Patching Windows client operating systems have historically been extremely time-consuming and tedious for administrators. In addition, conventional patching technologies and processes have been centered around on-premises technologies such as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and other enterprise solutions to keep Windows clients and servers patched. However, cloud technologies like Microsoft Intune as part of Endpoint Manager are helping transform Windows client updates. Recently, Microsoft has released a new way that organizations will have available to keep clients patched. It is called Windows Autopatch.
What is Windows Autopatch?
First, what is Windows Autopatch? Windows Autopatch is a new cloud-centric service as part of the Microsoft cloud that allows organizations to automate applying the latest patches to their Windows clients. Microsoft has mentioned that it will turn “patch Tuesday” into just another Tuesday. The product promises to provide “continuous” updates for your endpoints.
So, what do the patches include? Windows Autopatch applies the latest patches to Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams.
Windows Autopatch takes the heavy lifting and complexity out of applying patches to your Windows clients registered in Microsoft Endpoint manager. Windows Autopatch includes the following areas of management for updates in your organization:
- Windows 10/11 quality updates – Windows Autopatch manages all aspects of update rings applied to your endpoints
- Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise updates – Devices will receive updates from the Monthly Enterprise Channel with Windows Autopatch
- Microsoft Edge – With Windows Autopatch, devices benefit from Microsoft Edge’s progressive rollouts on the Stable channel. Support is also provided for issues with Microsoft Edge updates.
- Microsoft Teams – Windows Autopatch enables benefiting from standard automatic update channels and will provide support for issues with Teams updates
Windows Autopatch performs eligibility requirements for each management area mentioned above to determine if devices will receive those specific updates. The eligibility requirements check to make sure the components of your Microsoft cloud services meet the requirements of Windows Autopatch. These checks include:
- Microsoft Intune settings
- Azure Active Directory settings
- Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise settings
Below, you can see the Windows Autopatch readiness checks have been satisfied in Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
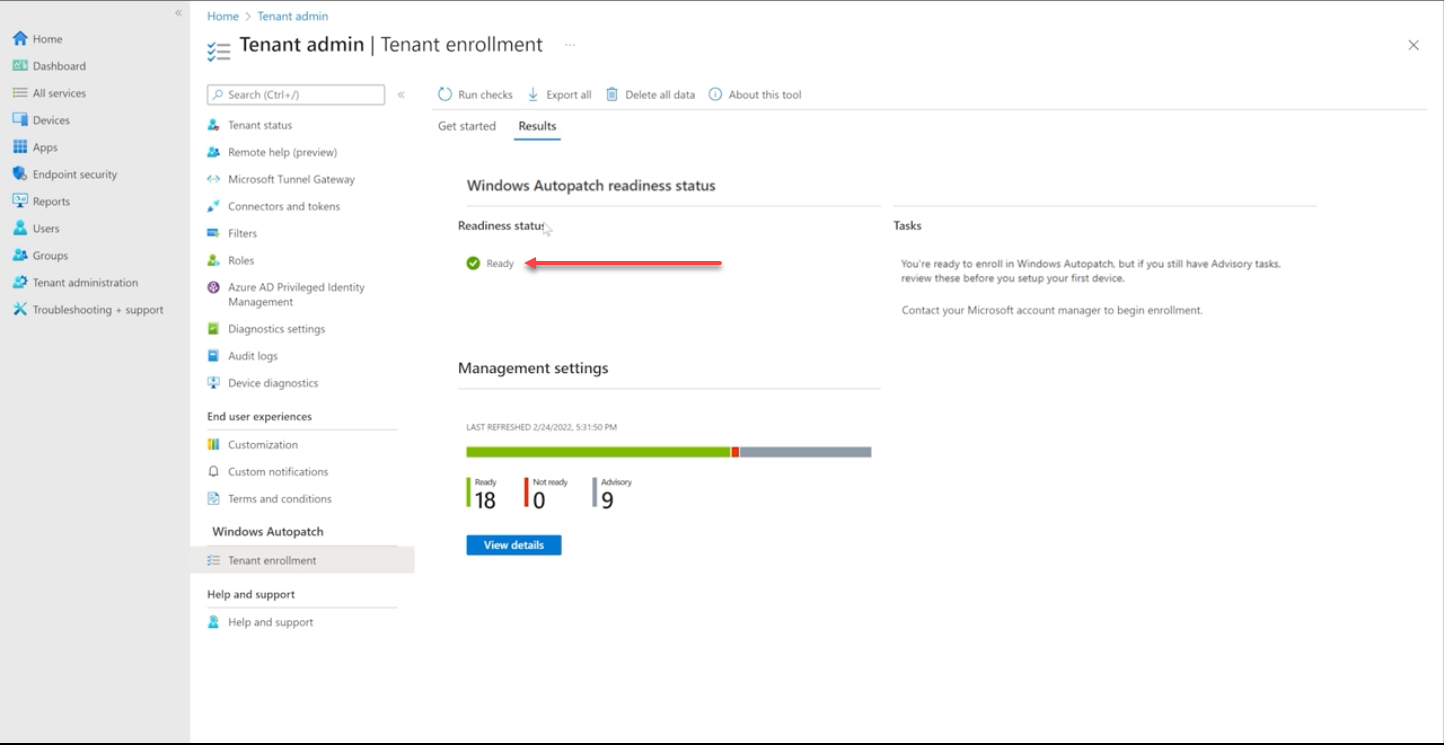 Readiness checks satisfied
Readiness checks satisfied
Once eligibility requirements have been satisfied, devices are labeled as “healthy.” Those devices that do not meet the criteria are labeled as unhealthy. Windows Autopatch monitors the state of updates in progress to determine the state of the process. Windows Autopatch may decide to expedite the update being rolled out if an update is critical, such as a critical security patch.
Microsoft has set different monitoring and update control capabilities for each management area, so admins must review each area to become familiar with the details associated with each service.
Windows Autopatch requirements
Microsoft has designed Windows Autopatch to roll out quickly and easily. However, first, organizations must meet the requirements of Windows Autopatch. Note the following:
- Licensing – Windows Autopatch requires Windows 10 & 11 Enterprise E3 or higher to be assigned to your end-users. Additional licensing requirements include Azure Active Directory Premium and Microsoft Intune
- Connectivity – Connectivity is required to Microsoft update services endpoints. These endpoints include the below. For a complete list, see the official documentation here.
– mmdcustomer.microsoft.com
– mmdls.microsoft.com
– logcollection.mmd.microsoft.com
– support.mmd.microsoft.com
- Azure Active Directory – There are two options available as requirements from the Azure AD side of things. You can use Azure Active Directory as the source of authority for all user accounts, or using the Hybrid Azure Active Directory Domain join, you can also synchronize your users from on-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS).
- Device management – Your devices need to be managed by Microsoft Intune. You must set Microsoft Intune as the Mobile Device Management (MDM) authority, or co-management must be used. Minimally, you must have the following configured in Microsoft Intune: Windows Update, Device configuration, and Office click-to-run apps workloads. Notably, devices must be corporate-owned, with no BYOD. Your devices must be in contact with Microsoft Intune in the last 28 days and be Internet-connected.
Licensing requirements
What are the specific licensing requirements for Windows Autopatch? These include the following:
- Window 10/11 Enterprise E3 or higher
- Azure AD Premium (for Co-management)
- Microsoft Intune (includes Configuration Manager 2010 or greater via co-management)
Unique features of Windows Autopatch
With the challenges and complexities facing organizations today, including the hybrid workforce, cloud infrastructure and services help to ease many of the daily tasks and activities that plague on-premises infrastructure and services. Windows Autopatch has been designed to help alleviate one of the longstanding burdens on IT, taking care of Windows patches and other business-critical applications.
Note the following features of the Autopatch solution:
- Increased cybersecurity posture – One of the tremendously challenging tasks facing organizations today is maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture. Threats are seemingly everywhere. Keeping software up-to-date is one of the most productive tasks regarding your cybersecurity posture. Unfortunately, attackers often take advantage of software vulnerabilities found in unpatched systems. Windows Autopatch helps to close this gap by helping to keep your endpoints up-to-date and patched with the latest security patches and updated software.
- Access to the latest tools and apps – Windows Autopatch ensures your end users are up-to-date with the latest software. In addition to containing the latest security patches, the latest software means your users have access to the latest features, capabilities, and functionality in their business-critical apps. These often lead to your users being more productive and able to collaborate and communicate more efficiently.
- Decreased burden on IT – With IT resources already in short supply, Windows Autopatch helps to alleviate one of the burdens facing IT by automating the process of patching your endpoints. It allows IT more time to focus on other critical tasks in the environment.
- Reduced on-premises footprint – With fewer resources needed for patching and other infrastructure-related tasks associated with updates, Windows Autopatch helps organizations reduce their on-premises infrastructure footprint, leading to lower CapEx investments and unseen costs associated with the lifecycle management of on-premises enterprise datacenters.
- It is easy to get started – Windows Autopatch is designed to be easy to use and easy for IT admins to get started patching endpoints. There is no complex infrastructure or “nerd knobs” that need to be turned and tweaked. Instead, the onboarding process in Endpoint Manager is straightforward.
- Minimize disruption – With Windows Autopatch, you can minimize the disruption typically associated with patches. Windows Autopatch essentially moves patching to the more modern “update rings” style approach, responding to reliability and compatibility signals from Endpoint Manager, and disruptions to your end-users is reduced.
What is the difference between Windows Update for Business and Windows Autopatch?
You may wonder, doesn’t Microsoft already have Windows Update for Business positioned in the cloud? So how does Windows Autopatch different from Windows Update for Business. With Windows Update for Business, IT still needs to manage and operate the process of applying updates to clients.
Windows Autopatch takes ownership of the entire process of managing and maintaining updates on clients, removing this burden completely from the IT staff.
How does Windows Autopatch work?
The Windows Autopatch service uses the Windows update “rings” underneath the hood. It automatically samples the devices in your organization to detect variations among the endpoints in the device estate. It dynamically creates 4 testing rings:
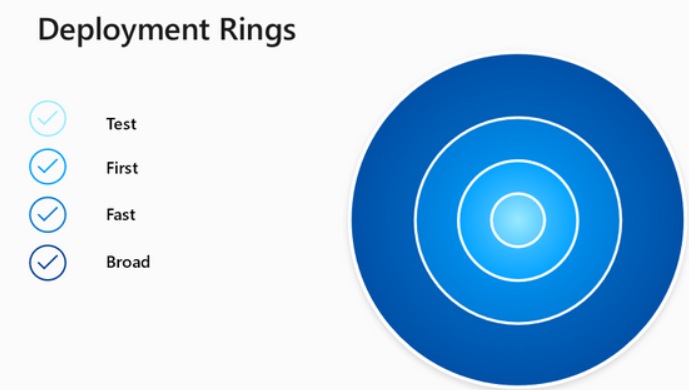 Windows Autopatch testing rings
Windows Autopatch testing rings
Ring groups and their relative populations from your client estate look like the following. So it dynamically creates the test ring, which is a minimum number of devices, then the “first” ring, which is only 1% of devices. The “fast” ring is 9% of devices and the remaining 90% are assigned to the “broad” ring.
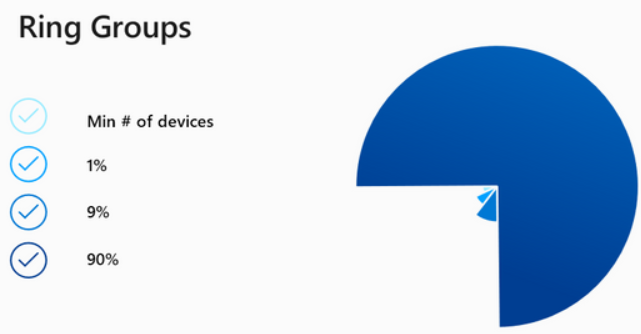 Device populations in the update rings are managed by Windows Autopatch
Device populations in the update rings are managed by Windows Autopatch
Microsoft mentions enterprise IT will be able to move specific devices from one ring to another to have the granular control needed for specific clients and devices across the organizations. Intuitively, Windows Autopatch deploys updates progressively. Devices in the “test” ring get the updates first and are validated for a period of time. Updates then progress to the next ring and so on. Microsoft mentions that each ring is afforded 30 days so that users have an opportunity to interact with software and report any issues that can’t be detected automatically.
What about Quality and Feature updates?
- Quality updates – These updates ones that contain security, firmware, and other ‘essential’ functionality. These are rolled out quickly.
- Feature updates – These may involve user interfaces or user experience changes and are rolled out more slowly
Enrolling in Windows Autopatch
Let’s look at the process to enroll in Windows Autopatch. First, navigate to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center and navigate to Tenant Enrollment.
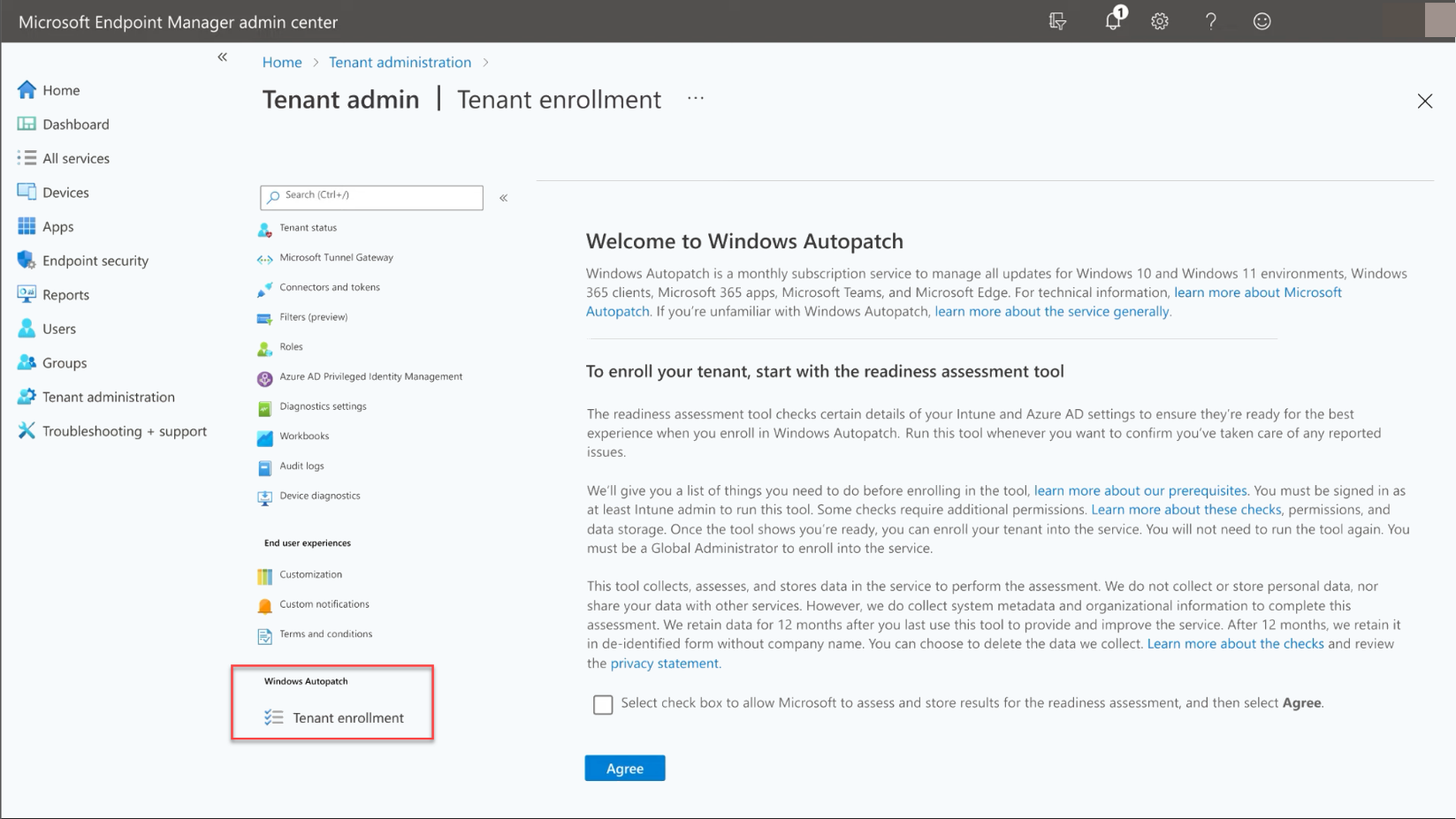 Viewing Windows Autopatch in tenant enrollment
Viewing Windows Autopatch in tenant enrollment
Accept the EULA for the readiness assessment tool.
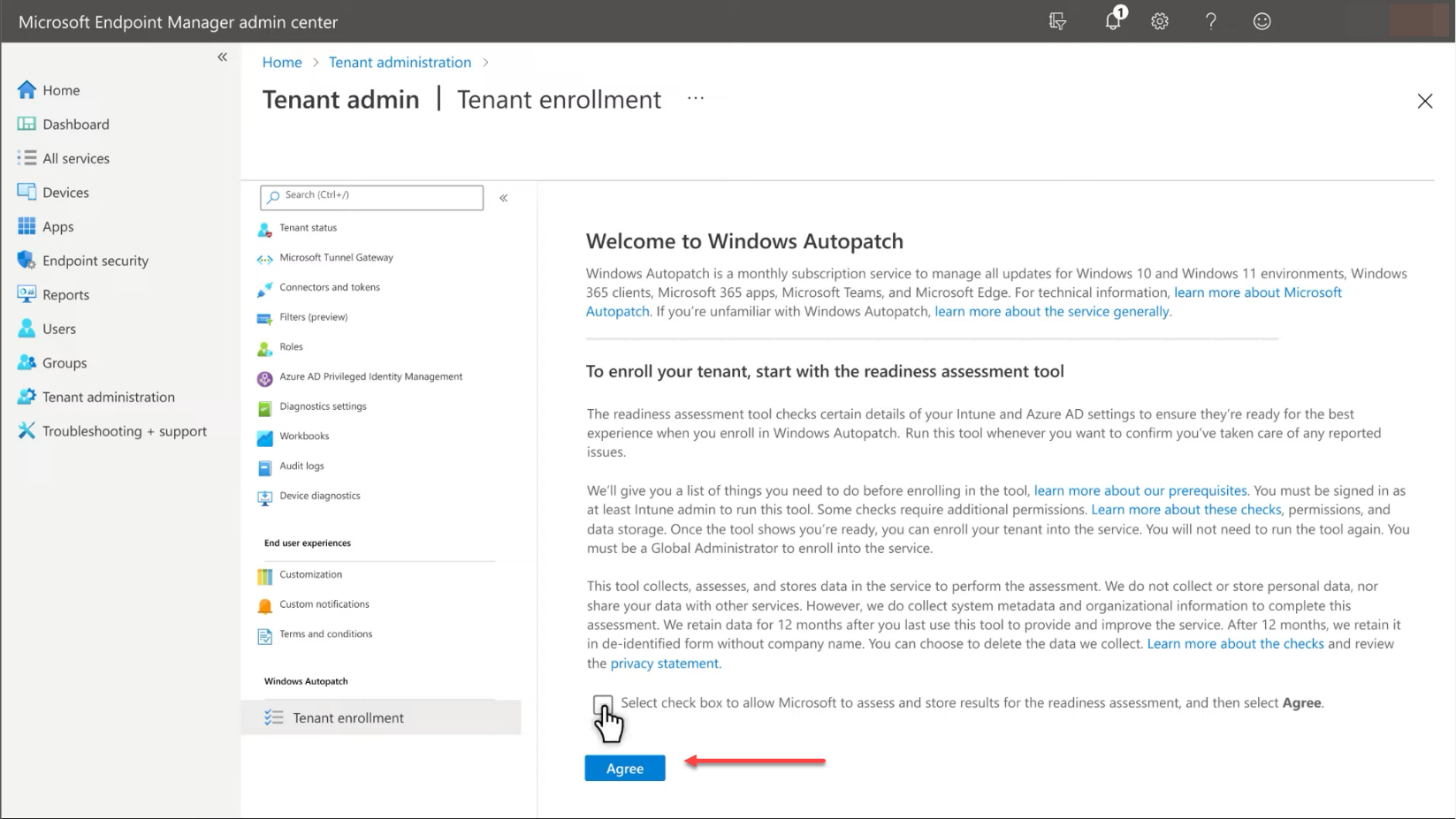 Accept the EULA for the readiness assessment tool
Accept the EULA for the readiness assessment tool
Click the Enroll button.
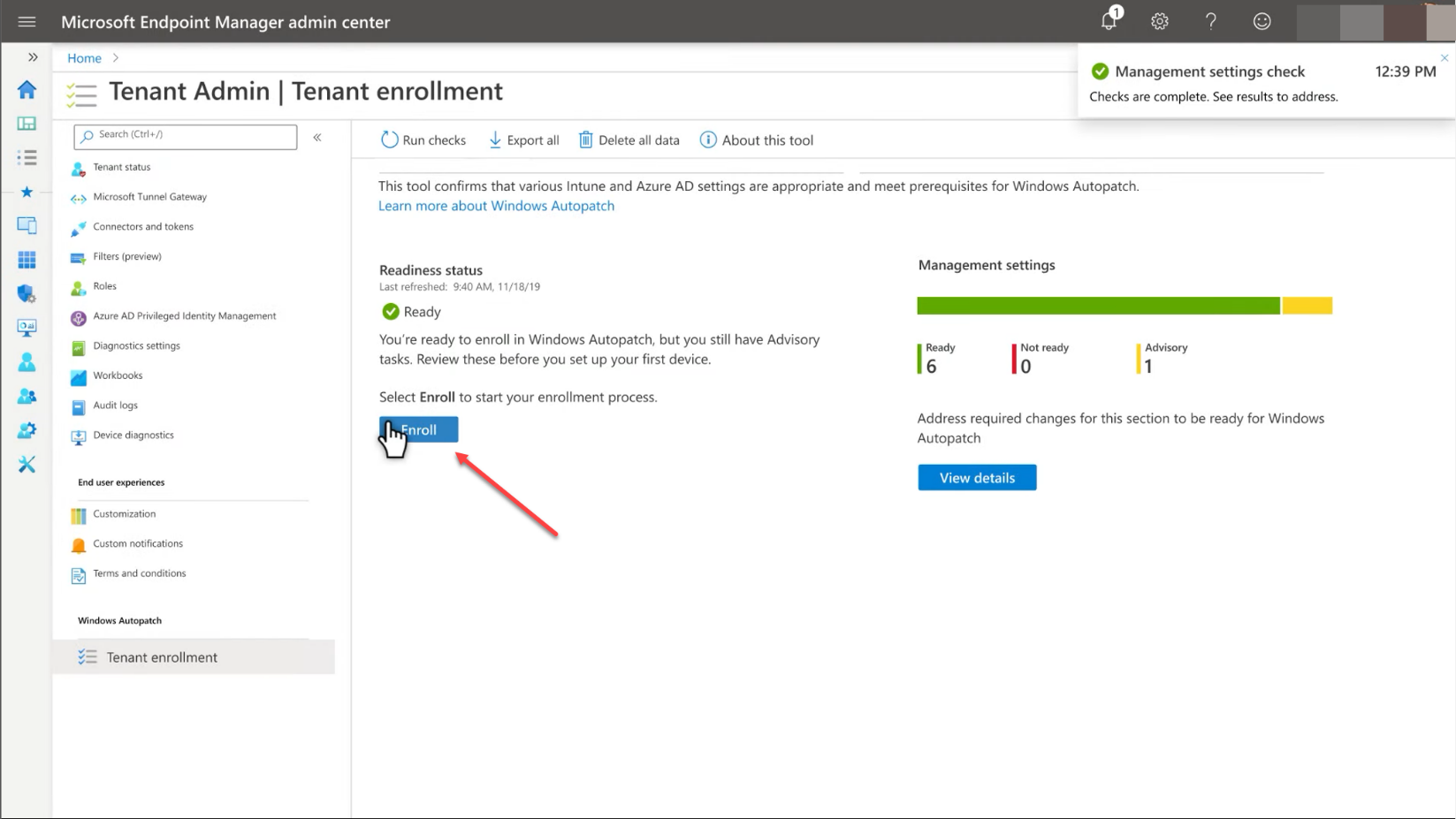 Click the Enroll button to enroll in Windows Autopatch
Click the Enroll button to enroll in Windows Autopatch
The final step is to consent to Microsoft managing the updates for you. The page notes the steps that Microsoft will take to automate the process. Those steps include:
- Create accounts to manage your tenant devices
- Manage devices using Intune
- Deploy applications using Intune
- Monitor and take actions based on security
- Collect and share info on use, status, and compliance for devices and apps
- Remove Microsoft administrator accounts from multi-factor authentication and conditional access policies
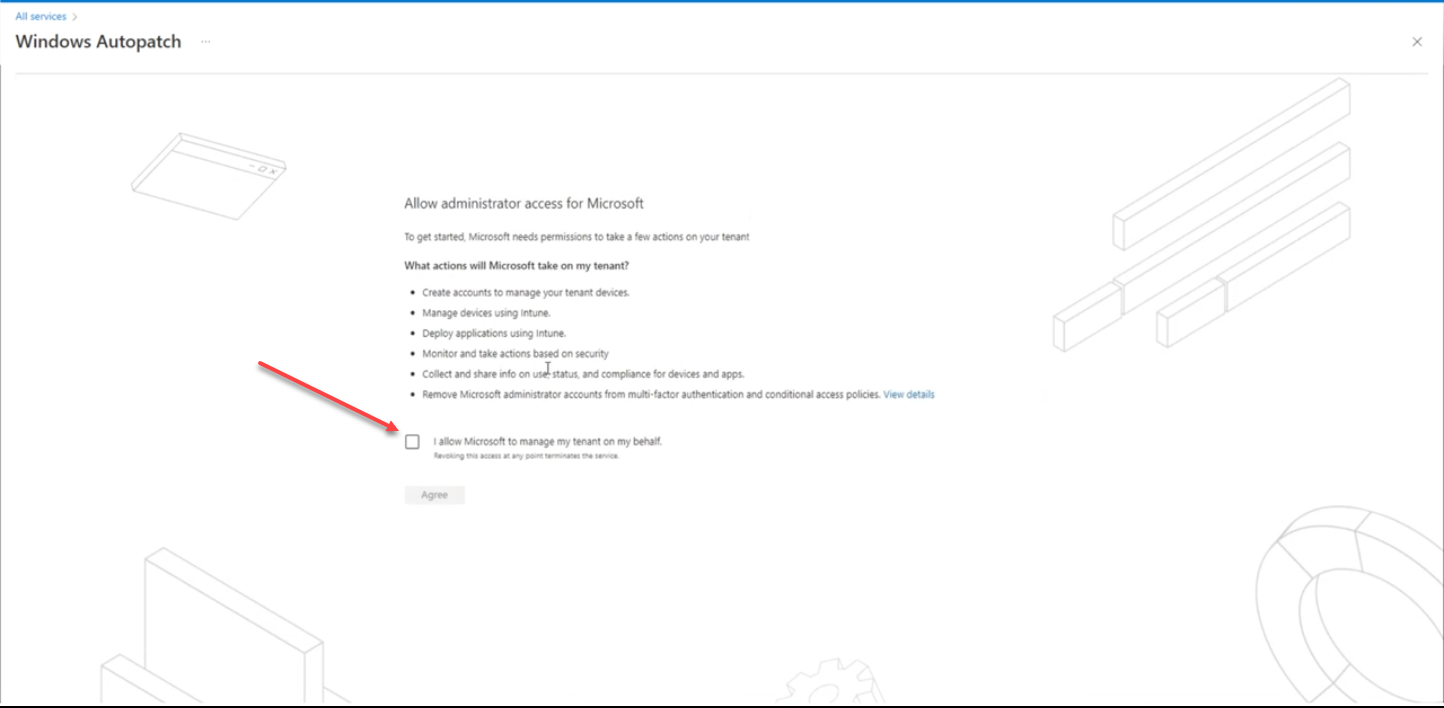 Agreeing to let Microsoft manage your patches using Windows Autopatch
Agreeing to let Microsoft manage your patches using Windows Autopatch
Final Notes
Windows Autopatch is a great new solution from Microsoft, enabling organizations to have even more robust automation for rolling out patches in the environment. Since keeping clients patched has always been a tedious and challenging task requiring a tremendous amount of time for IT pros, Windows Autopatch will help to free up the time required to manage and deploy patches across the environment. However, it still allows IT admins to retain some control over which rings in which devices are placed. While Autopatch does this automatically, admins can still move devices out of specific rings and into others.
Learn more about Windows Autopatch here:




