VMware vCenter server Appliance 6.7 U1 (VCSA) is a VM running Photon OS, which is hardened and optimized VMware Linux distribution.
All future releases will only be available as VCSA which is the preferred deployment method of vCenter Server.
If you’re running an older version of vCenter server on Windows, you can migrate to VCSA via a built-in migration tool. The migration process is quite easy, but today we’ll focus only on clean installation and configuration of VCSA in a new environment.
Software Requirements:
- You must use ESXi host with version 5.5 and higher.
- The minimum hosts that can be connected as a part of the datacenter managed by VCSA 6.7 must be ESXi 6.0 and higher.
- You can check version compatibility with other VMware products see the Product Interoperability Matrix.
Architecture:
- Recommended VMware architecture is now a vCenter server and Platform Service controller (PSC) within a single VM.
- The VCSA with embedded PSC requires the following hardware resources (disk can be thin provisioned)
– Tiny (up to 10 hosts, 100 VMs) – 2 CPUs, 10 GB RAM
– Small (up to 100 hosts, 1000 VMs) – 4 CPUs, 16 GB RAM.
– Medium (up to 400 hosts, 4000 VMs) – 8 CPUs, 24 GB RAM.
– Large (up to 1000 hosts, 10,000 VMs) – 16 CPUs, 32 GB RAM.
– X-Large (up to 2000 hosts, 35,000 VMs) – 24 CPUs, 48 GB RAM
- Configure proper DNS with forward and reverse records. FQDN resolution should be in place when deploying vCenter Server.
- If you have firewall between vCenter and the rest of infrastructure, a Required Ports for vCenter Server and PSC can be found here.
Learn from this video about:
- The advantages of adding VCSA to Microsoft AD
- Requirements for joining VCSA to Microsoft AD domain
- Guidance on how to add VCSA to Microsoft AD
Installation Steps
vCenter 6.7 U1 Download
It is a large ISO file. In our case, the latest version is this one: “VMware-VCSA-all-6.7.0-10244745.iso”
Installing the appliance is a two-stage process. The first stage will simply deploy a new appliance to the target vCenter Server or ESXi host. The second stage will finalize the setup of the deployed appliance.
First mount the ISO and navigate to the folder which corresponds to the OS you have on your management workstation you’re trying to install from. You can use Windows, Linux or MAC to install VMware VCSA.
The folder is “vcsa-ui-installer” and inside you have 3 different folders. If you’re in Windows, simply chose the win32 folder. If you’re on Linux, chose the “lin64” etc.
Then launch the installer.exe (example under Windows).
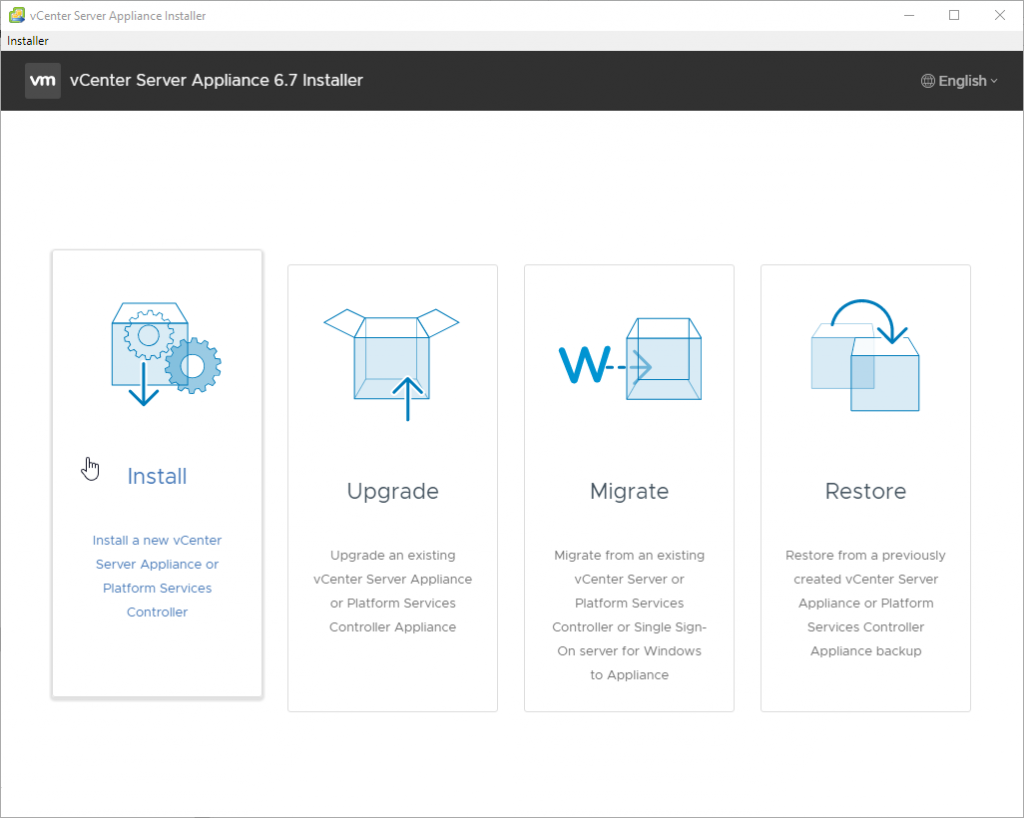
Install a New vCenter Server Appliance
As you can see, other possibilities which the installer offers are Upgrade, Migrate or Restore. We’ll do a Migrate in one of our future posts.
Next, you’ll just follow the assistant which will walks you through. Remember to configure your DNS prior to continuing and make sure to check whether the resolution works.
You can test this with an “nslookup” command through a command line window.
Unless you really need to separate vCenter Server and PSC, keep the pre-selected option called “Embedded Platform Service Controller”, which keeps both components together in a single VM. It greatly simplifies management, upgrades and patching.
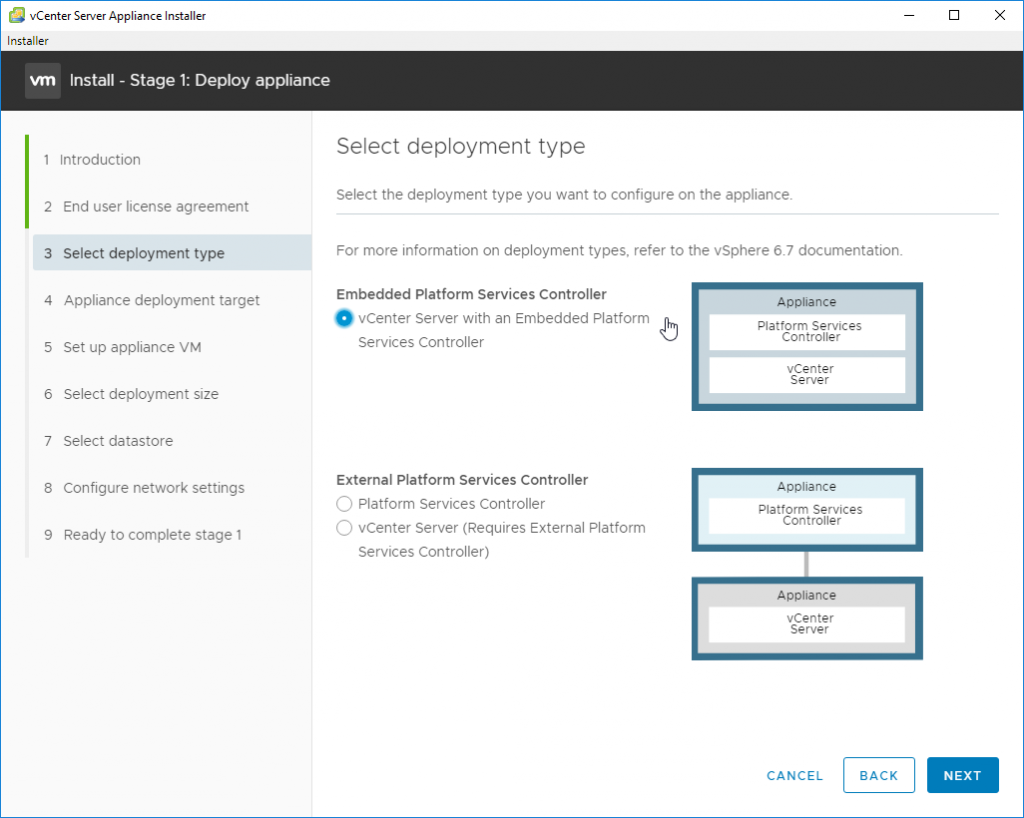
Use Embedded vCenter and PSC ratio button option
Next screen invites us to specify target for our deployment. It can be vCenter server or individual host. If you have individual host, just put an IP address of the individual host.
In my case I have small lab where I’m using vCenter server so I point to my current vCenter.
Enter the FQDN or IP address of the host, or vCenter upon which you wish to deploy the new VCSA. Enter the credentials of an administrative or root user and click Next. The installer will validate access, if prompted with an untrusted SSL certificate message click.
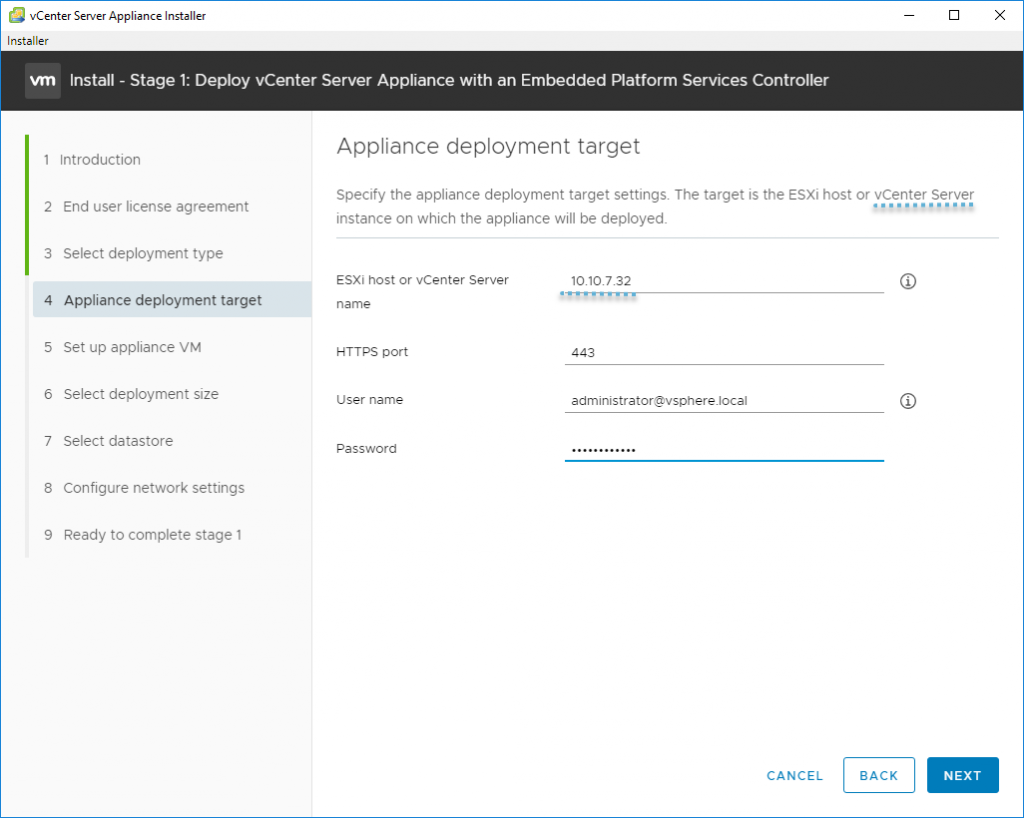
Specify deployment target
Click Next to continue.
After this, we’ll continue with the assistant and have a view of our datacenter. We must choose a location where this VM will be registered and on which host/cluster.
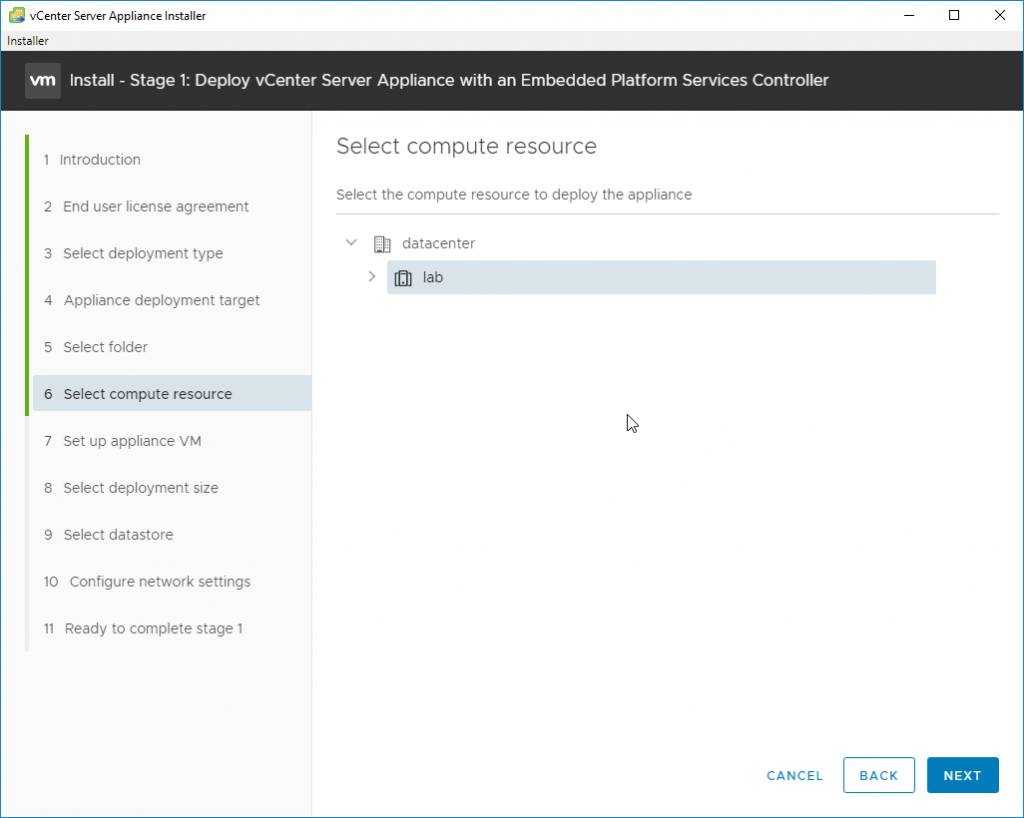
Select compute resource
Ensure that DRS is set to manual for the cluster temporarily so that the VMs for the Source and Target do not get moved during the upgrade.
And then provide the VM name and root password which must be complex enough and match. If not, the assistant won’t let you to continue.
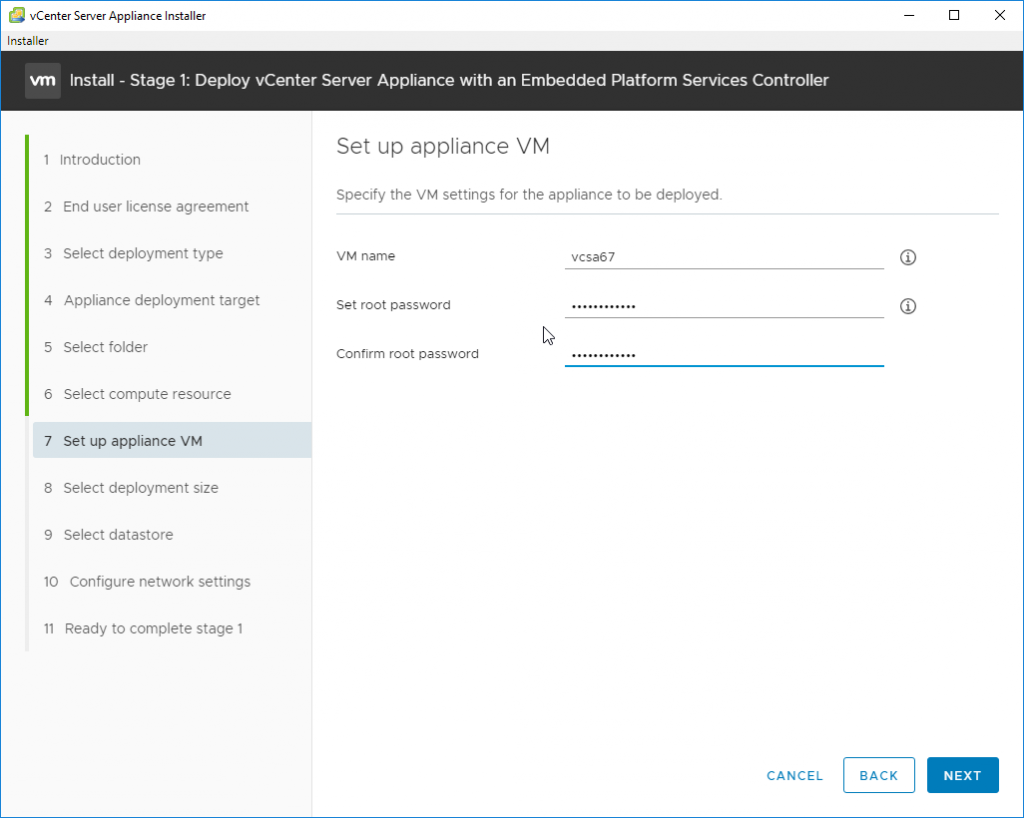
Provide VM name and root password
On the next screen we’ll chose a deployment size. We can choose between:
Tiny, Small, Medium, Large or X-Large. We can also increase the storage size of the VMDKs disks via the drop-down menu.
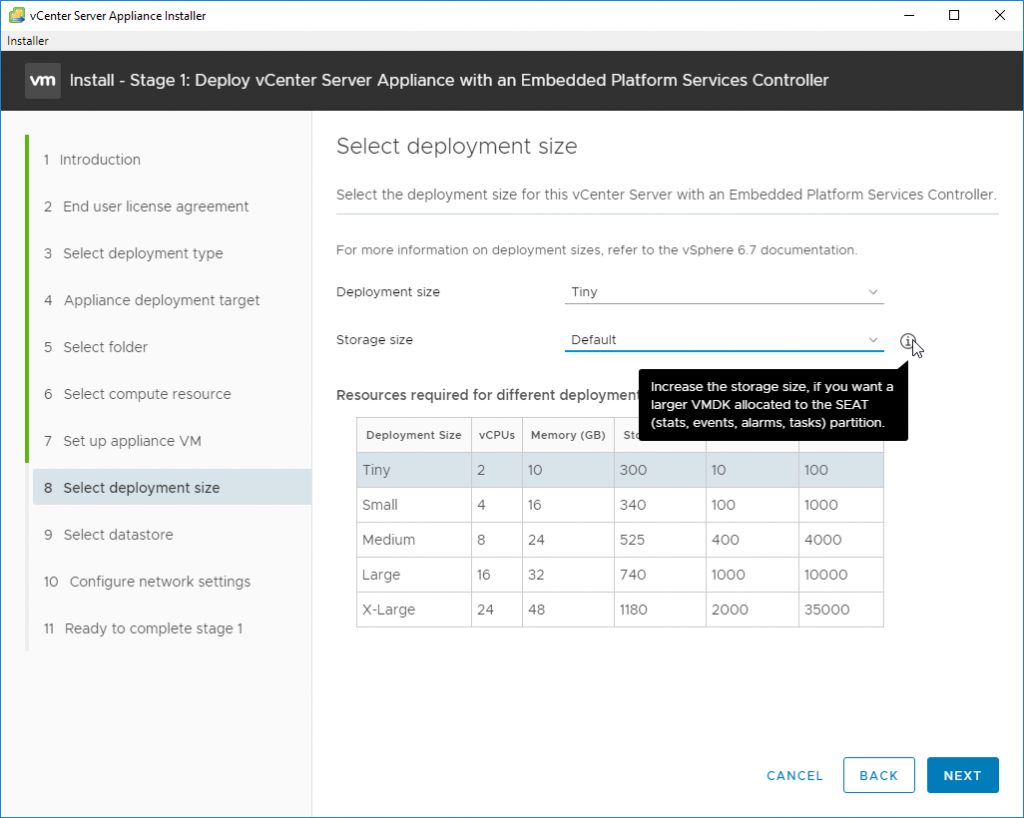
Choose storage size depending on your environment
And on the next screen we’ll need to select a datastore location for our VMDKs, VM’s config files and other files will be stored.
Note that we have an option to enable Think disk mode, which allows us to save some disk space.
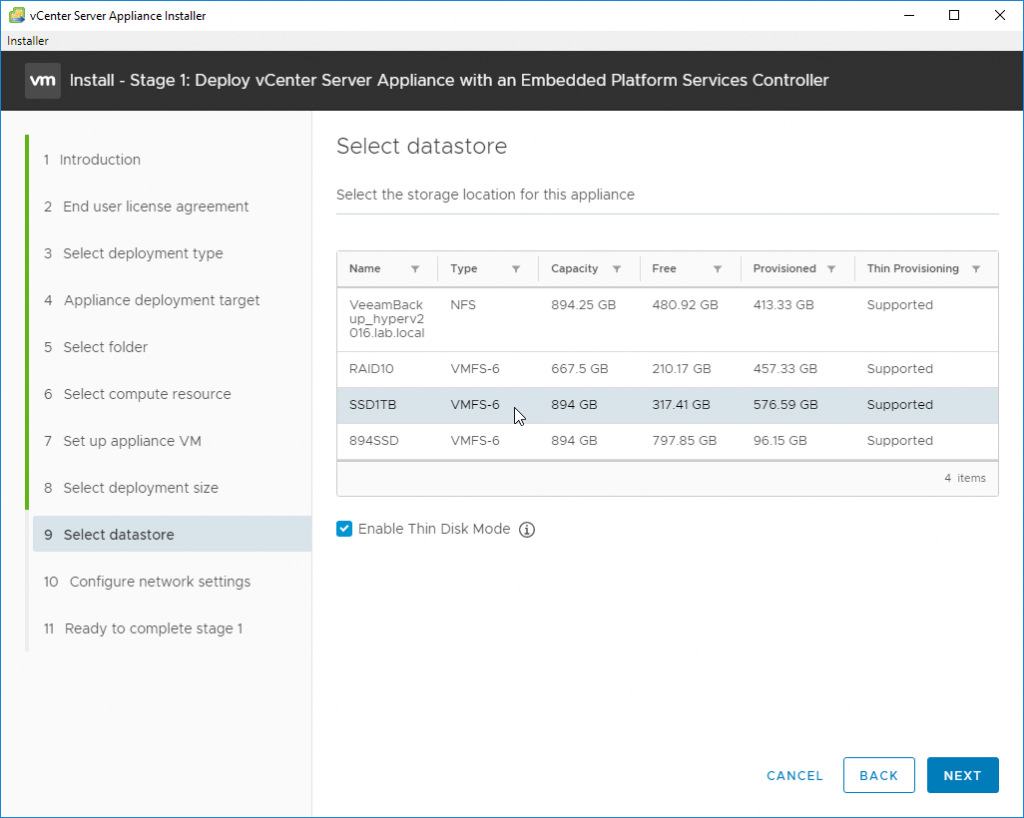
Select datastore where those VMDKs will be stored.
One last step is to configure network settings. Make sure you enter the correct values which depends on your environment.
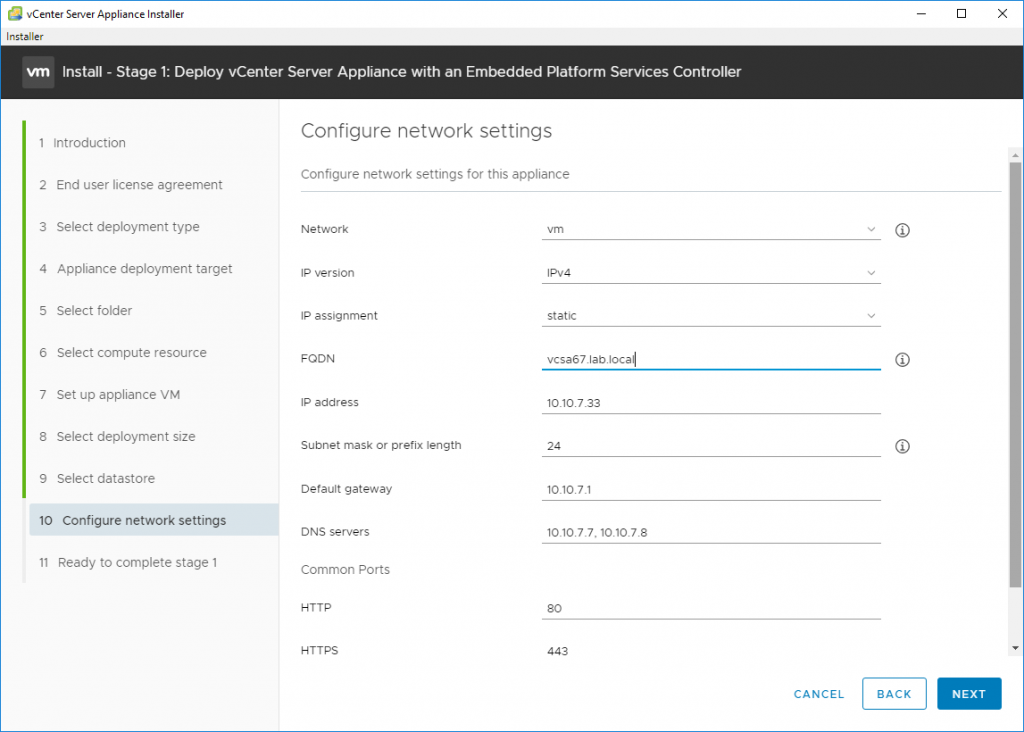
Configure network settings of your VCSA
After the recap screen, this closes the stage 1
You’ll see the deployment process to continue.
Stage 1 is deploying the VCSA appliance
Then you can click Continue for the phase 2 configuration.
Continue with Stage 2
It will check the config and retrieve information before starting another assistant. Follow the assistant.
You’ll have an option to enable SSH and chose Time Synchronization Method. While you can do that during the configuration, there is also possibility to do that later when configuring and monitoring the VCSA appliance itself.
Next, we need to configure VMware SSO and Administrator’s password. We are creating new SSO domain as it is a greenfield installation.
You can also choose to join existing SSO domain if you’re installing another vCenter server within the same installation.
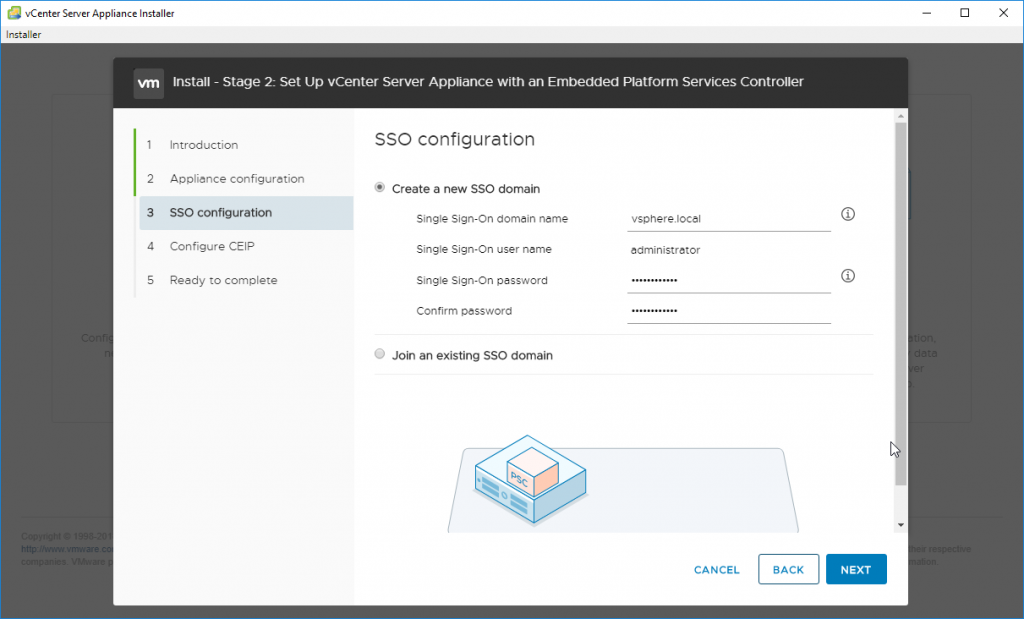
VMware SSO configuration
You can opt-in and join VMware customer experience improvement program (CEIP) which helps VMware to improve its products and services, to fix problems, and to advise you on how best to deploy and use their products.
However, VMware collects technical information about your organization, but not much. The advantage of joining the CEIP is that when you ask for a support, VMware has much more insight from your installation than if you haven’t checked that. They can see firmware/driver versions on host and also misconfigurations. This greatly helps in troubleshooting.
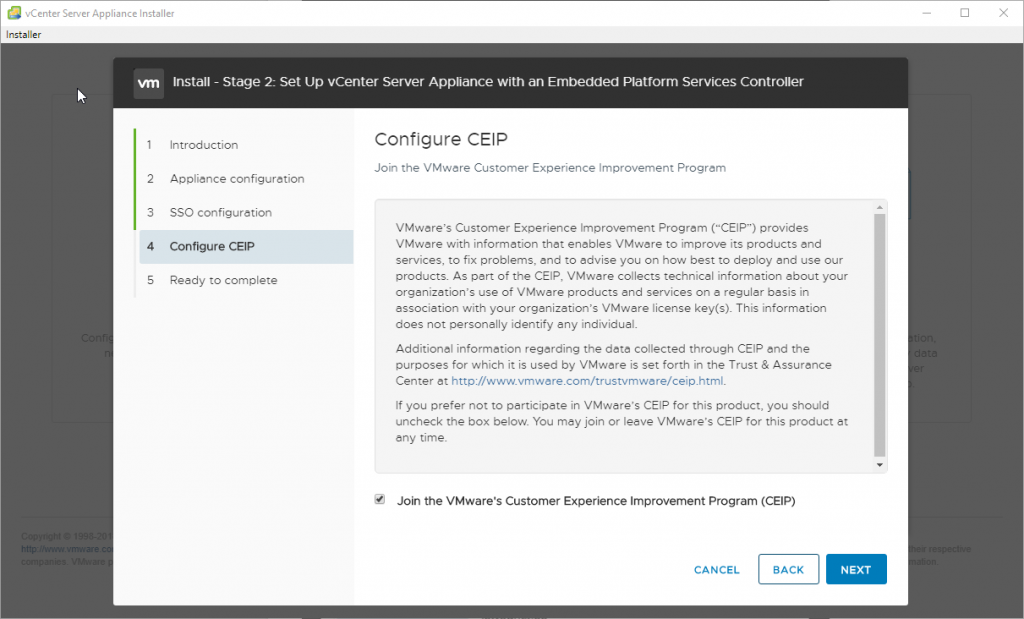
You can join VMware CEIP
And the final screen looks like this.
Stage 2 completed
And at the end you can launch either the HTML 5 web client or the Flex based web client. Both works, but the Flex based client will not be developed further.
Post-Installation
Connect to the vCenter post install using the IP or FQDN of the vCenter. You’ll still have a choice between HTML5 vSphere client and Flex based vSphere client. You’ll have 60 days to apply a license key.
Launch vSphere HTML5 Web client
If it’s a fresh deployment, and If you have installed your hosts, you can now start to add them to your vCenter server.
You would start by creating Datacenter object, cluster object and add host after host to the cluster.
Basically, this is the end of our post on Installing and configuring VMware vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) 6.7 U1.
Even though it is a Linux appliance, the process is very straightforward and simple. VMware has done a good job to keep things simple.
By slowly eliminating any plugins (old Flash based client is going slowly away) and providing good and simple workflows with form checks for password correction and network requirements, there is very few thins which could possibly go wrong.





