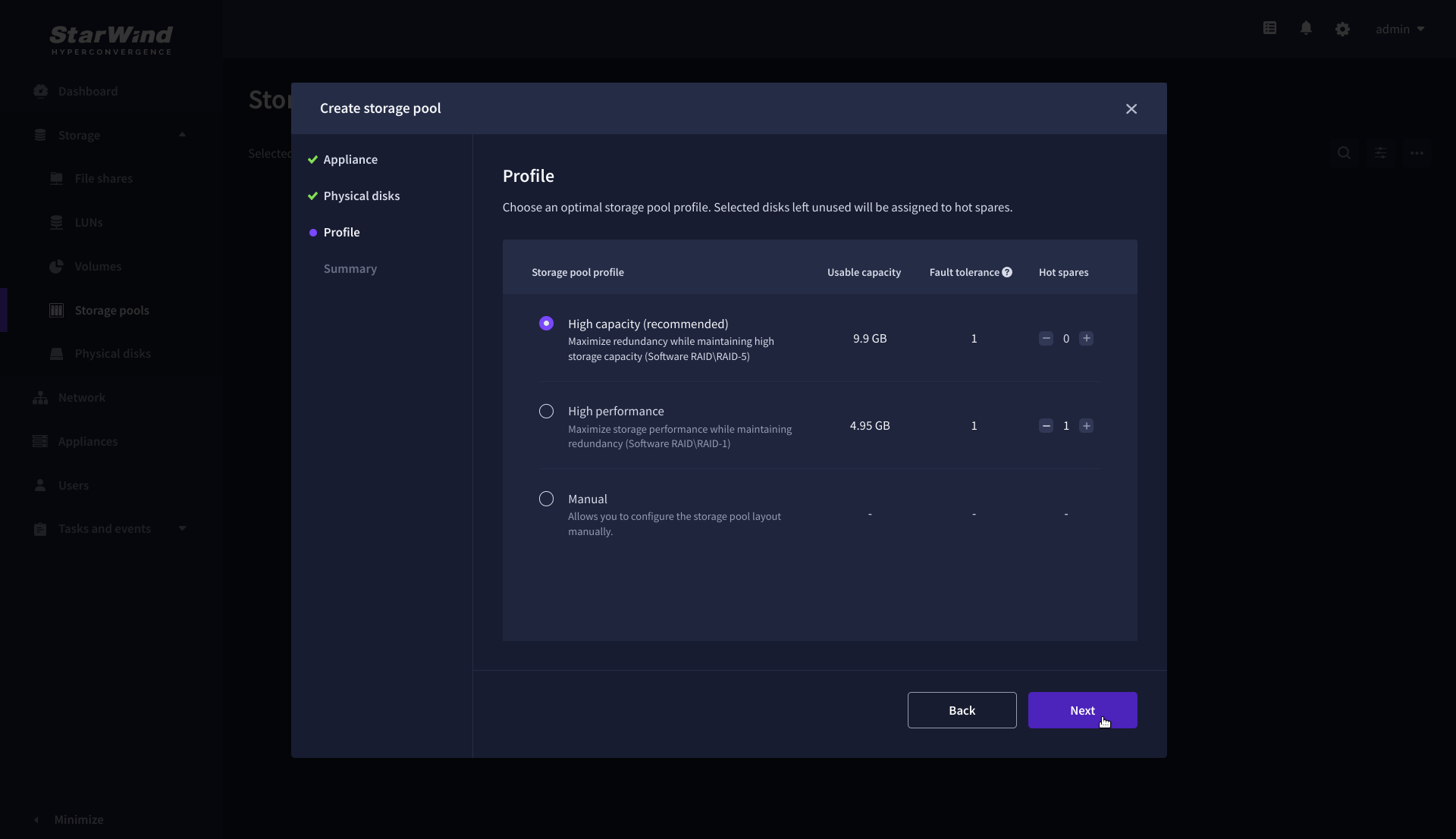
Hardware RAID, Linux Software RAID, and ZFS storage pools are supported and integrated into the StarWind CVM web interface. To make easier the storage pool configuration, the preconfigured storage profiles are provided to configure the recommended pool type and layout according to the direct-attached storage:
- hardware RAID – configures Hardware RAID’s virtual disk as a storage pool. It is available only if a hardware RAID controller is passed through to the CVM
- high performance – creates Linux Software RAID-10 to maximize storage performance while maintaining redundancy
- high capacity – creates Linux Software RAID-5 to maximize storage capacity while maintaining
redundancy - better redundancy – creates ZFS Stripped RAID-Z2 (RAID 60)) to maximize redundancy while maintaining high storage capacity
- manual – allows users to configure any storage pool type and layout with attached storage
5. Review “Summary” and click the “Create” button to create the pools on storage servers simultaneously.
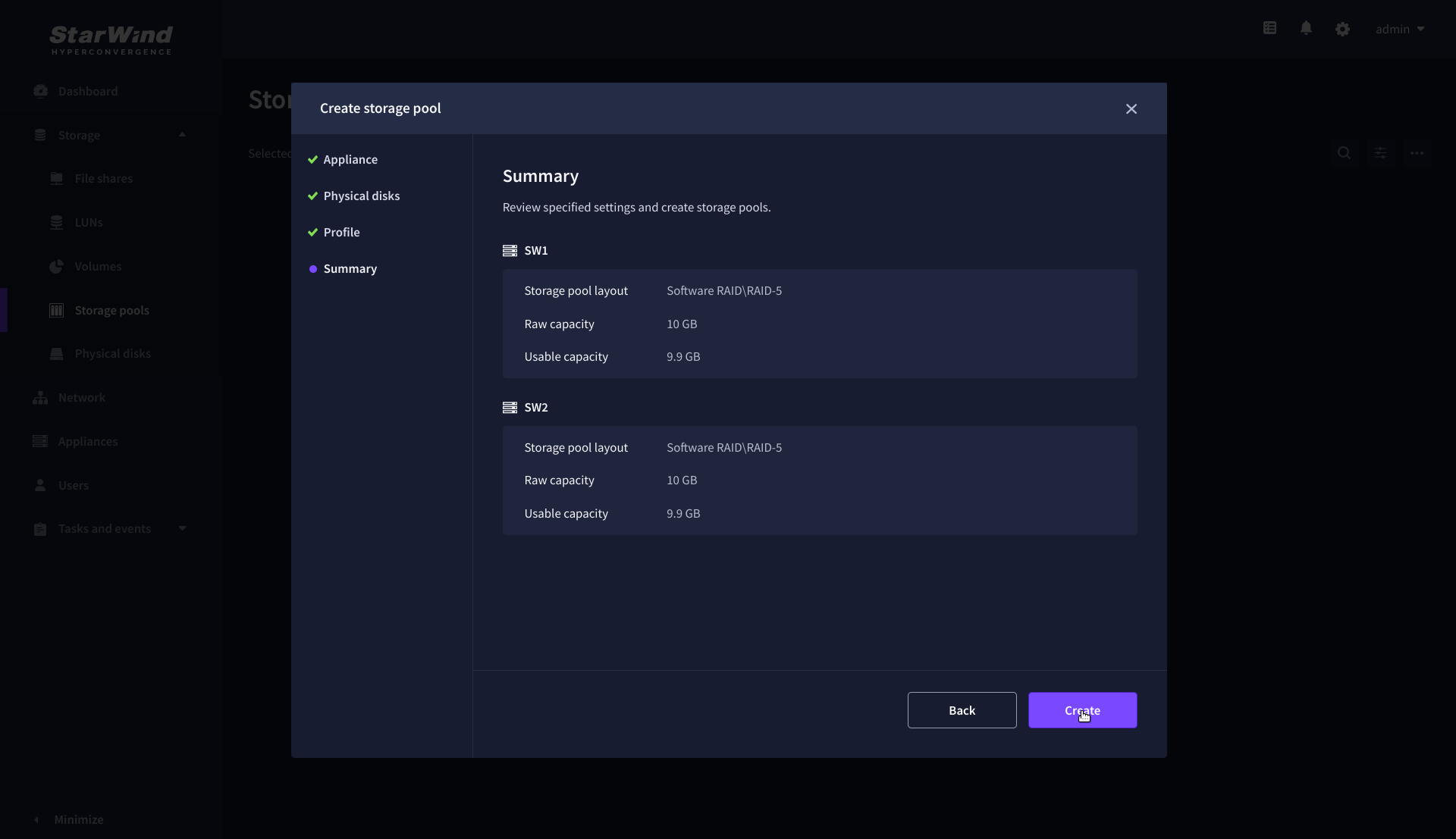
Create Volume
1. To create volumes, click the “Add” button.
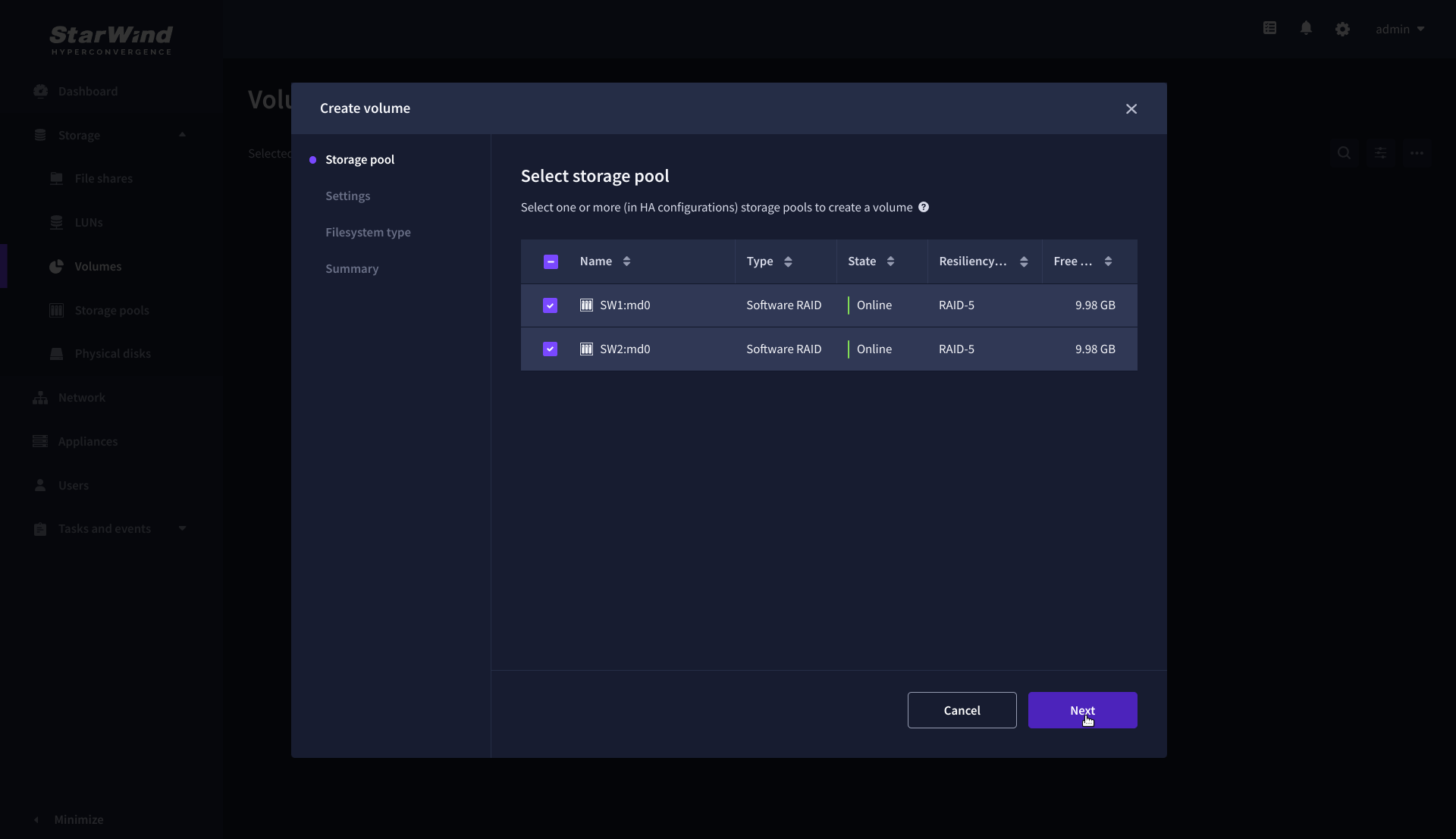
2. Select two identical storage pools to create a volume simultaneously.
3. Specify volume name and capacity.

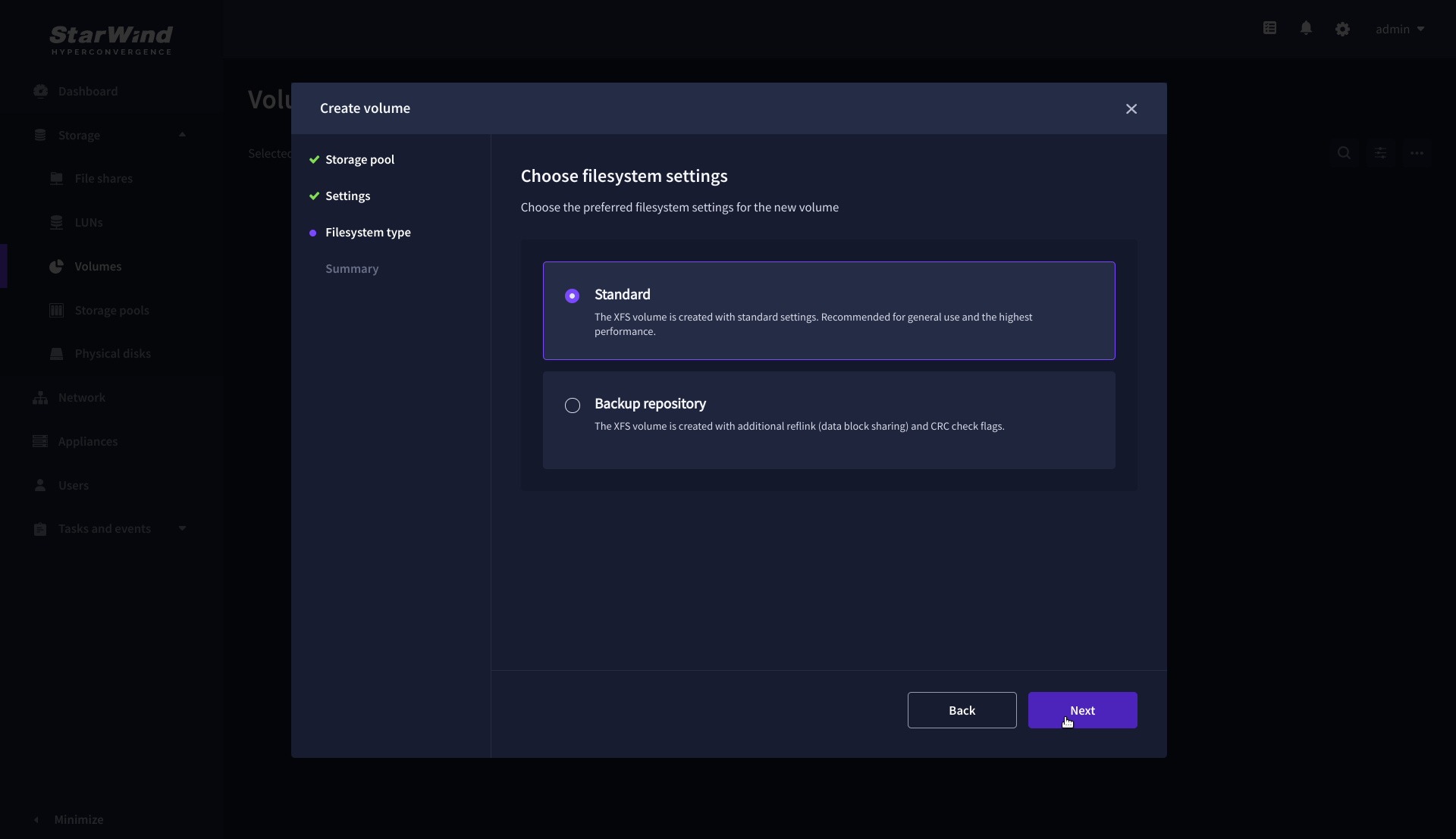
4. Select the Standard volume type.
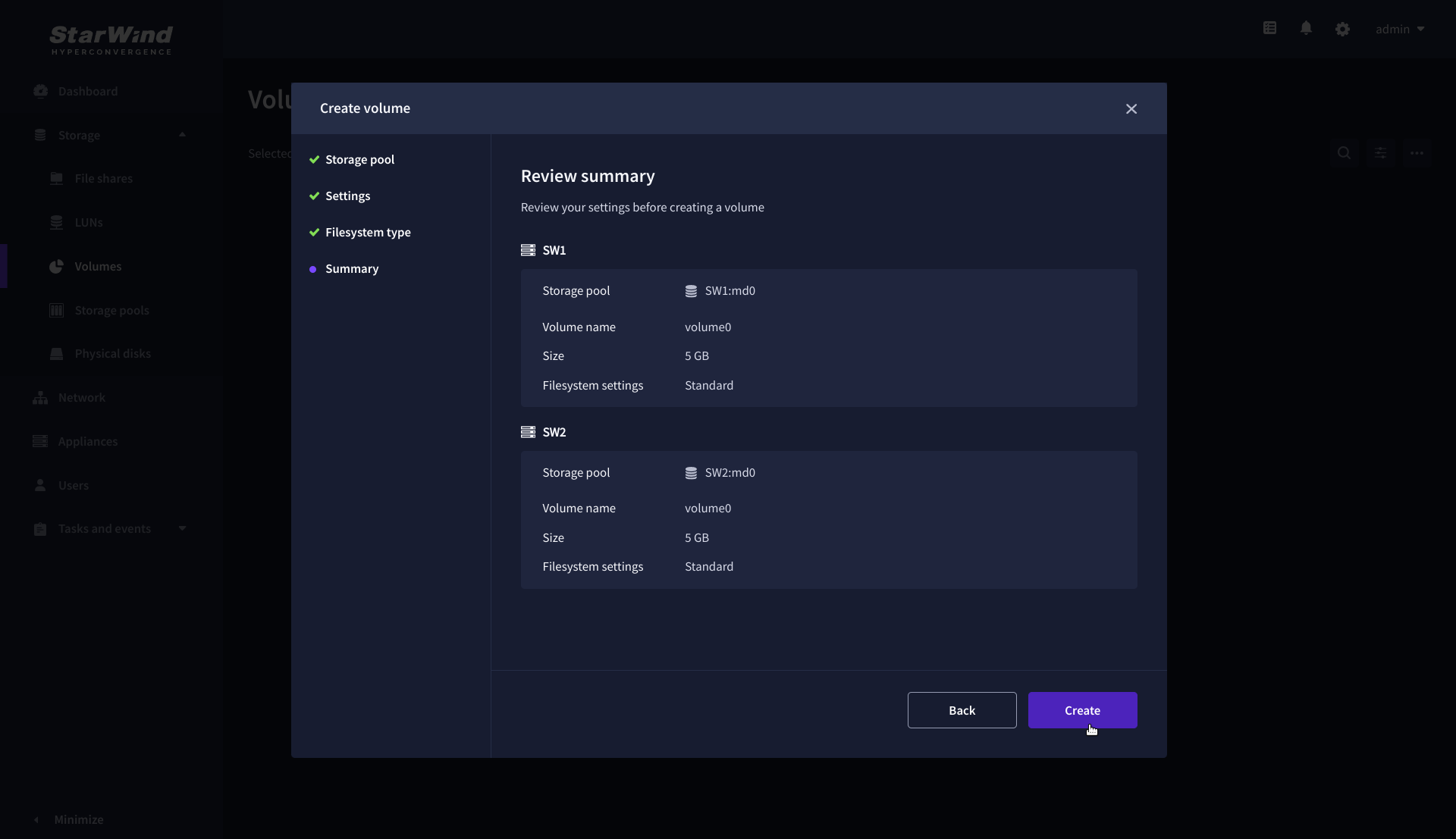
5. Review “Summary” and click the “Create” button to create the pool.
Create HA LUN
The LUN availability for StarWind LUN can be Standalone and High availability (2-way or 3-way replication) and is narrowed by your license.
1. To create a virtual disk, click the Add button.
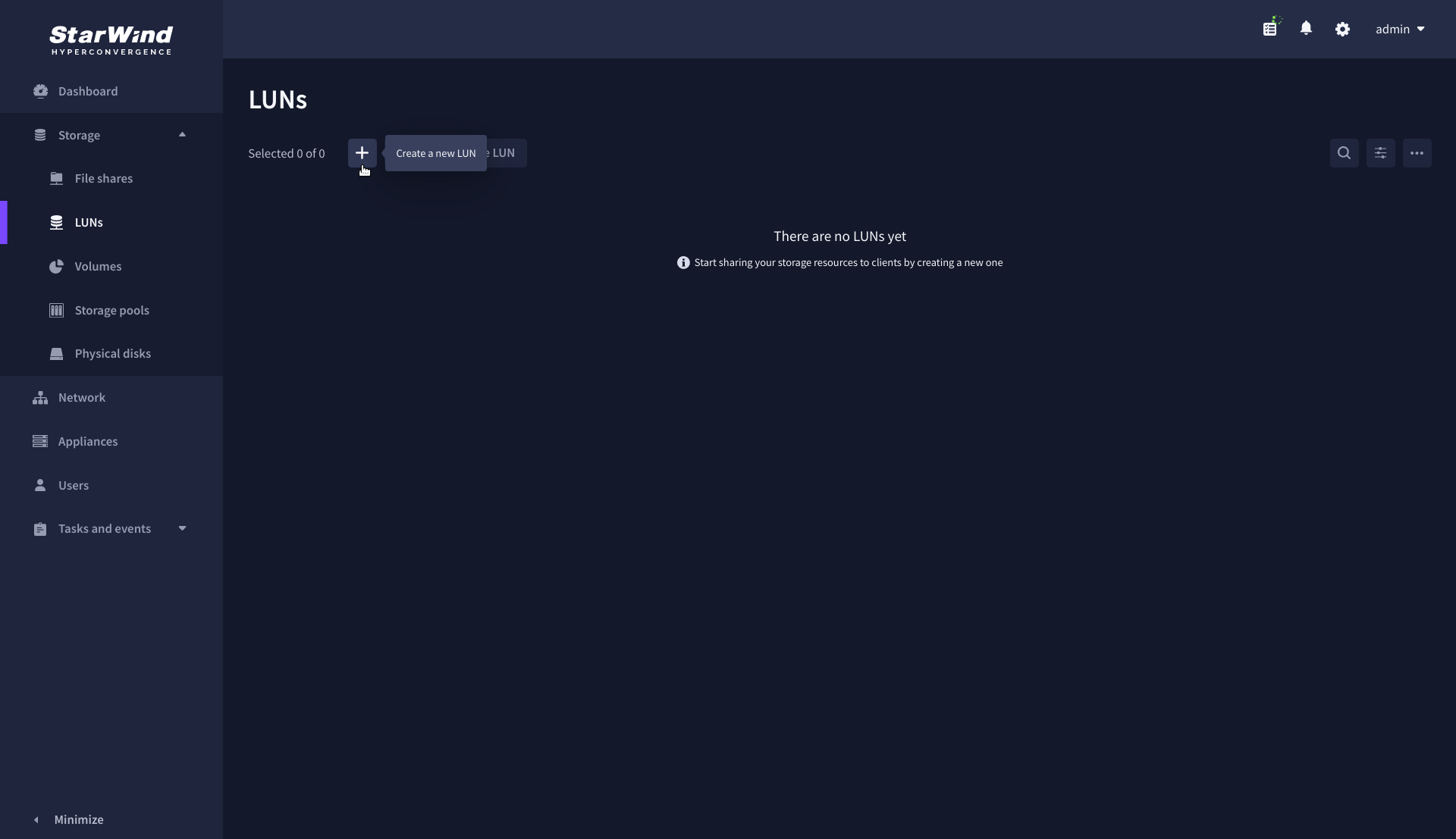
2. Select the protocol.
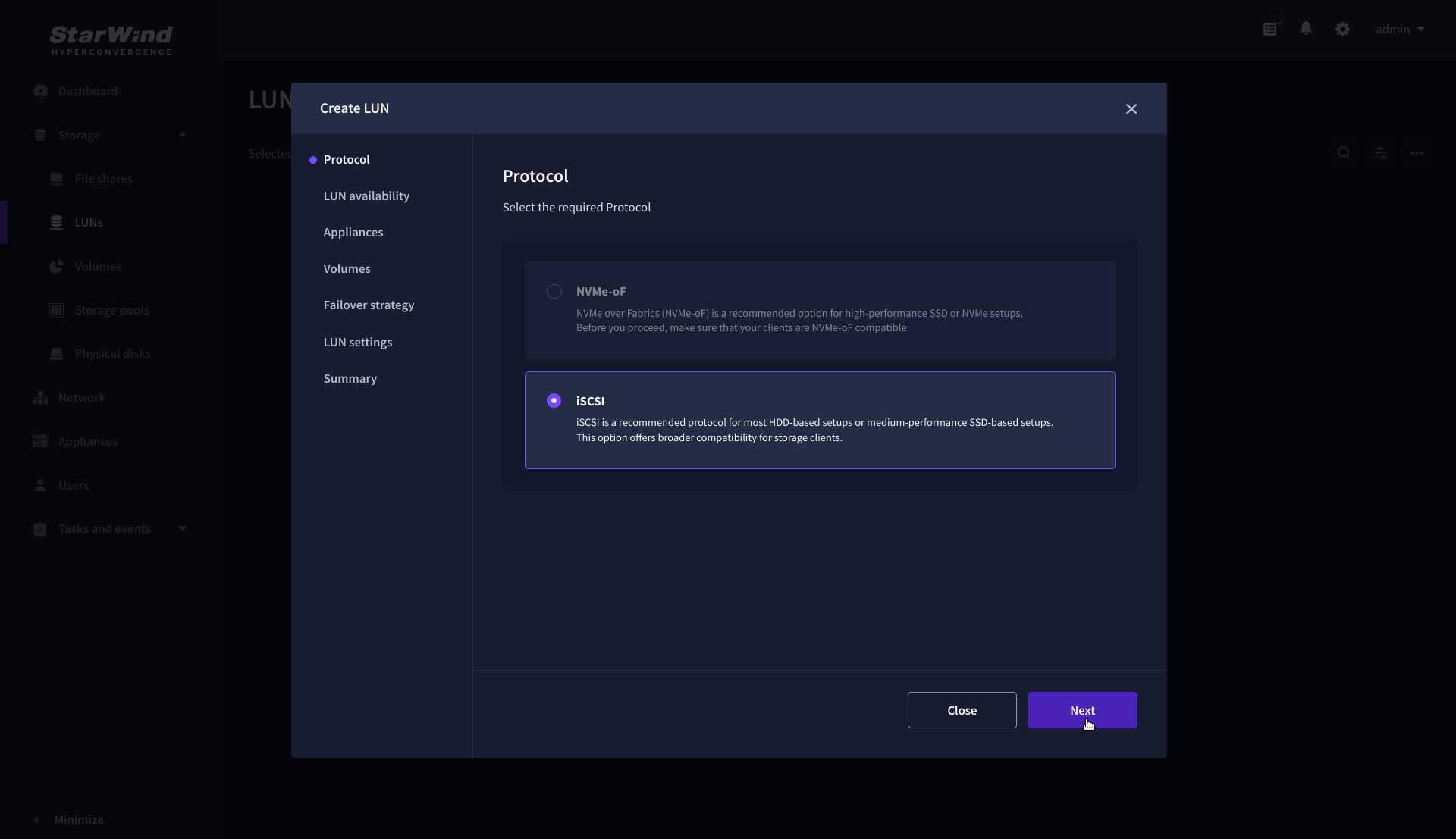
3. Choose the “High availability” LUN availability type.
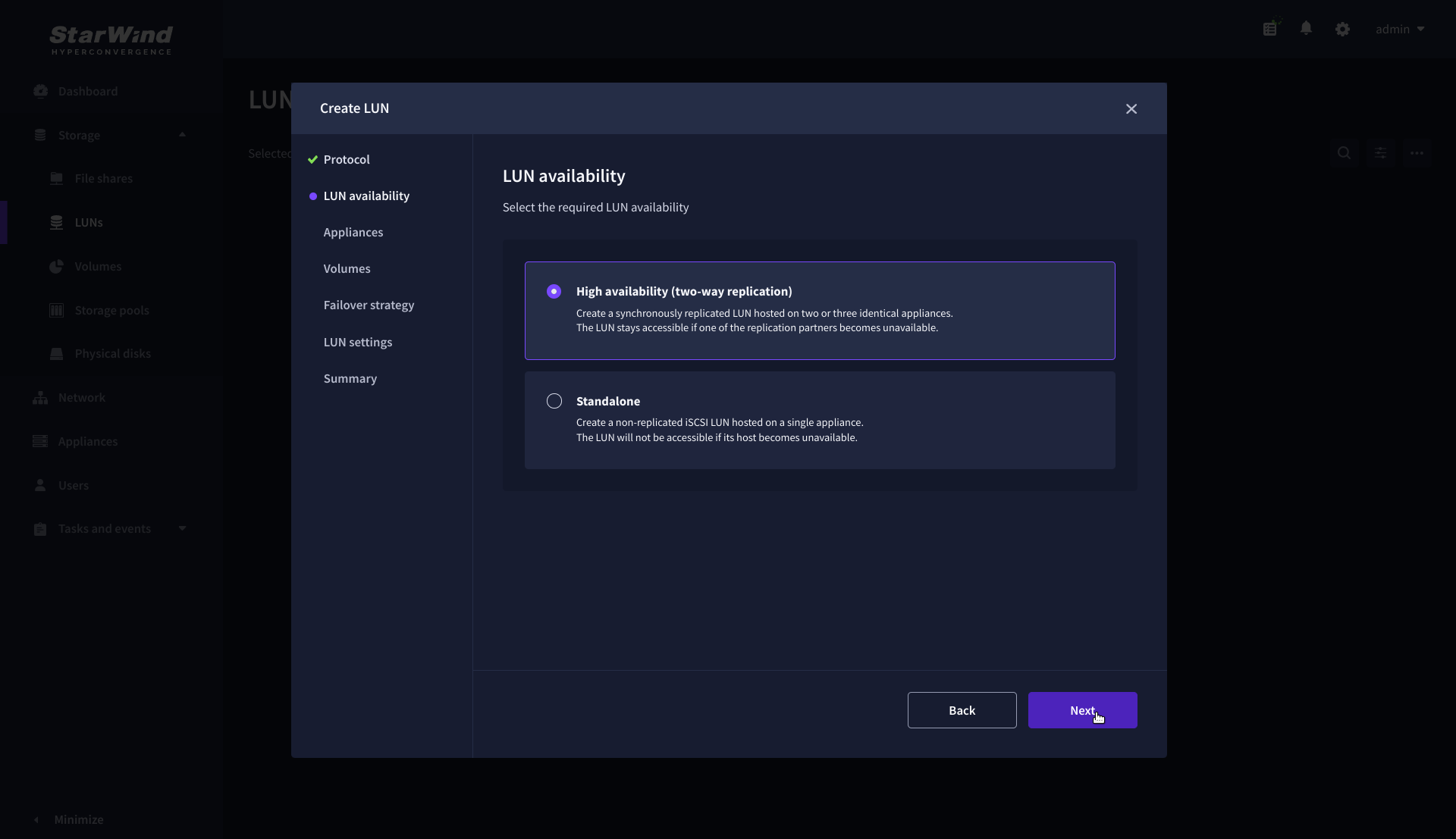
4. Select the appliances that will host the LUN. Partner appliances must have identical hardware configurations, including CPU, RAM, storage, and networking.
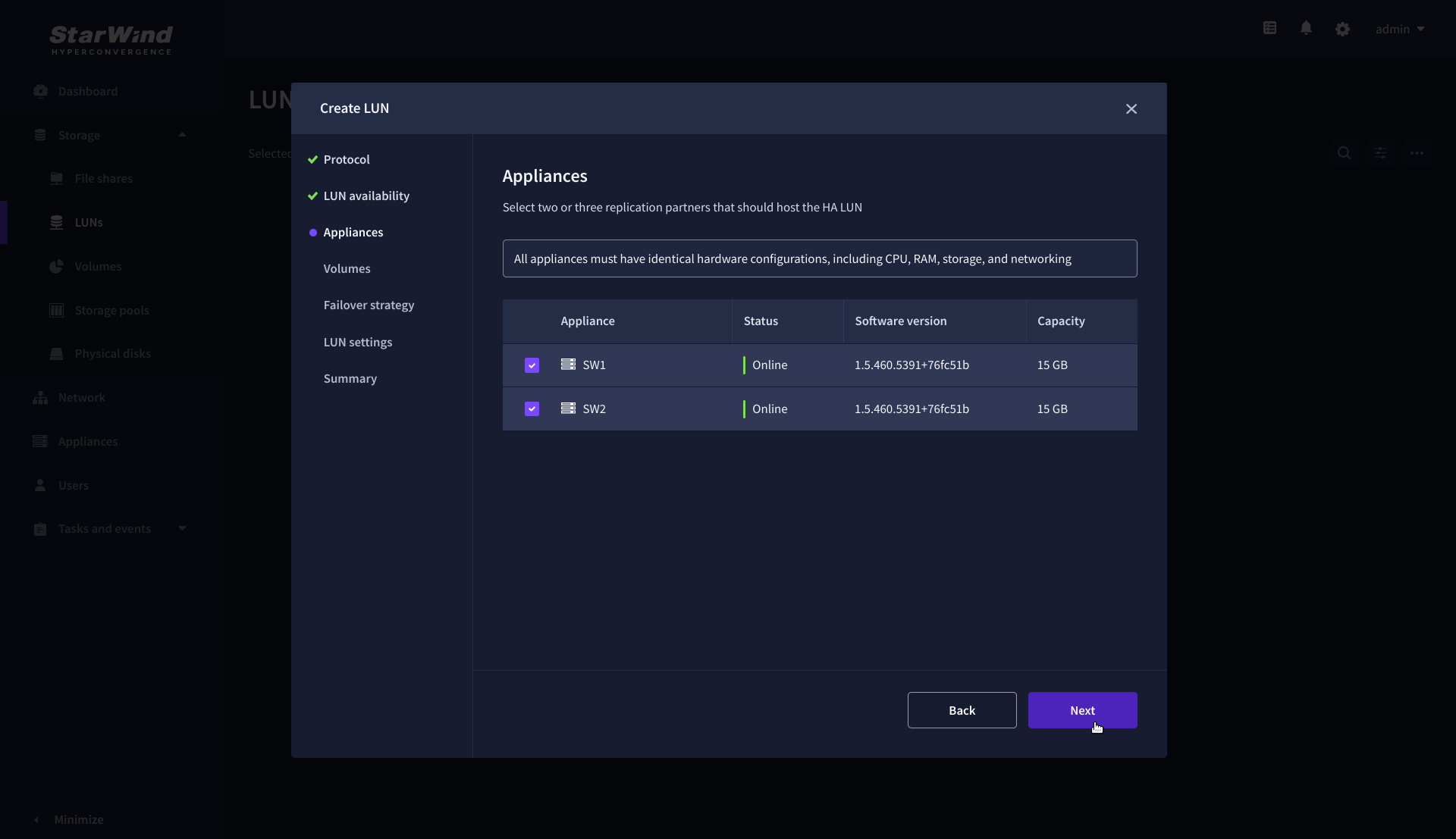
5. Select a volume to store the LUN data. Selected volumes must have identical storage configurations.
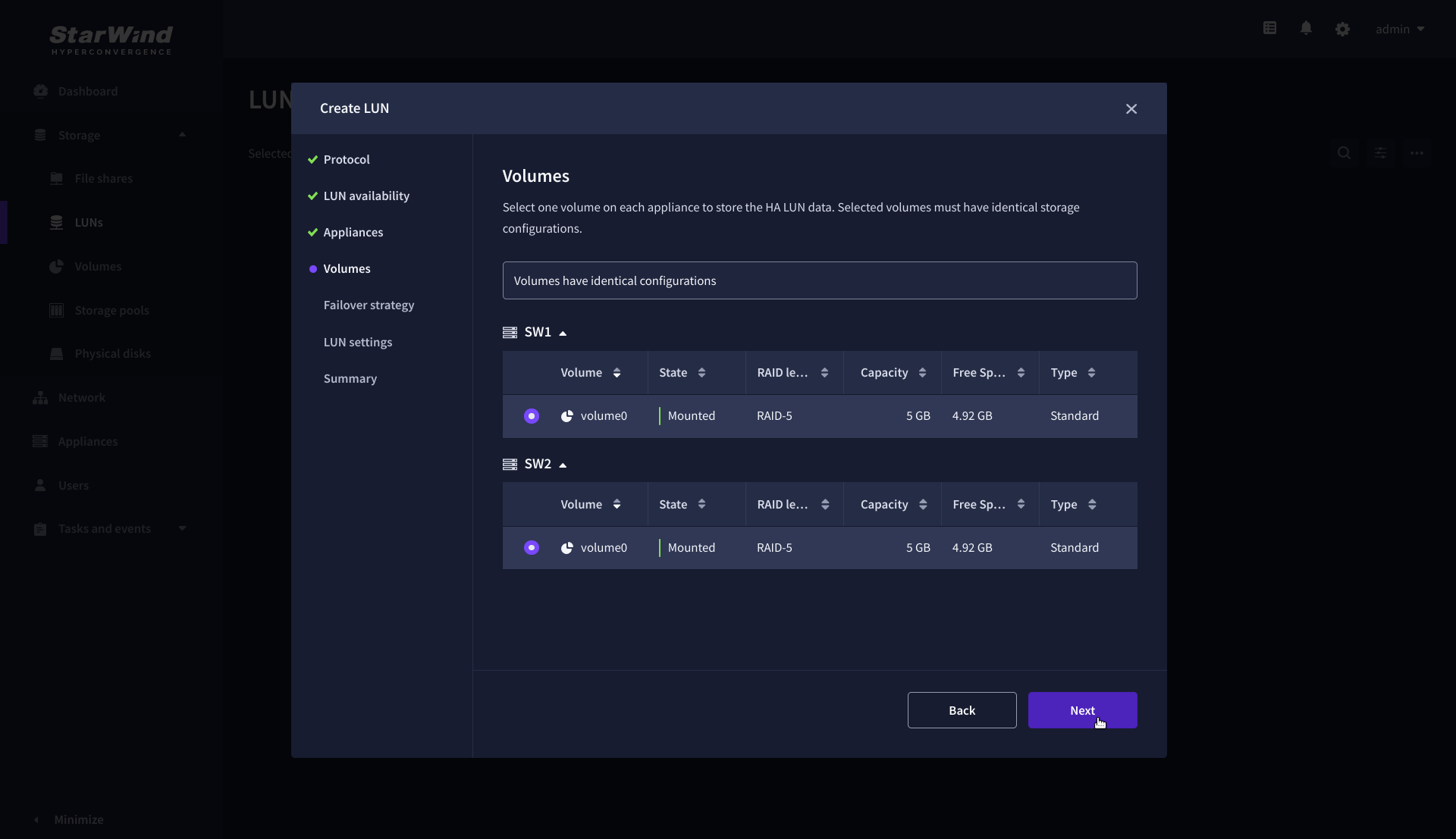
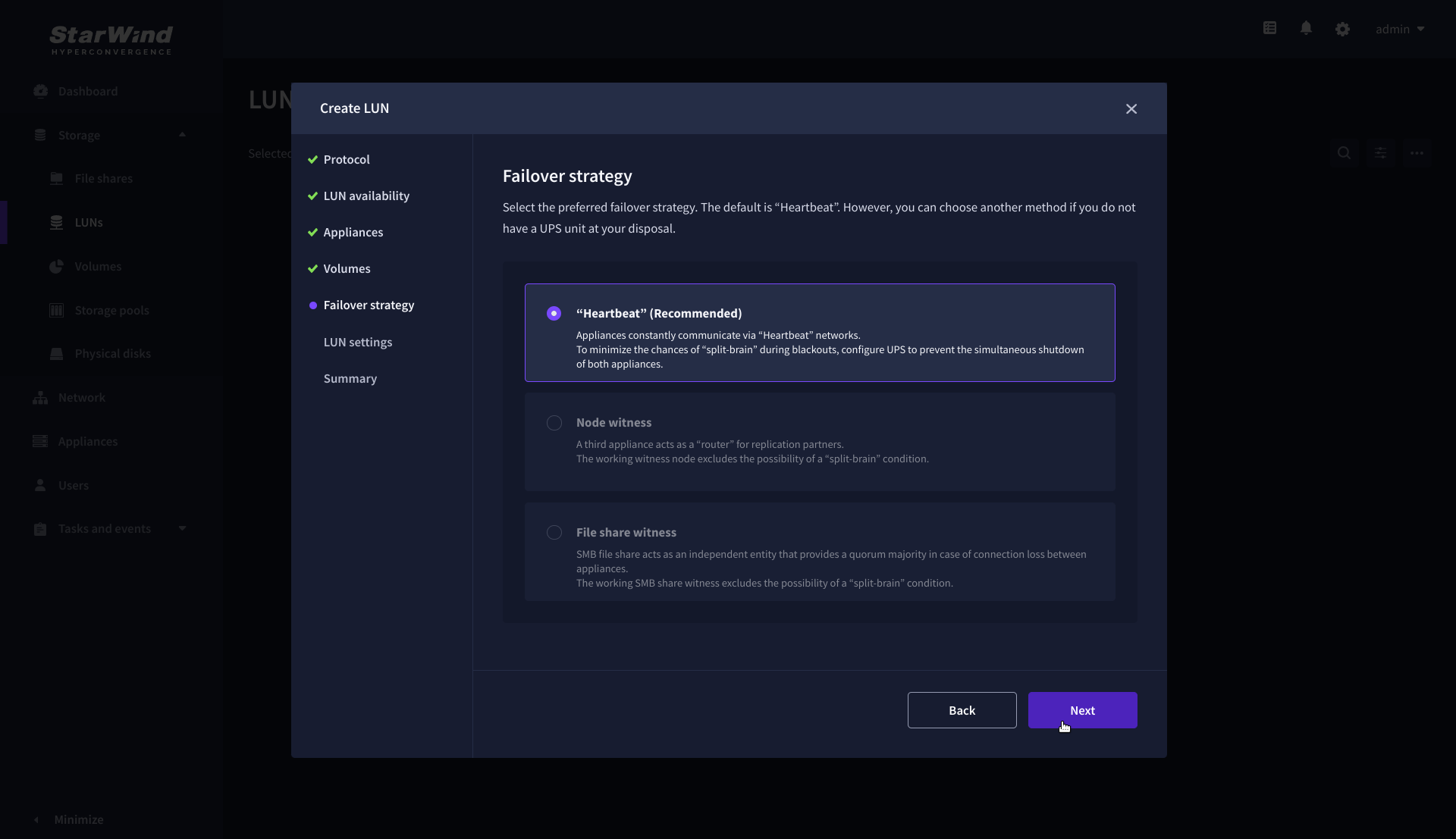
6. Select the “Heartbeat” failover strategy.
NOTE: To use the Node witness or the File share witness failover strategies, the appliances should have these features licensed.
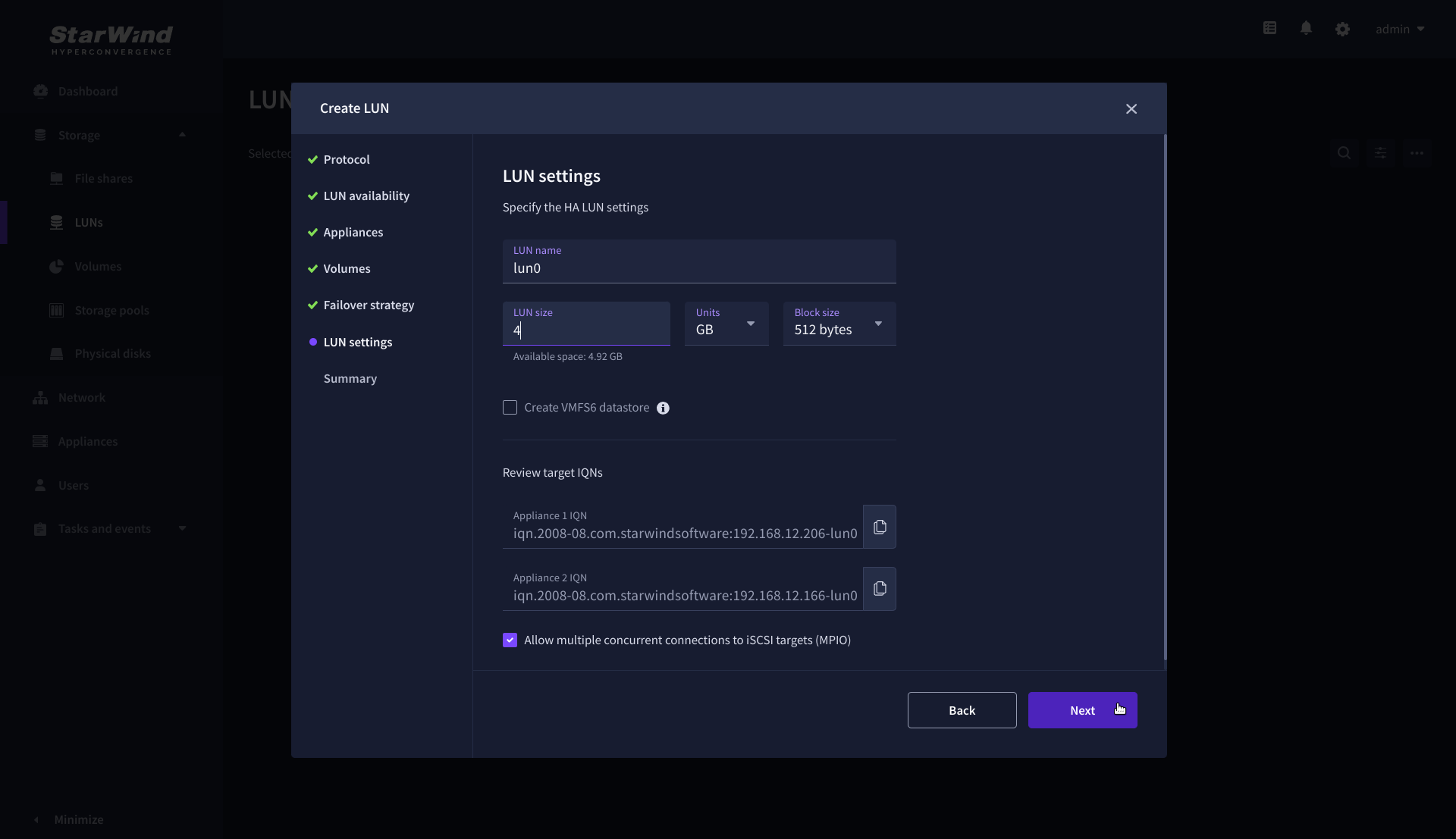
7. Specify the HA LUN settings, e.g. name, size, and block size. Click Next.
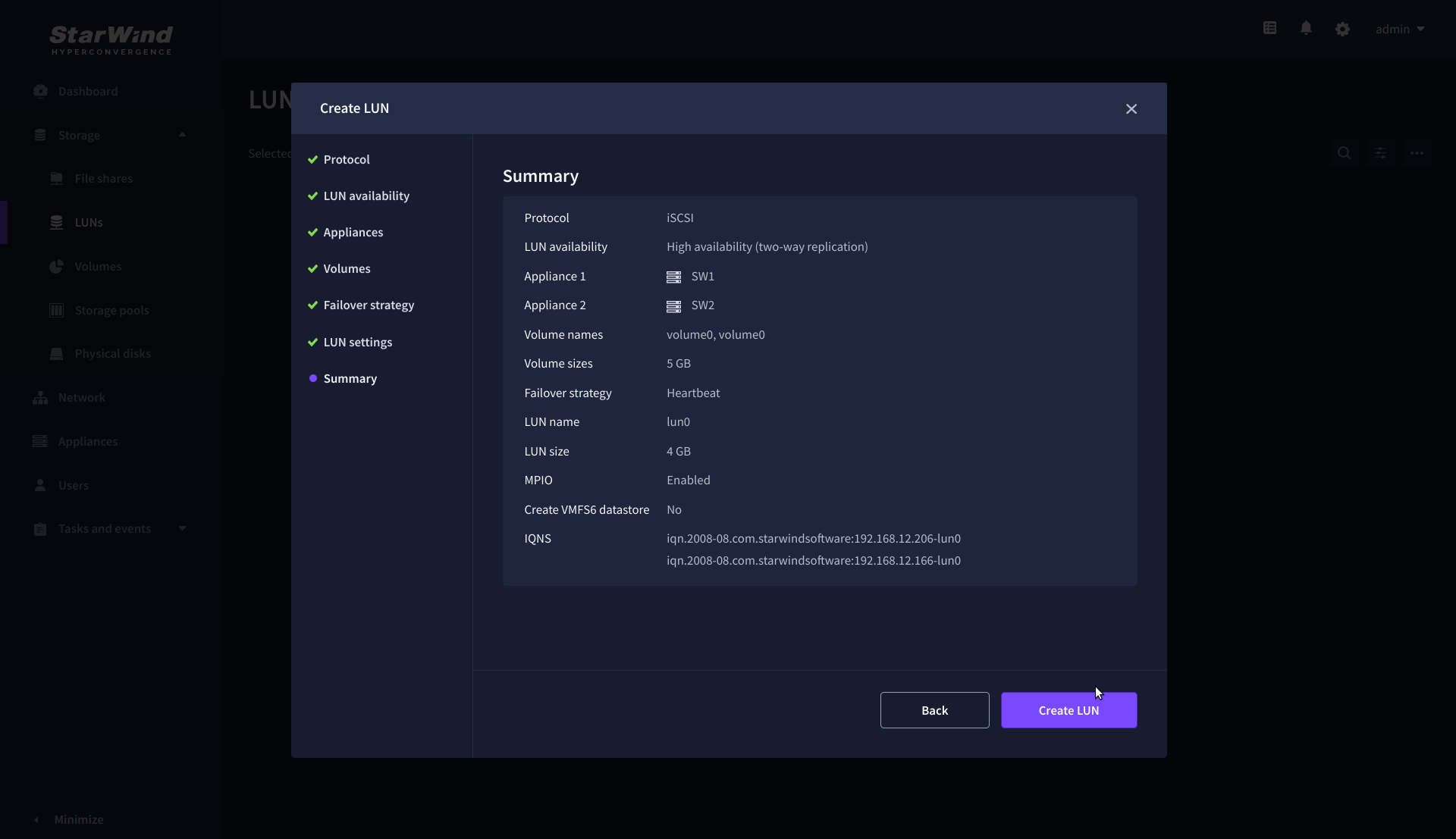
8. Review “Summary” and click the “Create” button to create the LUN.
Connecting StarWind virtual disk to Hyper-V servers
Enabling Multipath Support on Hyper-V Servers
1. Install the Multipath I/O feature by executing the following command in the PowerShell window:
|
1 |
dism /online /enable-feature:MultipathIo |
2. Open MPIO Properties by executing the following command in the CMD window:
|
1 |
mpioctl |
3. In the Discover Multi-Paths tab, select the Add support for iSCSI devices checkbox and click Add.
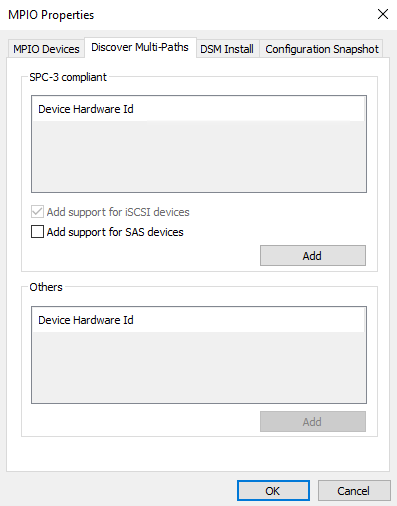
4. When prompted to restart the server, click Yes to proceed.
5. Repeat the same procedure on the other compute server that will be connected to SAN & NAS appliance.
Provisioning StarWind SAN & NAS Storage to Hyper-V Server Hosts
1. Launch Microsoft iSCSI Initiator by executing the following command in the CMD window:
|
1 |
iscsicpl |
2. Navigate to the Discovery tab.
3. Click the Discover Portal button. The Discover Target Portal dialog appears. Type the IP address assigned to iSCSI/Data interface, i.e. 172.16.10.100.
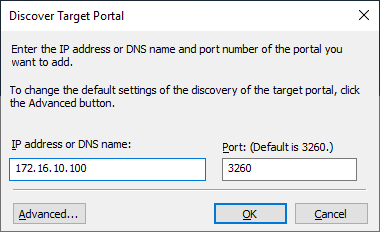
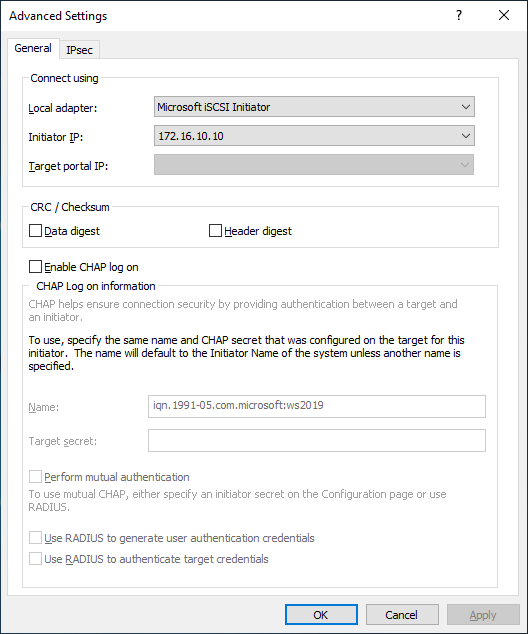
4. Click the Advanced button. Select Microsoft iSCSI Initiator as a Local adapter and as Initiator IP select the IP address of a network adapter connected to the Data\iSCSI virtual switch. Confirm the actions to complete the Target Portal discovery.
5. The target portals are added on this server.
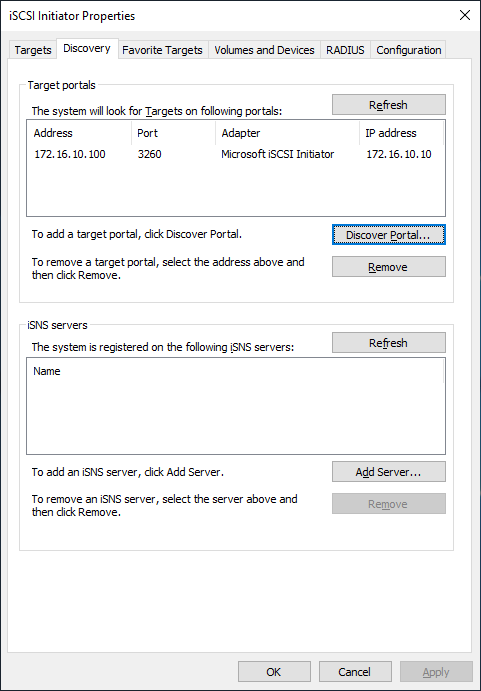
6. Click the Targets tab. The previously created targets (virtual disks) are listed in the Discovered Targets section.
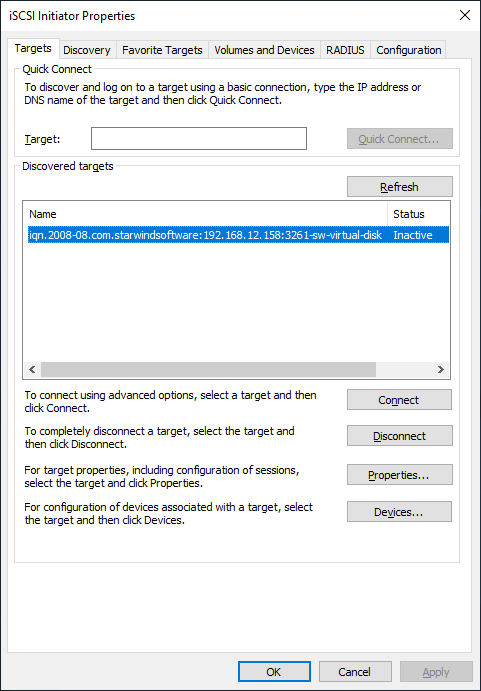
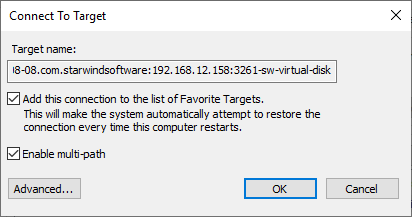
7. Select the target created in StarWind SAN & NAS web console and click Connect.
8. Enable checkboxes as shown in the image below. Click Advanced.
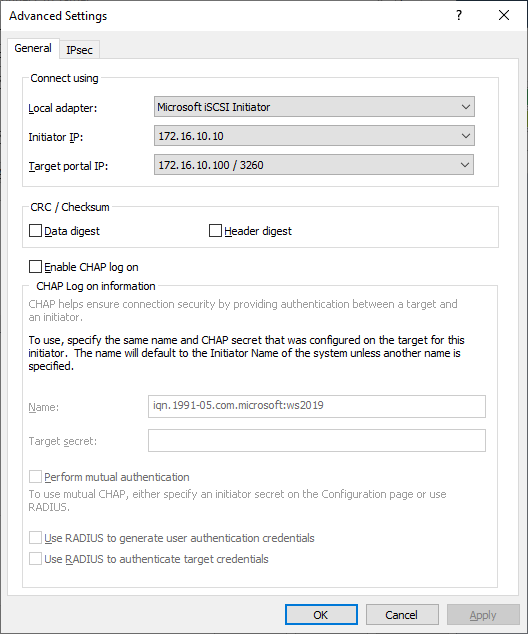
9. Select Microsoft iSCSI Initiator in the Local adapter dropdown menu. In the Initiator IP field, select the IP address for the Data/iSCSI channel. In the Target portal IP, select the corresponding portal IP from the same subnet. Confirm the actions.
10. Repeat steps 1-9 for all remaining device targets.
11. Repeat steps 1-9 on the other compute servers, specifying corresponding Data/iSCSI channel IP addresses.
Connecting Disks to Servers
To initialize the connected iSCSI target disks and create the partitions on them use DISKPART.
1. Run diskpart in the CMD window:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
List disk Select disk X //where X is the number of the disk to be processed Online disk Clean Attributes disk clear readonly Convert GPT Create Partition Primary Format fs=ntfs label=X quick //where X is the name of the Volume |
NOTE: It is recommended to initialize the disks as GPT.
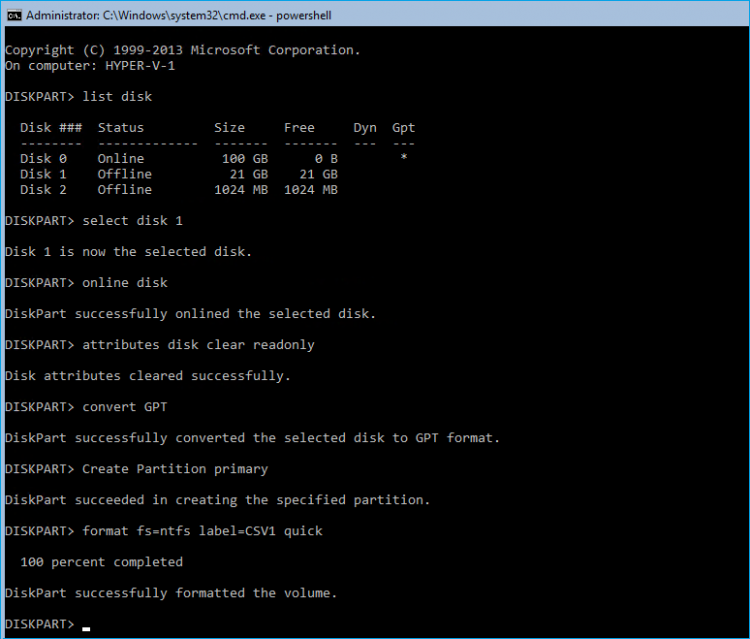
2. Perform the steps above on other compute servers.
Creating a Failover Cluster in Windows Server
NOTE: To avoid issues during the cluster validation configuration, it is recommended to install the latest Microsoft updates on each node.
NOTE: Server Manager can be opened on the server with desktop experience enabled (necessary features should be installed). Alternatively, the Failover cluster can be managed with Remote Server Administration Tools:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/remote/remote-server-administration-tools
NOTE: For converged deployment (SAN & NAS running as a dedicated storage cluster) the Microsoft Failover Cluster is deployed on separate computing nodes. Additionally, for the converged deployment scenario, the storage nodes that host StarWind SAN & NAS as CVM or bare metal do not require a domain controller and Failover Cluster to operate.
1. Open Server Manager. Select the Failover Cluster Manager item from the Tools menu.
2. Click the Create Cluster link in the Actions section of Failover Cluster Manager.
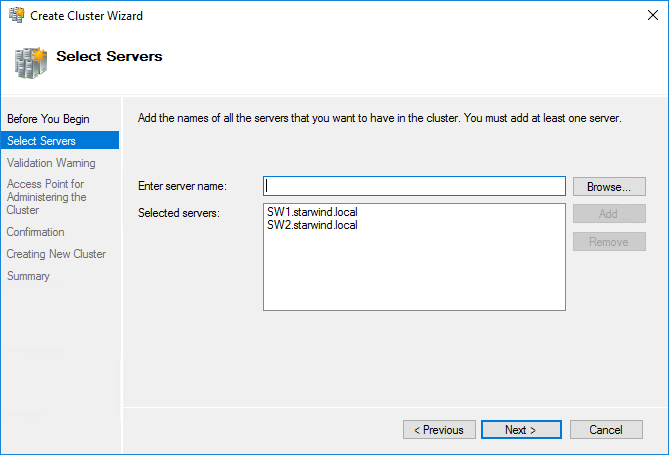
3. Specify the servers to be added to the cluster. Click Next to continue.
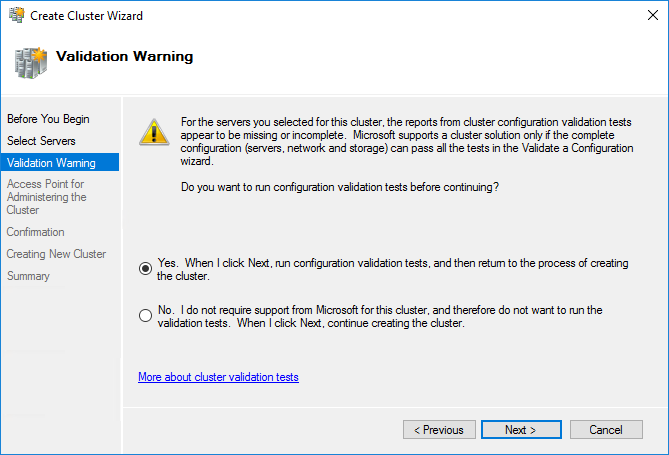
4. Validate the configuration by running the cluster validation tests: select Yes… and click Next to continue.
5. Specify the cluster name.
NOTE: If the cluster servers get IP addresses over DHCP, the cluster also gets its IP address over DHCP. If the IP addresses are set statically, set the cluster IP address manually.
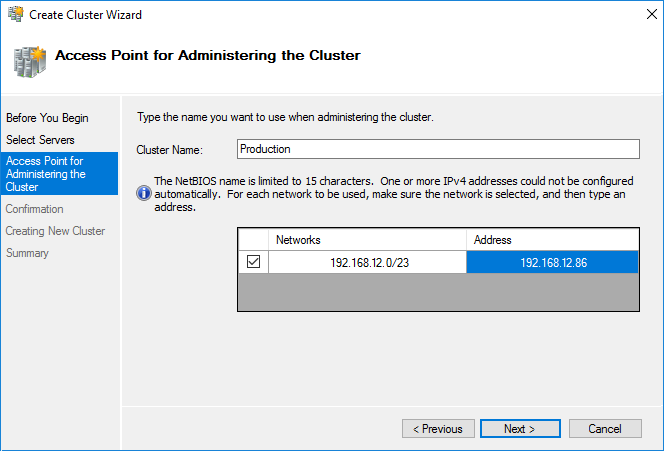
6. Make sure that all settings are correct. Click Previous to make any changes or Next to proceed.
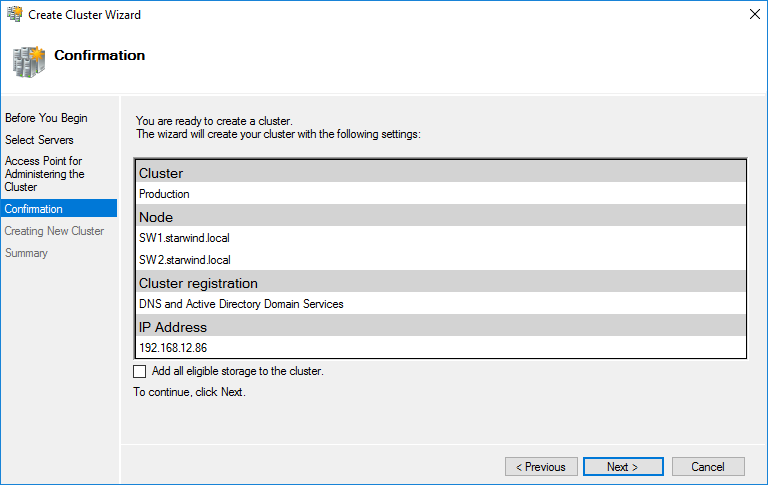
NOTE: If checkbox Add all eligible storage to the cluster is selected, the wizard will add all disks to the cluster automatically. The device with the smallest storage volume will be assigned as a Witness. It is recommended to uncheck this option before clicking Next and add cluster disks and the Witness drive manually.
7. The process of the cluster creation starts. Upon the completion, the system displays the summary with the detailed information. Click Finish to close the wizard.
Adding Storage to the Cluster
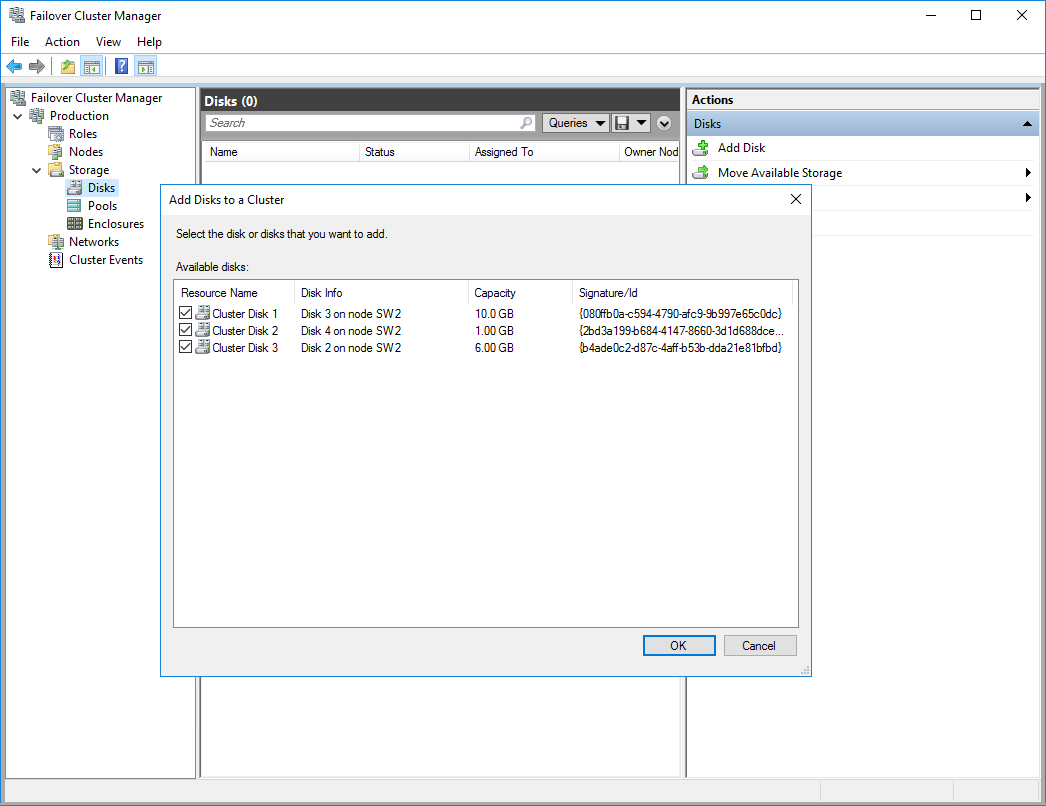
1. In Failover Cluster Manager, navigate to Cluster -> Storage -> Disks. Click Add Disk in the Actions panel, choose StarWind disks from the list and confirm the selection.
2. To configure the cluster witness disk, right-click on Cluster and proceed to More Actions -> Configure Cluster Quorum Settings.
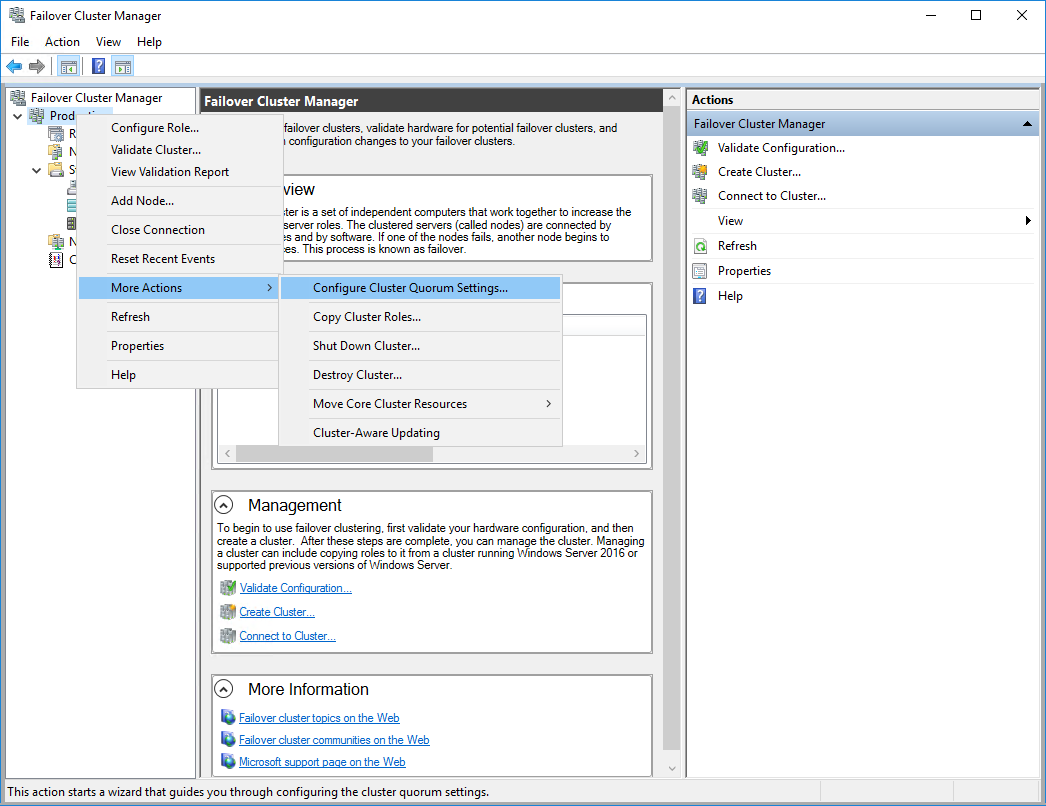
3. Follow the wizard and use the Select the quorum witness option. Click Next.
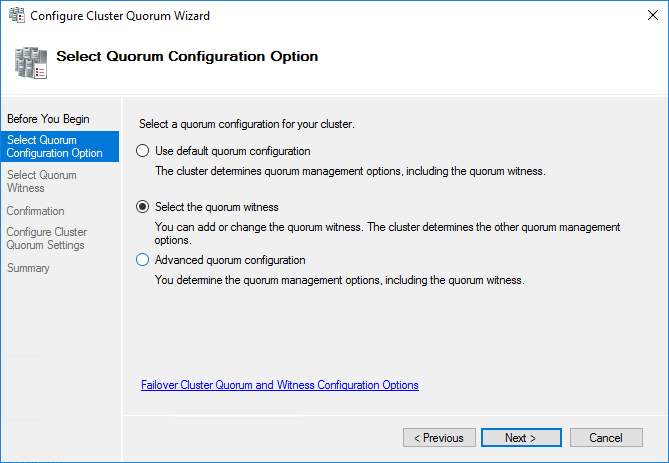
4. Select Configure a disk witness. Click Next.
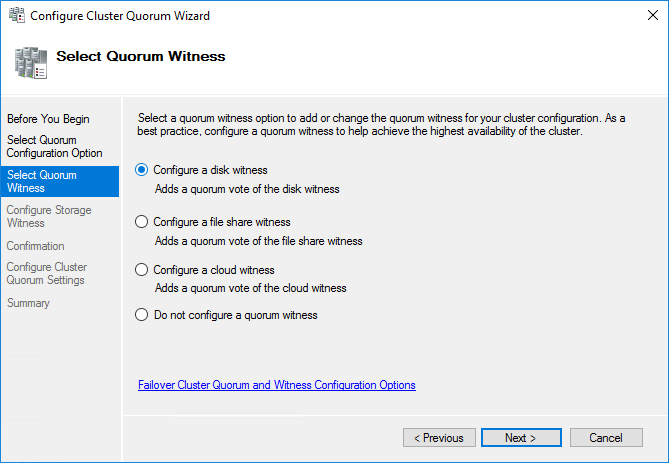
5. Select the Witness disk to be assigned as the cluster witness disk. Click Next and press Finish to complete the operation.
6. In Failover Cluster Manager, Right-click the disk and select Add to Cluster Shared Volumes.
7. If renaming of the cluster shared volume is required, right-click on the disk and select Properties. Type the new name for the disk and click Apply followed by OK.
8. Perform the steps 6-7 for any other disk in Failover Cluster Manager. The resulting list of disks will look similar to the screenshot below.
Configuring Cluster Network Preferences
1. In the Networks section of the Failover Cluster Manager, right-click on the network from the list. Set its new name if required to identify the network by its subnet. Apply the change and press OK.
NOTE: Please double-check that cluster communication is configured with redundant networks:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/failover-clustering/smb-multichannel
2. Rename other networks as described above, if required.
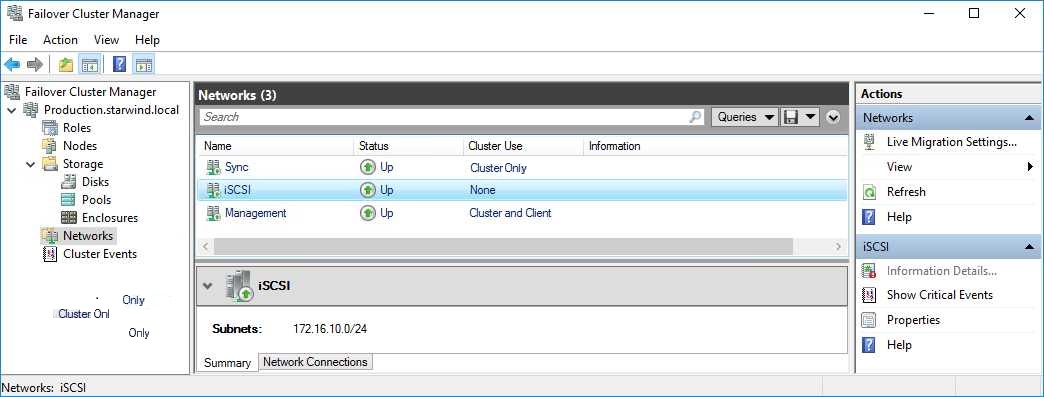
3. In the Actions tab, click Live Migration Settings. Uncheck the synchronization network, while the iSCSI network can be used if it is 10+ Gbps. Apply the changes and click OK.
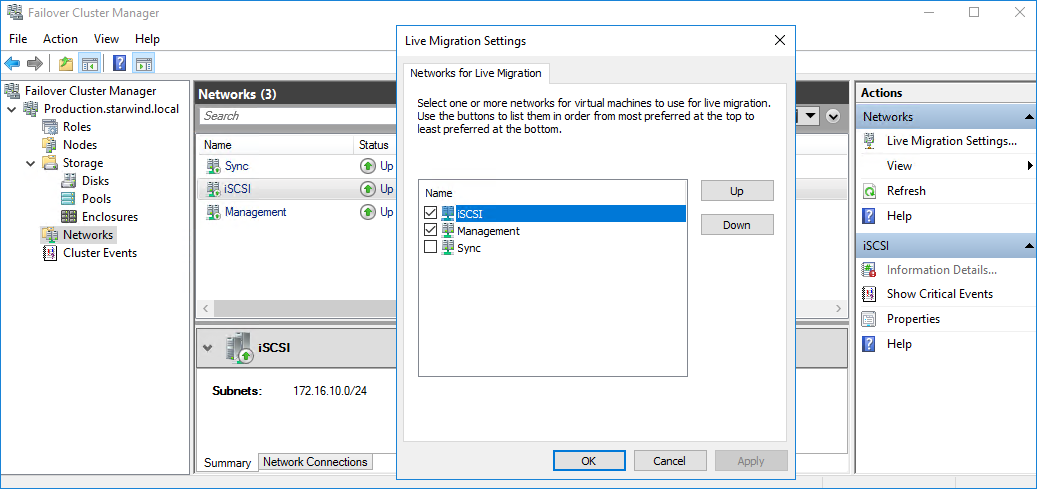
The cluster configuration is completed and it is ready for virtual machines deployment. Select Roles and in the Action tab, click Virtual Machines -> New Virtual Machine. Complete the wizard.
Configuring File Shares
Please follow the steps below if file shares should be configured on cluster nodes.
Configuring the Scale-Out File Server Role
1. To configure the Scale-Out File Server Role, open Failover Cluster Manager.
2. Right-click the cluster name, then click Configure Role and click Next to continue.
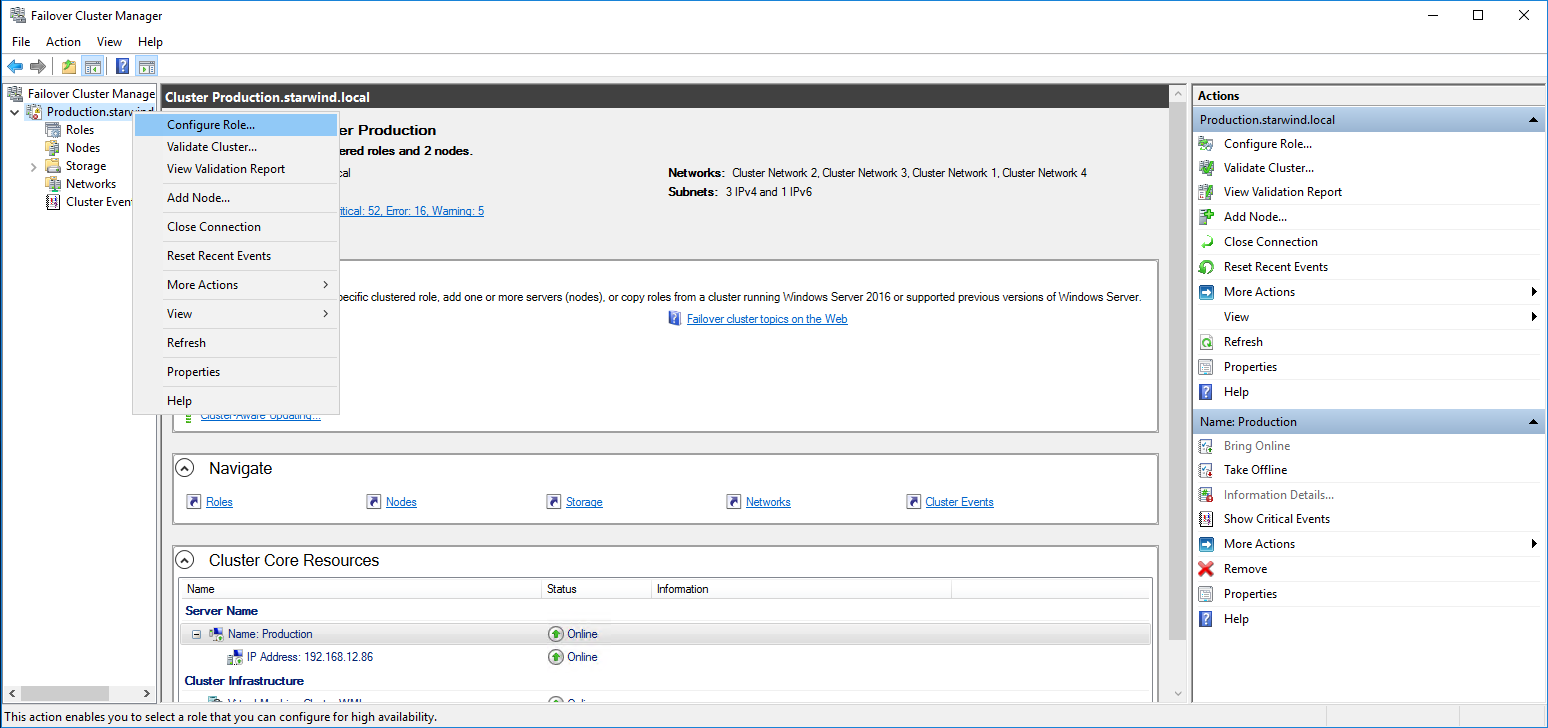
3. Select the File Server item from the list in High Availability Wizard and click Next to continue.
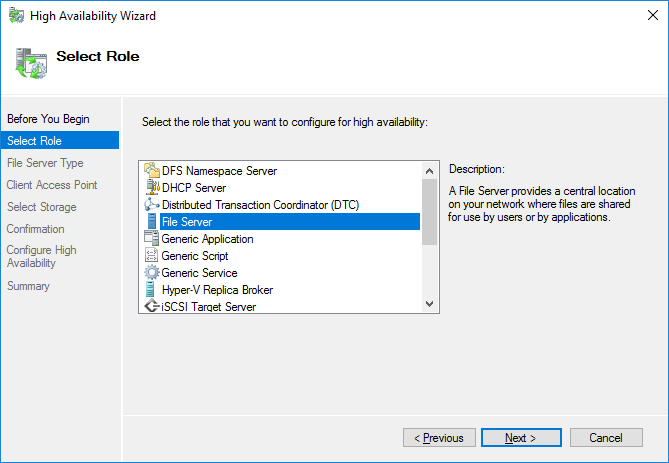
4. Select Scale-Out File Server for application data and click Next.
5. On the Client Access Point page, in the Name text field, type the NetBIOS name that will be used to access a Scale-Out File Server.
Click Next to continue.
6. Check whether the specified information is correct. Click Next to continue or Previous to change the settings.
7. Once the installation is finished successfully, the Wizard should now look like the screenshot below.
Click Finish to close the Wizard.
8. The newly created role should now look like the screenshot below.

NOTE: If the role status is Failed and it is unable to Start, please, follow the next steps:
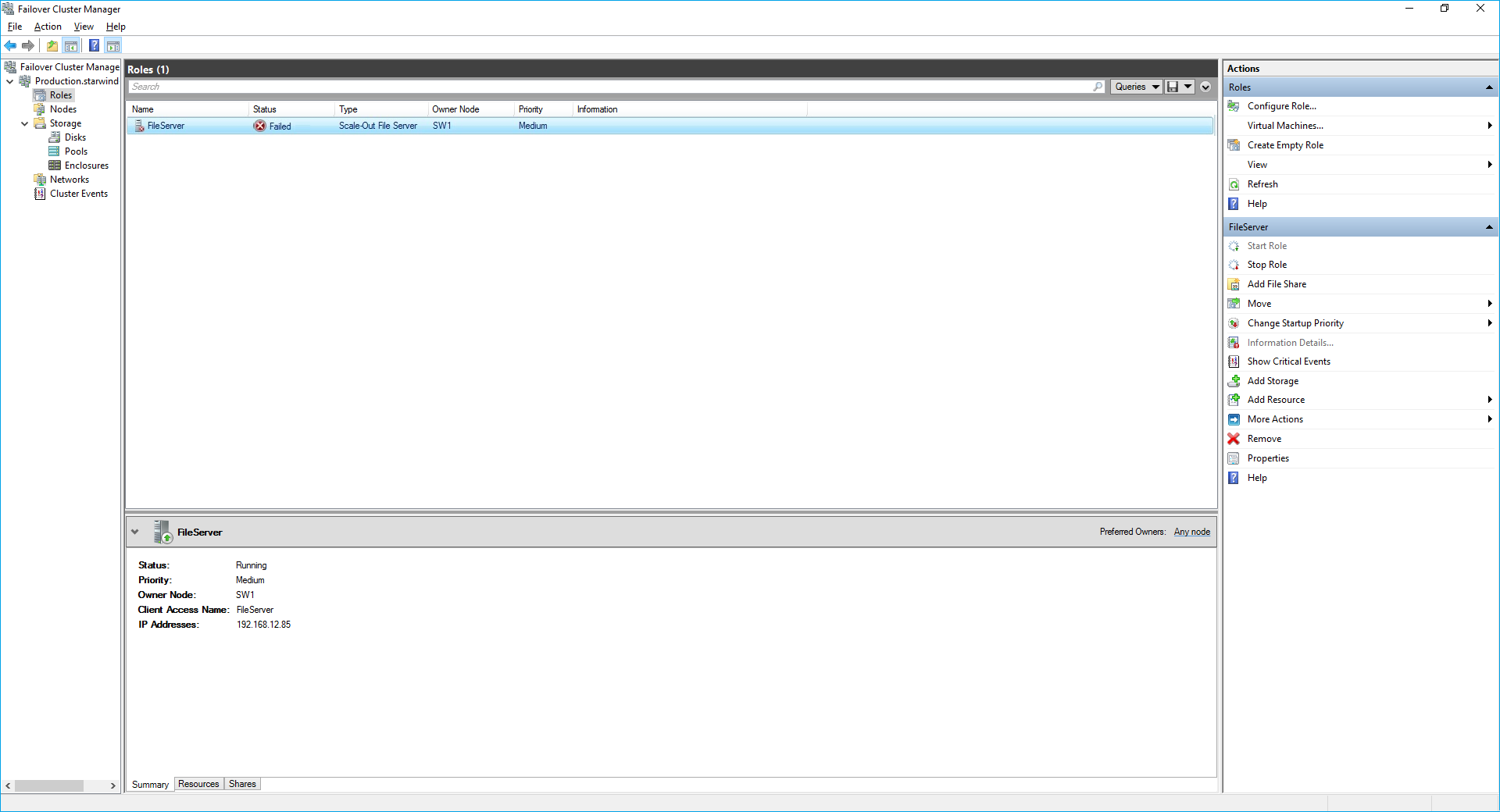
- open Active Directory Users and Computers
- enable the Advanced view if it is not enabled
- edit the properties of the OU containing the cluster computer object (in this case – Production)
- open the Security tab and click Advanced
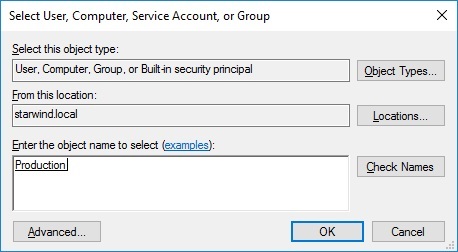
- in the appeared window, press Add (the Permission Entry dialog box opens), click Select a principal
- in the appeared window, click Object Types, select Computers, and click OK
- enter the name of the cluster computer object (in this case – Production)
- go back to Permission Entry dialog, scroll down, and select Create Computer Objects,
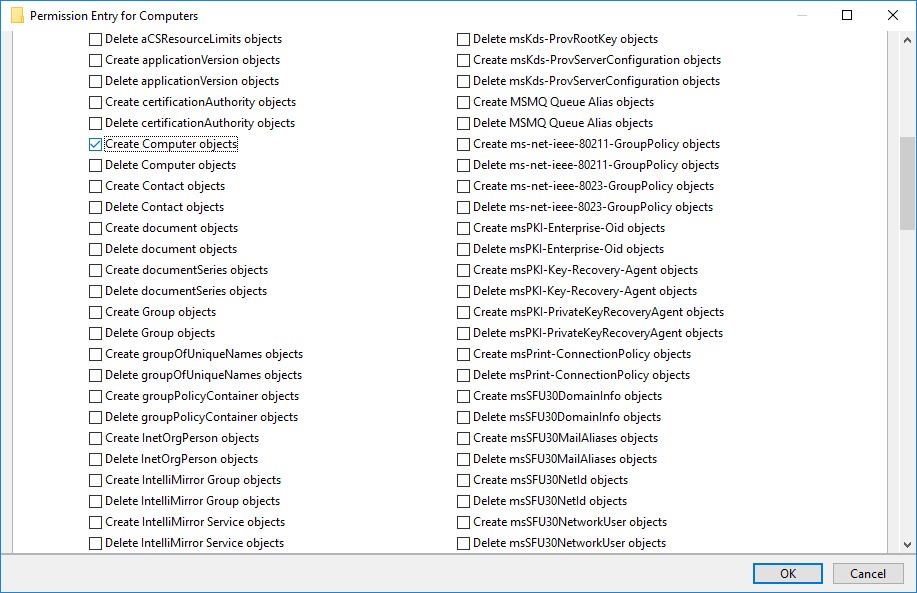
- click OK on all opened windows to confirm the changes
- open Failover Cluster Manager, right-click SOFS role and click Start Role
Configuring File Share
To Add File Share:
- open Failover Cluster Manager
- expand the cluster and then click Roles
- right-click the file server role and then press Add File Share
- on the Select the profile for this share page, click SMB Share – Applications and then click Next
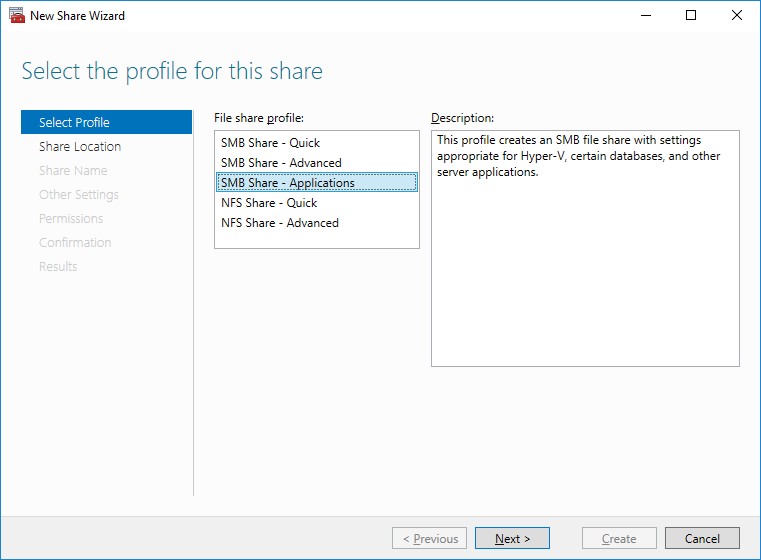
5. Select a CSV to host the share. Click Next to proceed.
6. Type in the file share name and click Next.
7. Make sure that the Enable Continuous Availability box is checked. Click Next to proceed.
8. Specify the access permissions for the file share.
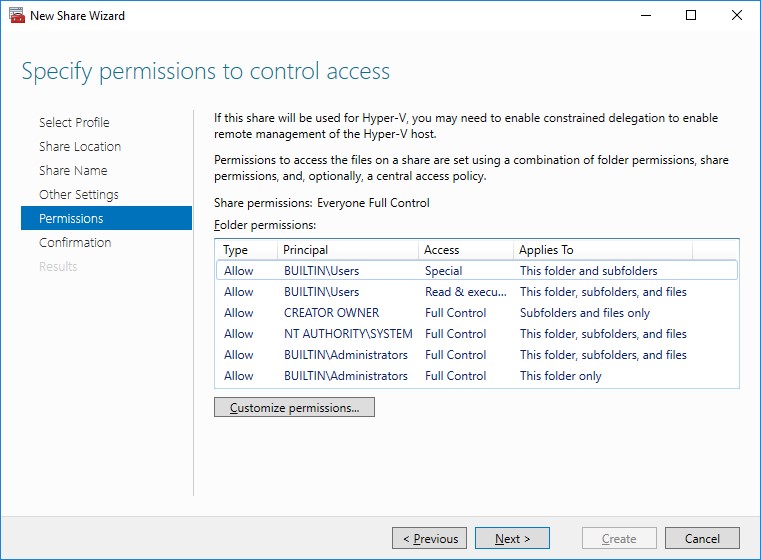
NOTE:
- for the Scale-Out File Server for Hyper-V, all Hyper-V computer accounts, the SYSTEM account, and all Hyper-V administrators must be provided with the full control on the share and file system
- for the Scale-Out File Server on Microsoft SQL Server, the SQL Server service account must be granted full control on the share and the file system
9. Check whether specified settings are correct. Click Previous to make any changes or click Create to proceed.
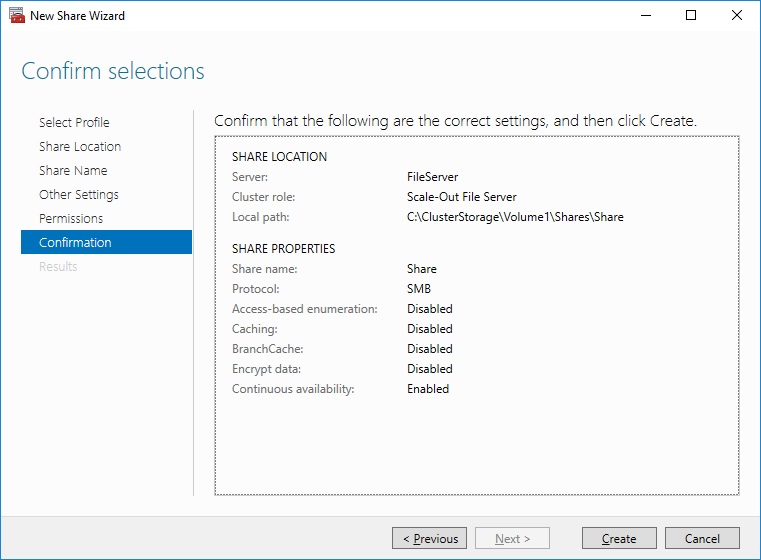
10. Check the summary and click Close to close the Wizard.
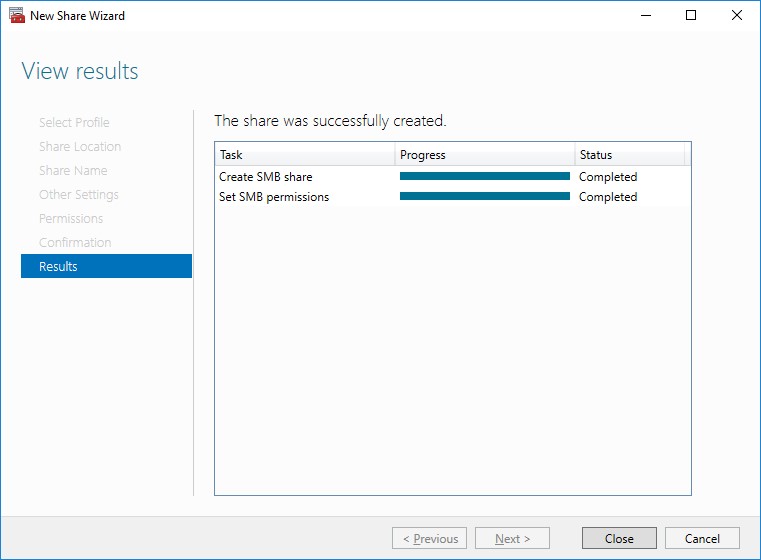
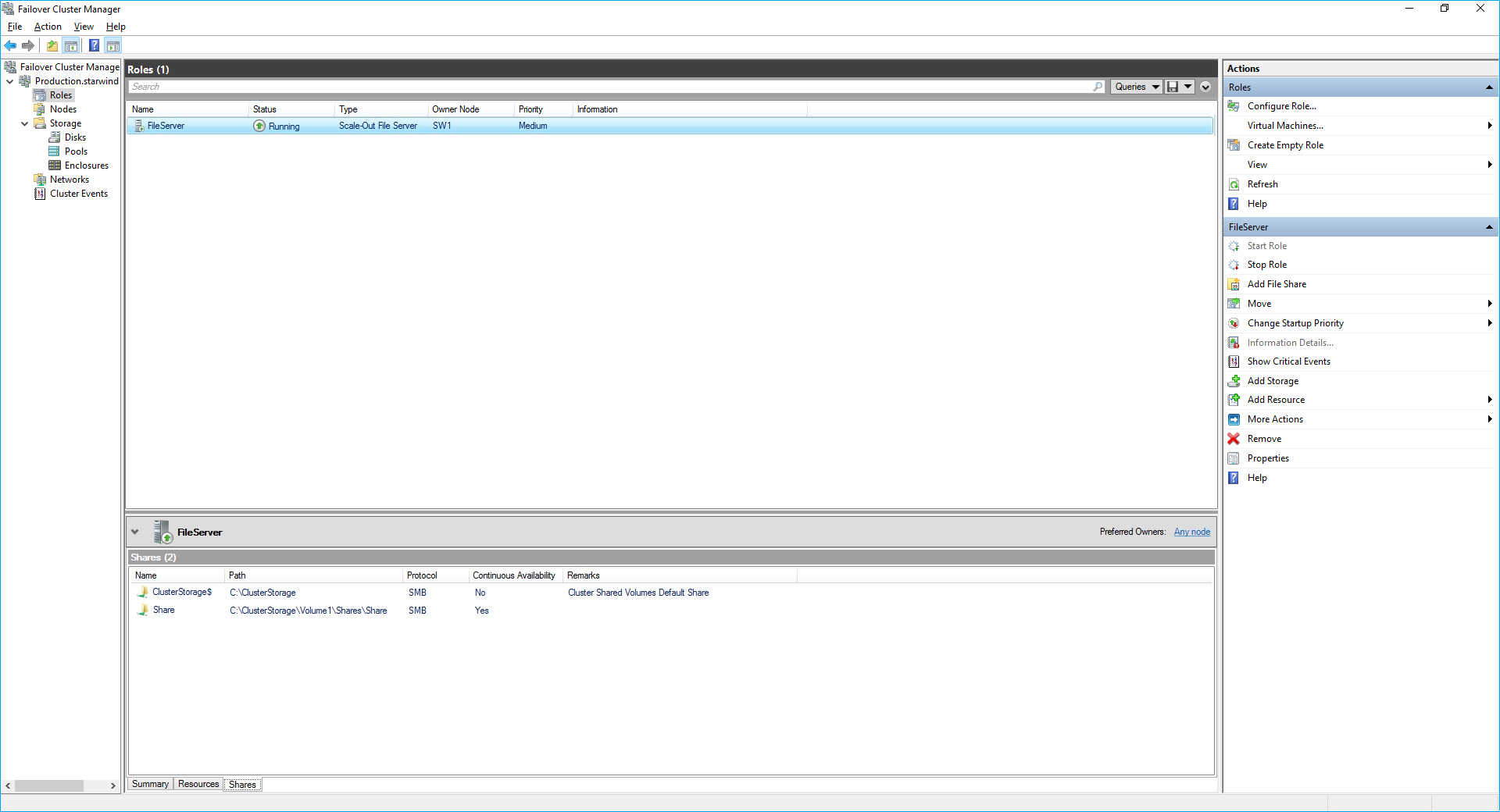
To Manage Created File Shares:
- open Failover Cluster Manager
- expand the cluster and click Roles
- choose the file share role, select the Shares tab, right-click the created file share, and select Properties:
Configuring the File Server for General Use Role
NOTE: To configure File Server for General Use, the cluster should have available storage
1. To configure the File Server for General Use role, open Failover Cluster Manager.
2. Right-click on the cluster name, then click Configure Role and click Next to continue.

3. Select the File Server item from the list in High Availability Wizard and click Next to continue.

4. Select File Server for general use and click Next.
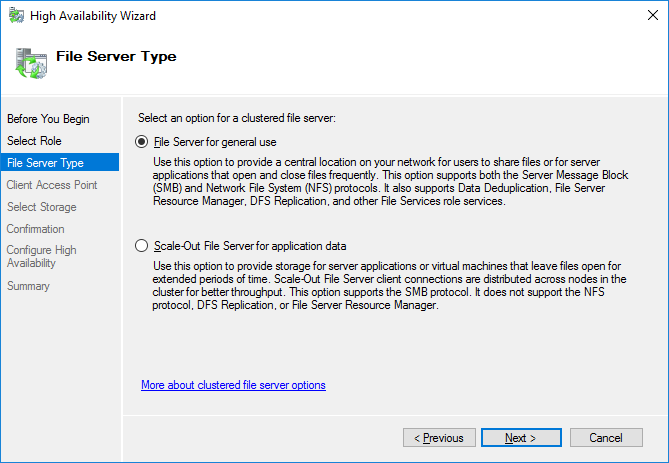
5. On the Client Access Point page, in the Name text field, type the NETBIOS name that will be used to access the File Server and IP for it.
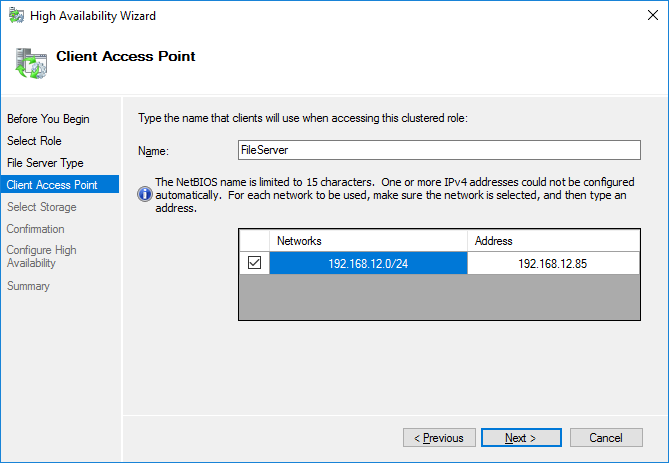
Click Next to continue.
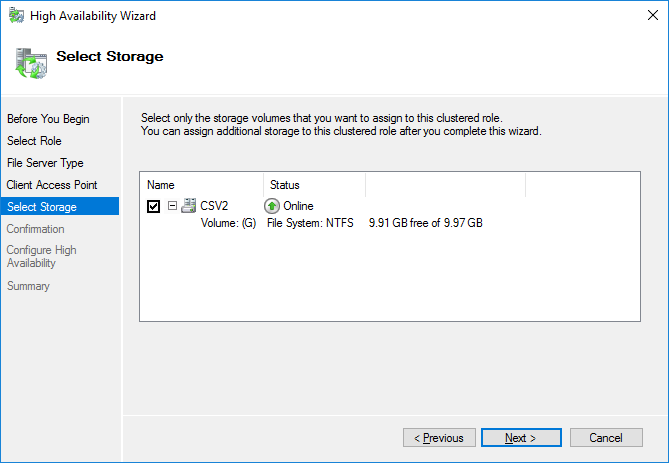
6. Select the Cluster disk and click Next.
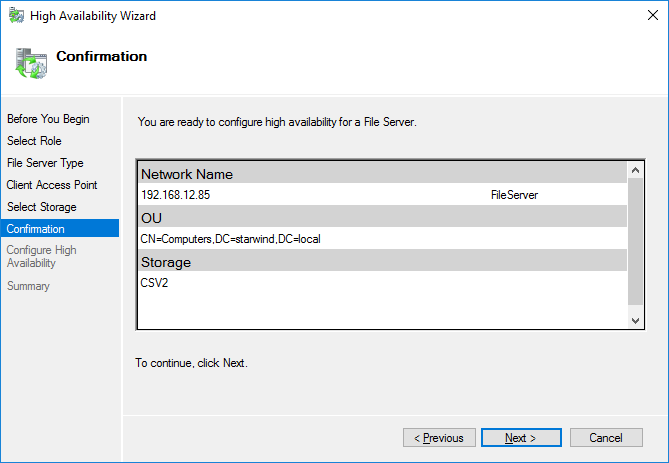
7. Check whether the specified information is correct. Click Next to proceed or Previous to change the settings.
8. Once the installation has been finished successfully, the Wizard should now look like the screenshot below.
Click Finish to close the Wizard.

9. The newly created role should now look like the screenshot below.
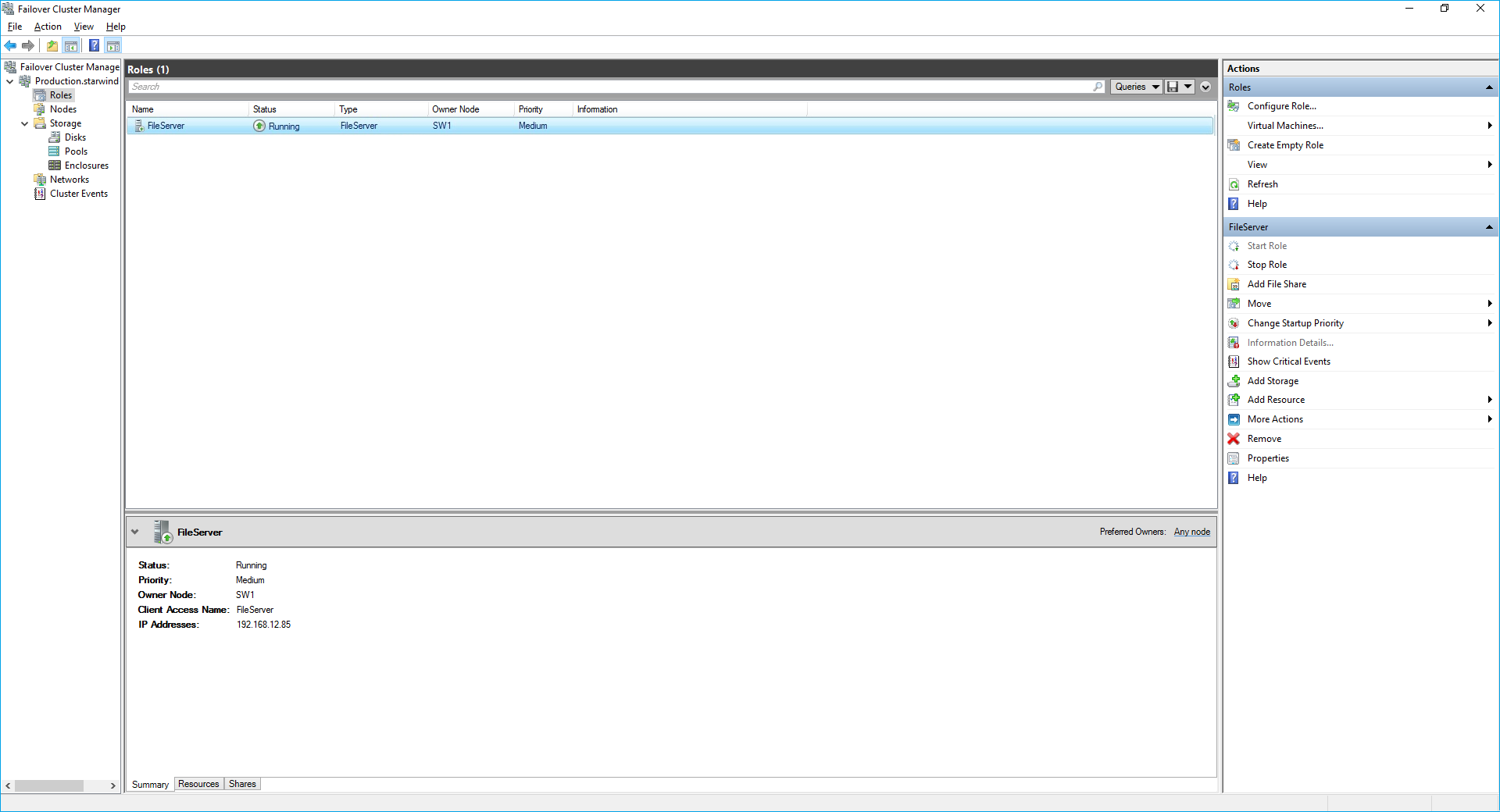
NOTE: If the role status is Failed and it is unable to Start, please, follow the next steps:
- open Active Directory Users and Computers
- enable the Advanced view if it is not enabled
- edit the properties of the OU containing the cluster computer object (in this case – Production)
- open the Security tab and click Advanced
- in the appeared window, press Add (the Permission Entry dialog box opens), click Select a principal
- in the appeared window, click Object Types, select Computers, and click OK
- enter the name of the cluster computer object (in this case – Production)

- go back to Permission Entry dialog, scroll down, and select Create Computer Objects
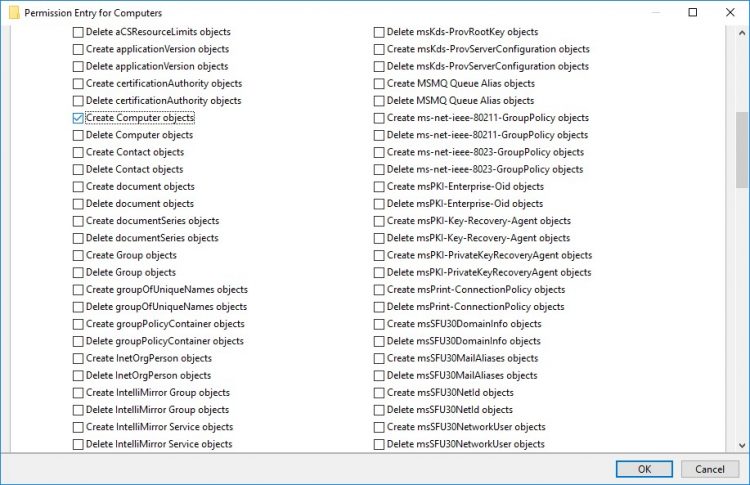
- click OK on all opened windows to confirm the changes
- open Failover Cluster Manager, right-click File Share role and click Start Role
Configuring SMB File Share
To Add SMB File Share
1. Open Failover Cluster Manager.
2. Expand the cluster and then click Roles.
3. Right-click the File Server role and then press Add File Share.
4. On the Select the profile for this share page, click SMB Share – Quick and then click Next.
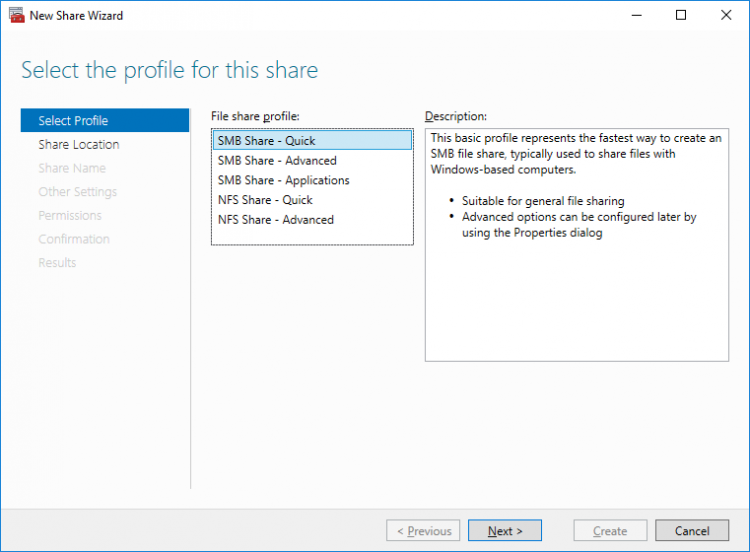
5. Select available storage to host the share. Click Next to continue.
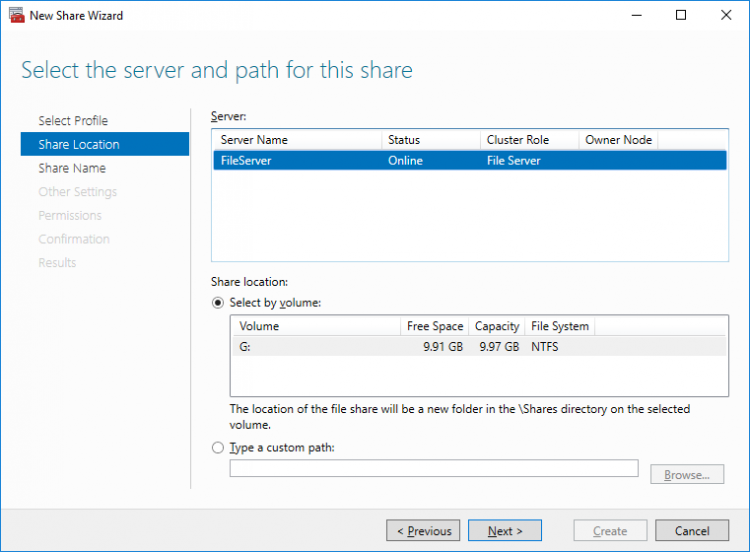
6. Type in the file share name and click Next.
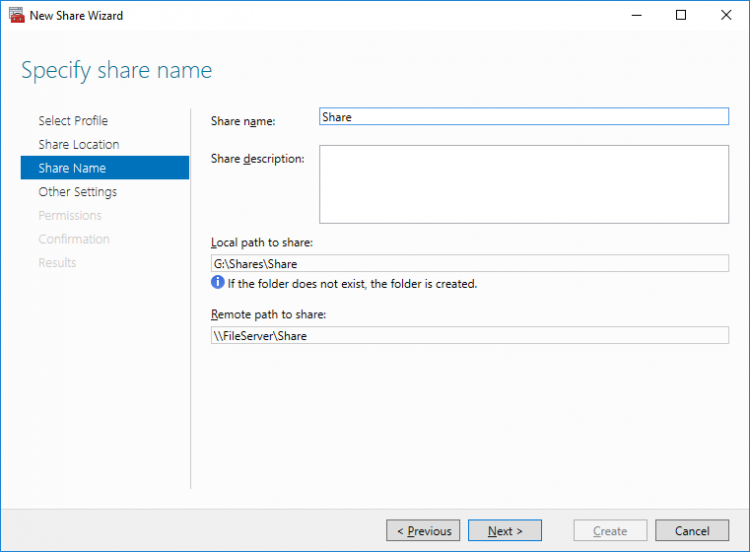
7. Make sure that the Enable Continuous Availability box is checked. Click Next to continue.
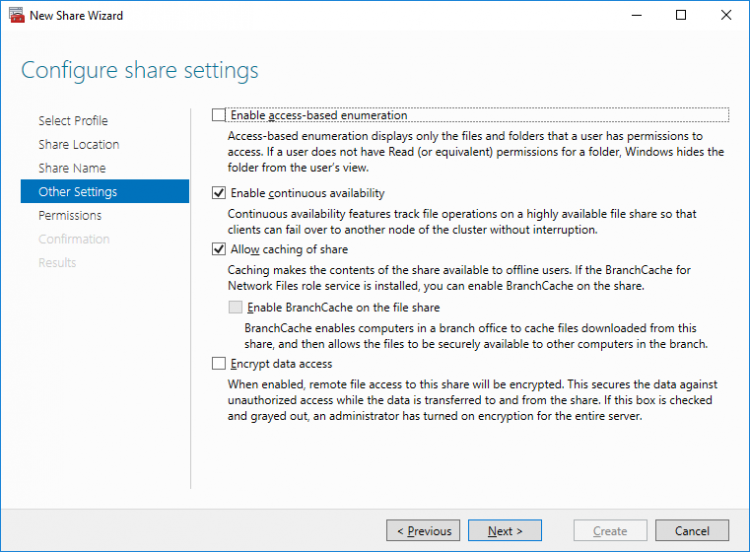
8.Specify the access permissions for the file share.
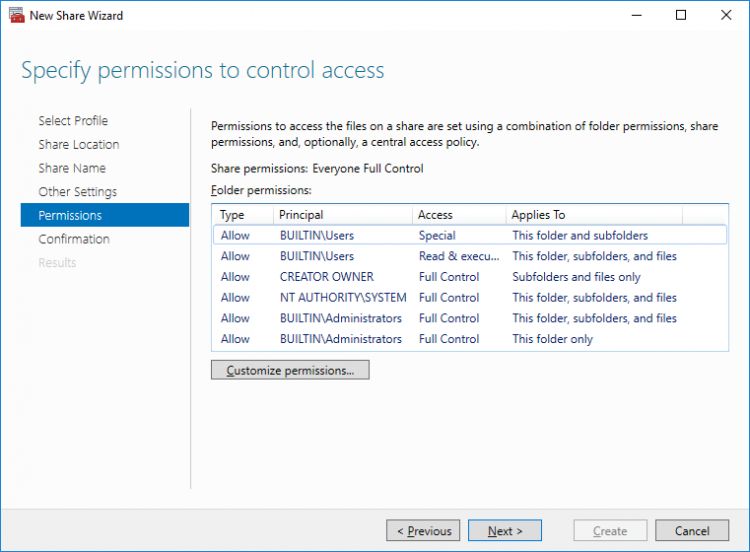
9. Check whether specified settings are correct. Click Previous to make any changes or Next/Create to continue.
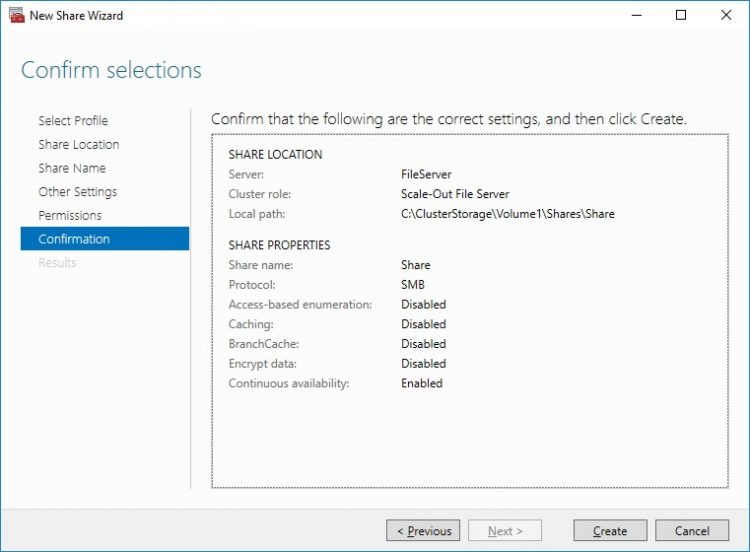
10. Check the summary and click Close.
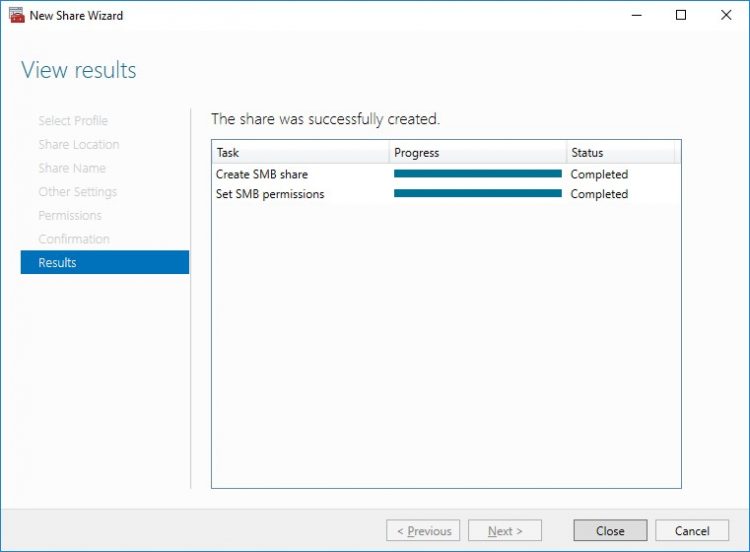
To manage created SMB File Shares
11. Open Failover Cluster Manager.
12. Expand the cluster and click Roles.
13. Choose the File Share role, select the Shares tab, right-click the created file share, and select Properties.
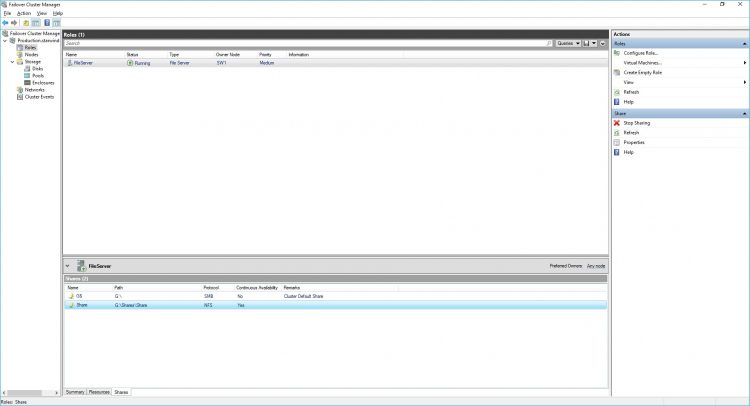
Configuring NFS file share
To Add NFS File Share
1. Open Failover Cluster Manager.
2. Expand the cluster and then click Roles.
3. Right-click the File Server role and then press Add File Share.
4. On the Select the profile for this share page, click NFS Share – Quick and then click Next.
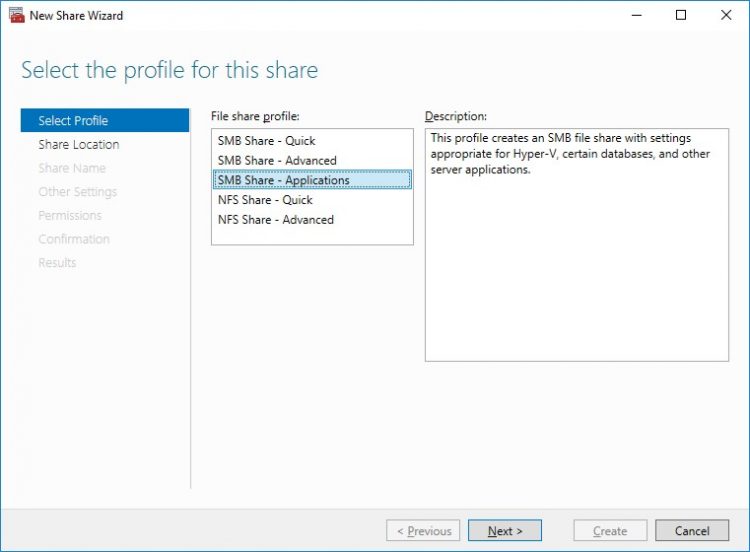
5. Select available storage to host the share. Click Next to continue.

6. Type in the file share name and click Next.
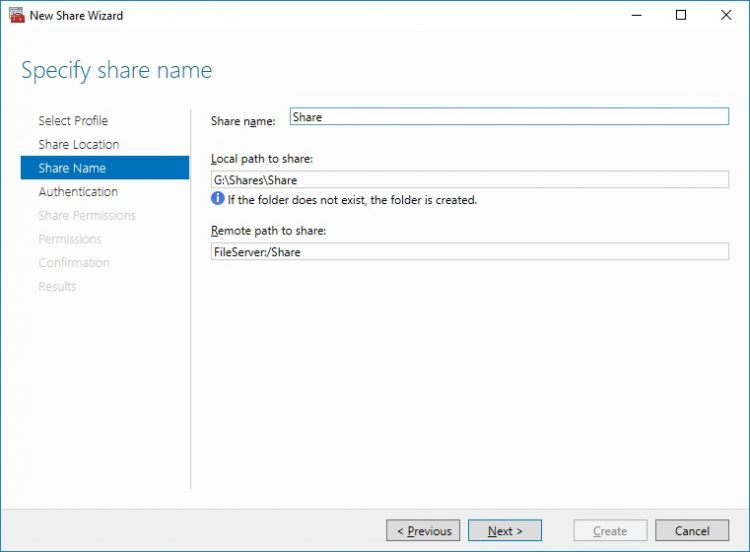
7. Specify the Authentication. Click Next and confirm the message in pop-up window to continue.
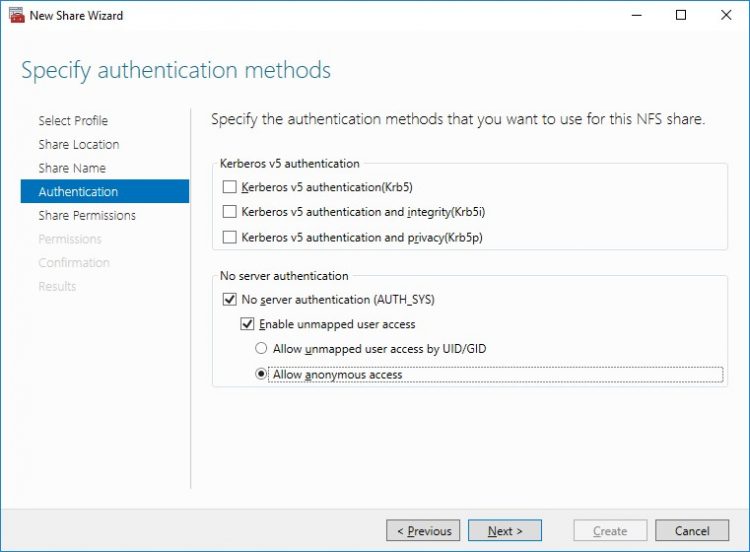
8. Click Add and specify Share Permissions.
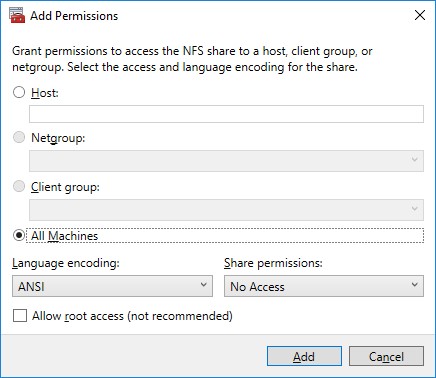
9. Specify the access permissions for the file share.

10. Check whether specified settings are correct. Click Previous to make any changes or click Create to continue.
11. Check a summary and click Close to close the Wizard.
To manage created NFS File Shares:
- open Failover Cluster Manager
- expand the cluster and click Roles
- choose the File Share role, select the Shares tab, right-click the created file share, and select Properties



