In part II, we add the Linux server to the Veeam managed servers, and we add the immutable repositories. We also demonstrate some of the incompatible backup job settings and repository configurations Veeam will block those for you if you try to configure them.
The Veeam configuration
Add the Linux server as a Veeam managed server
To add the Linux repository server to the Veeam VBR 11 Managed Servers with the new single-use credentials for the hardened repository feature, we must disable or bypass MFA on the account we use.
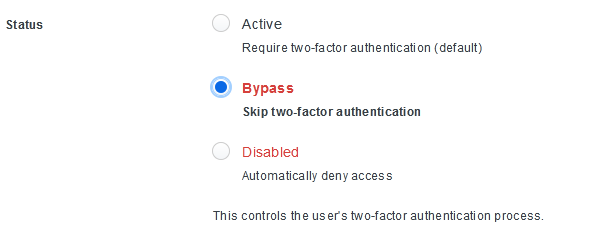
Figure 1: Temporarily bypass MFA
Launch the “Add Server” wizard

Figure 2: Add a Linux managed server
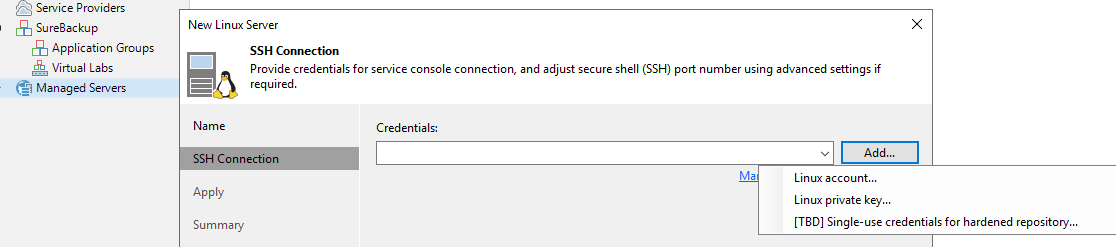
Figure 3: Single-use credentials for adding a hardened repository
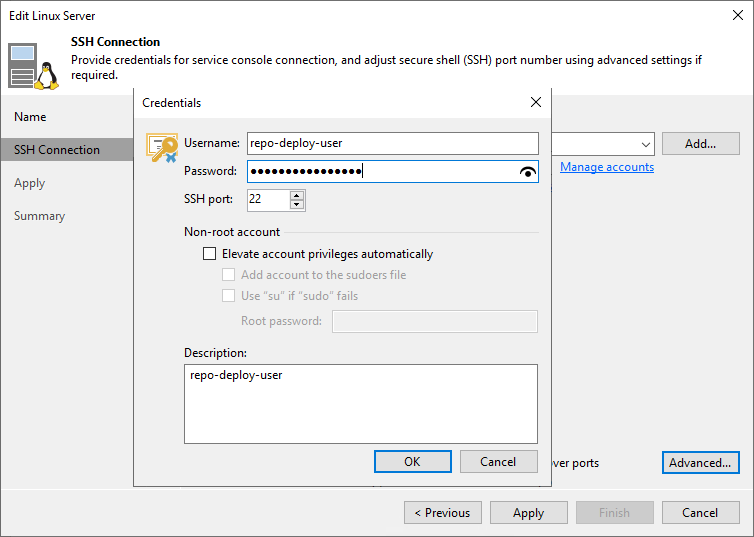
Figure 4: Fill out the username and password. Disable MFA for the user at this point!
Take a peek under the advanced connection settings. Noteworthy is that in v11, a single port, TCP/6162, is used for management by veeamtransport. By default, any port between TCP/2500-3300 is used for the data transfer by the veeamagent.
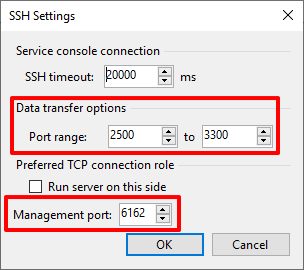
Figure 5: New in v11 is port 6162 for management
You can verify this once you have installed the Linux repository. When no backup job is running netstat -tpnul | grep -i veeam only returns the veeamtransport listening on tcp/6162.
![]()
Figure 6: An idle repository, only veeamtransport is listening on TCP/6162
During a backup job, extra ports from the range 2500-3300 opened by veeamagent. Run netstat -tpnul | grep -i Veeam | sort -n -k2 to see this.
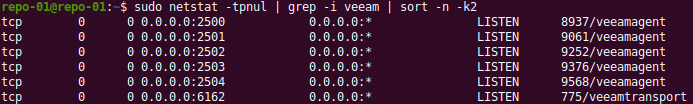
Figure 7: Starting at port TCP/2500 extra ports are opened during backup jobs
But that is for later. Let’s finish adding the Linux managed server.
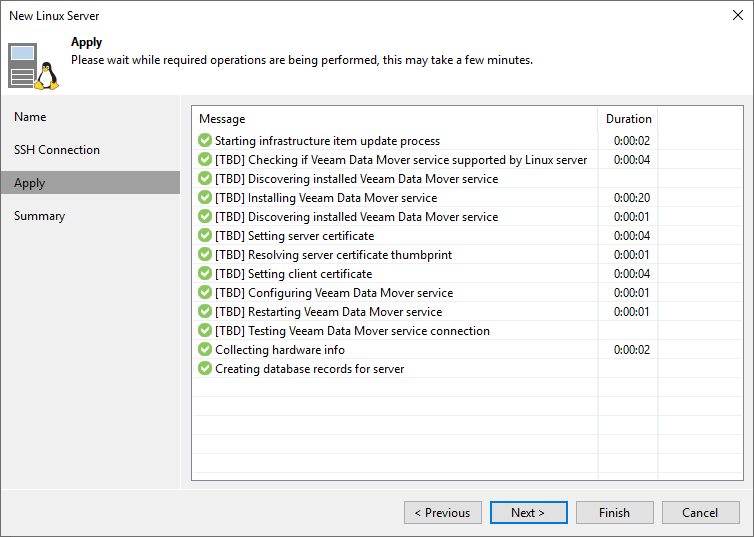
Figure 8: Veeam is installing the components. Note the setting of the server and client certificates
Those server and client certificates you see here serve to authenticate between Veeam components from now on. That allows for SSH to be disabled.
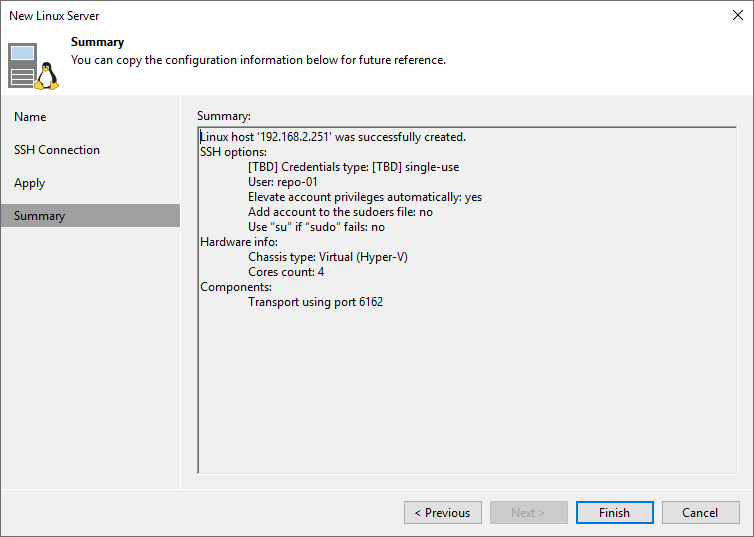
Figure 9: Done. Disable SSH or enable MFA. You’re good to go
Remember that the single-use credentials only exist on the hardened repository and are not stored on the VBR server. Right now, you must take away sudo rights from that user. They are not needed anymore.
|
1 |
sudo deluser veeamrepouser sudo |
Reenable MFA for that user or disable SSH on the repository host.
Add the hardened Linux backup repository
We add our Linux backup repository with the wizard.

Figure 10: Select Direct Attached Storage
Figure 11: Select Linux
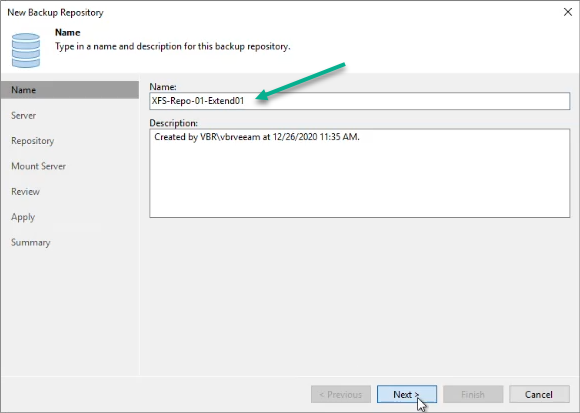
Figure 12: Fill out a repository name to use
Click Next. Click populate and select our XFS volume.
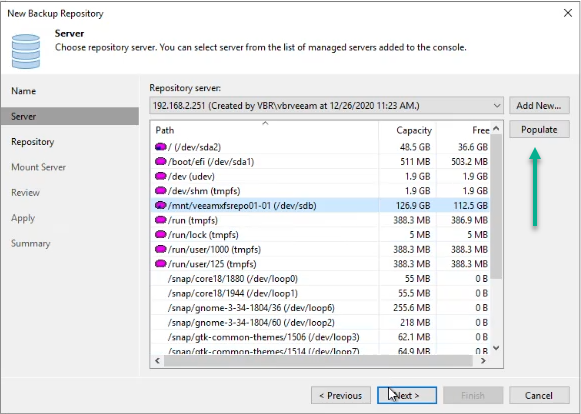
Figure 13: Populate the volumes and select the XFS volume
Click Next. As you can see, we select to use fast cloning on the XFS volume. We already explained why this is the way to go.
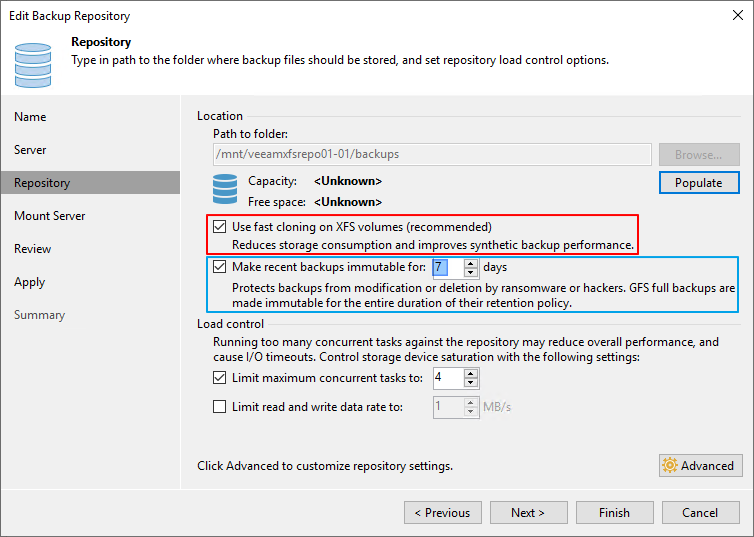
Figure 14: Use fast cloning and make the backup immutable
Note that the default value for the number of days to make backup immutable is 30. That makes sense as ransomware can linger inside your systems for a while before striking, and you need time for GFS to do its job. In the lab, we choose seven days for testing purposes. Note that seven days is the minimum. FYI, I use per VM backup chains almost exclusively,
Click Next. The rest is pretty standard for adding a Veeam repository.
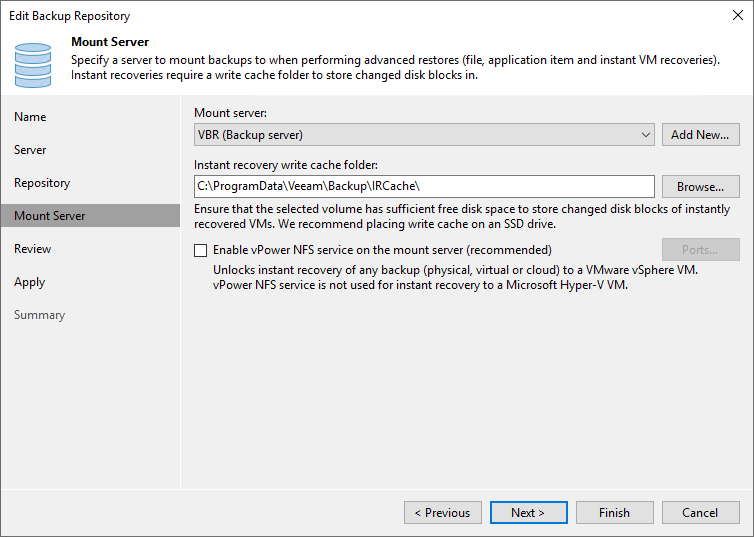
Figure 15: Mount server properties
I have a Hyper-V lab, so I don’t use the vPower NFS service. If you do, add it. Click Next, and the required Veeam components will install. If you get any errors here, be sure to verify the rights of the single-use user you used to add the server to the Veeam managed servers. Ensure it has rwx rights on the XFS volume.
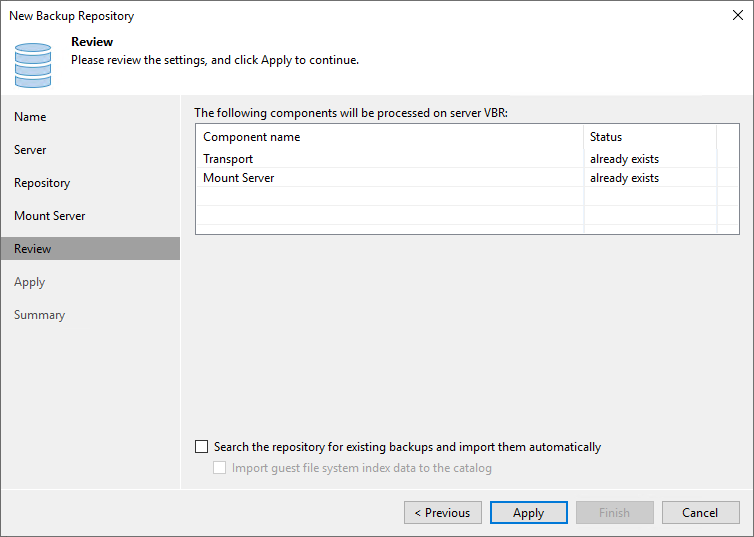
Figure 16: Install the required Veeam components
The critical thing to note here is that you can do all this with SSH on the server disabled or protected by MFA. The only time you needed to SSH into the Linux server is when creating the managed server object in Veeam.
Note: A repository host has to either host immutable repositories or standard (non-immutable) repositories. You cannot mix both on the same host. That is logical. In almost every case, you will add them as extents to a scale-out backup repository. You don’t want a SOBR with some extents being immutable and another not. That’s not consistent and won’t work out.
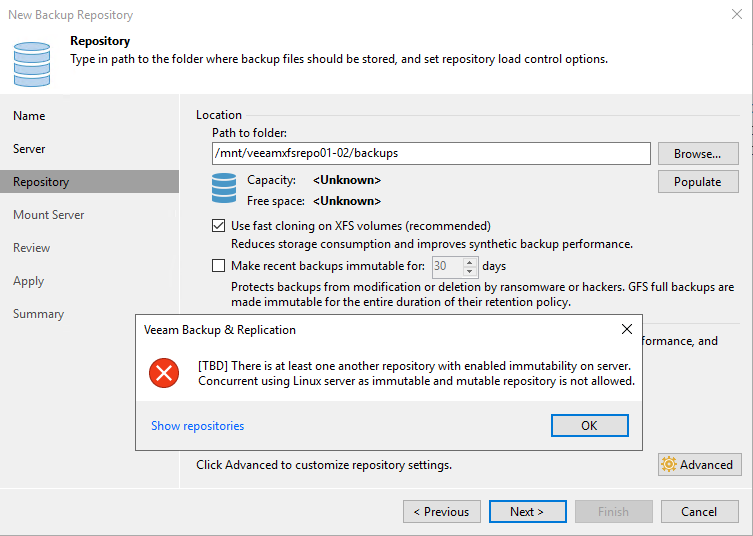
Figure 17: You cannot mix immutable and mutable repositories on the same host
Create some jobs and run some backups
Veeam protects us from unsupported configurations. A few examples below.
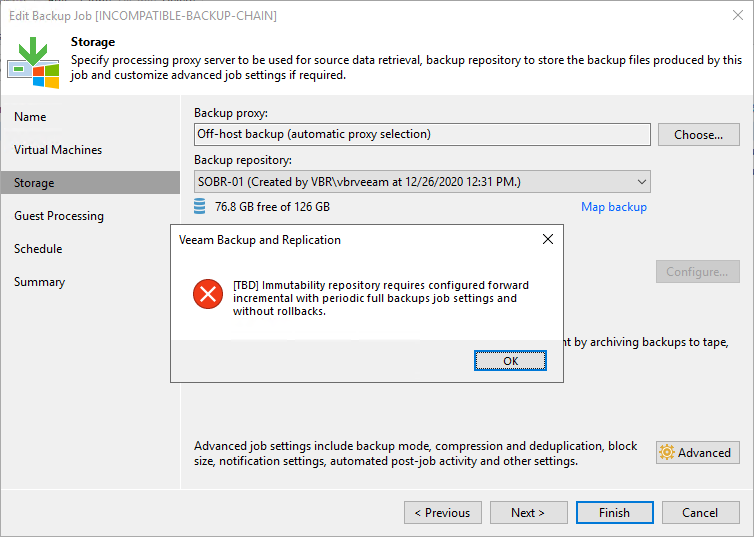
Figure 18: Changing or creating a backup job’s backup chain to an unsupported configuration: we turn off synthetic full backups
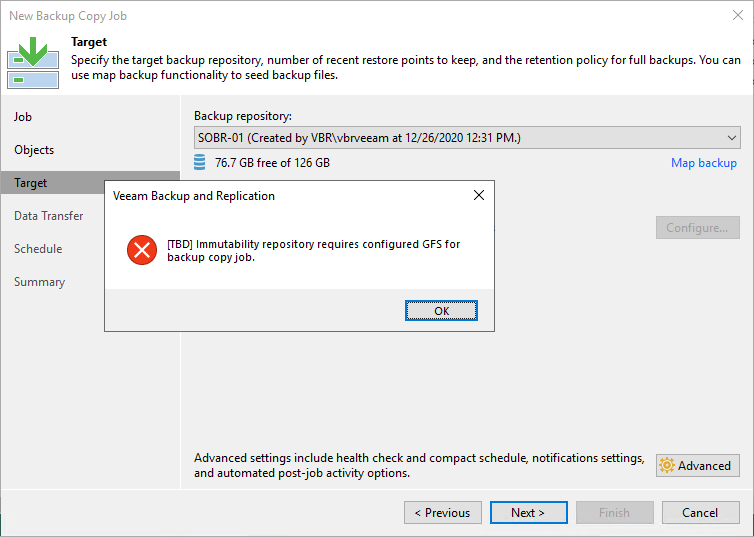
Figure 19: Creating a backup copy job without GFS configured
The backups run and look as any other Veeam backup job.
Figure 20: Veeam backup job
If we set the number of immutability days higher than the retention days or restore points, Veeam notifies us of this. It lets us know that the files are immutable longer than defined by the restore points. These files will remain on the repository until the immutability period has expired. According to your settings, Veeam does not need to care about these restore points in the console/database. At least, that is how I read that message.
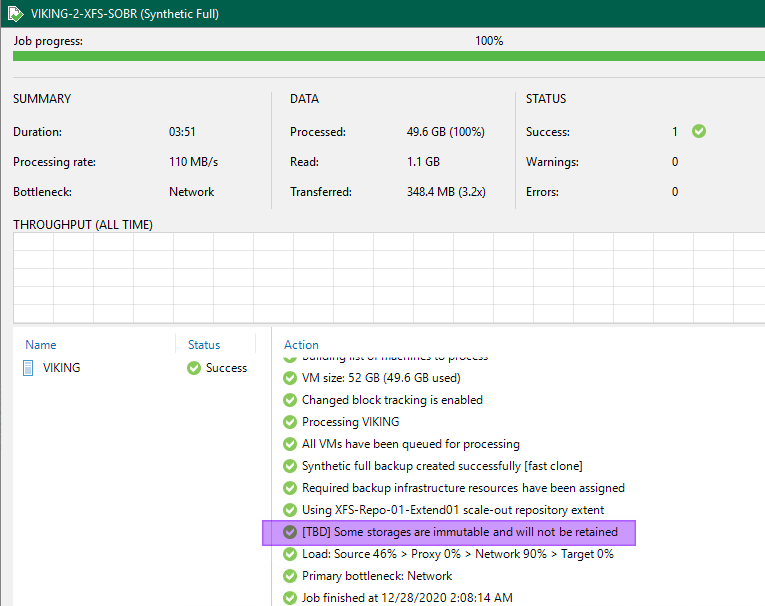
Figure 21: The immutability period will determine how long backup files will be around
Do note that thse backup files will become mutable after the immutability period has expired and at a next backup run will be cleard from the repository as well. I tested this and this works.



